
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g | |||
| Other Sizes |
Purity: ≥98%
Description: Vardenafil HCl Trihydrate (formerly also known as BAY 38-9456, trade names Levitra; Staxyn; Vivanza) is an approved medication acting as a phosphodiesterase/PDE inhibitor with important biological activity. It inhibits PDE5 and PDE1 with IC50s of 0.7 and 180 nM, respectively. Vardenafil has been approved used for treating erectile dysfunction. Vardenafil (VAR) is synthetic, highly selective, and potent inhibitor of phosphodiesterase-5 which competitively inhibits cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) hydrolysis and thus increases cGMP levels. It is clinically approved for treatment of erectile dysfunction in men, including diabetic and postprostatectomy patients.
| Targets |
PDE5 (IC50 = 0.7 nM); PDE6 (IC50 = 11 nM); PDE1 (IC50 = 180 nM); PDE3 (IC50 >1000 nM); PDE4 (IC50 >1000 nM)
|
|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
Vardenafil hydrochloride trihydrate inhibits PDE5-mediated cGMP hydrolysis with an IC50 of 0.7 nM[1]. Vardenafil hydrochloride trihydrate raises intracellular cGMP levels in the penis' cavernosum tissue, causing sinus dilation and increased blood flow [3].
|
| ln Vivo |
In rats suffering from cavernous nerve damage, vardenafil hydrochloride trihydrate (IV; 0.03 mg/kg) shows facilitative effects[4]. Vardenafil hydrochloride trihydrate (IV; 0.17 mg/kg once daily; 7 days) reduces the expression of iNOS and NF-���B in hepatic tissue and shields the liver from Con A-induced hepatitis[5]. In ZDF hearts, vardenafil hydrochloride trihydrate (PO; 10 mg/kg once daily; 25 weeks) inhibits both the rise in 3-NT production and the decrease in tissue cGMP levels [6].
|
| Enzyme Assay |
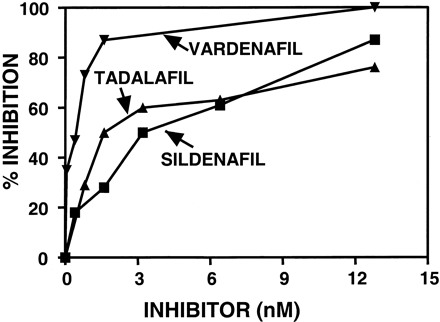
In this study, researchers investigated the potency and the selectivity profile of vardenafil on phosphodiesterase (PDEs) enzymes, its ability to modify cGMP metabolism and cause relaxation of penile smooth muscle and its effect on erections in vivo under conditions of exogenous nitric oxide (NO) stimulation. PDE isozymes were extracted and purified from human platelets (PDE5) or bovine sources (PDEs 1, 2, 3, 4 and 6). The inhibition of these PDEs and of human recombinant PDEs by vardenafil was determined. The ability to potentiate NO-mediated relaxation and influence cGMP levels in human corpus cavernosum strips was measured in vitro, and erection-inducing activity was demonstrated in conscious rabbits after oral administration together with intravenous doses of sodium nitroprusside (SNP). The effects of vardenafil were compared with those of the well-recognized PDE5 inhibitor, sildenafil (values for sildenafil in brackets). Vardenafil specifically inhibited the hydrolysis of cGMP by PDE5 with an IC50 of 0.7 nM (6.6 nM). In contrast, the IC50 of vardenafil for PDE1 was 180 nM; for PDE6, 11 nM; for PDE2, PDE3 and PDE4, more than 1000 nM. Relative to PDE5, the ratios of the IC50 for PDE1 were 257 (60), for PDE6 16 (7.4). Vardenafil significantly enhanced the SNP-induced relaxation of human trabecular smooth muscle at 3 nM (10 nM). Vardenafil also significantly potentiated both ACh-induced and transmural electrical stimulation-induced relaxation of trabecular smooth muscle. The minimum concentration of vardenafil that significantly potentiated SNP-induced cGMP accumulation was 3 nM (30 nM)[1].
|
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: Male rat (9weeks old) underwent surgery for laparotomy or bilateral cavernous nerve (CN) crush injury[4]
Doses: 0.03 mg/kg Route of Administration: intravenous (iv) injection Experimental Results: Restored normal erectile responses with a combined administration of BAY 60-4552 (0.03, 0.3 mg/kg). Animal/Disease Models: Liver injury induced by Con A in male Swiss albino mice (20 ± 2 g)[5] Doses: 0.17 mg/kg Route of Administration: intravenous (iv) injection; one time/day, for 7 days; as a pretreatment Experimental Results: decreased the levels of serum transaminases and alleviated Con A-induced hepatitis. Animal/Disease Models: Male 7weeks old Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rats (preserved ejection fraction, HFpEF)[6] Doses: 10 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage); one time/day, for 25 weeks Experimental Results: Improved myofilament function in diabetic rat hearts. |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption
Over the recommended dose range, vardenafil has a dose-proportional pharmacokinetics profile. In healthy male volunteers given a single oral dose of 20 mg of vardenafil, maximum plasma concentrations were reached between 30 minutes and 2 hours (median 60 minutes) after oral dosing in the fasted state, and 0.00018% of the dose was detected in semen 1.5 hours after dosing. Vardenafil has a bioavailability of approximately 15%. High-fat meals cause a Cmax reduction of 18%-50%; however, no changes were detected in AUC or Tmax. Route of Elimination Vardenafil is excreted as metabolites mainly through feces and urine. Approximately 91-95% of administered oral dose is found in feces, while 2-6% of administered oral dose is found in urine. Volume of Distribution Vardenafil has a steady-state volume of distribution of 208 L. Clearance Vardenafil has a total body clearance of 56 L/h. Protein binding: Very high: 95% bound to plasma proteins; reversible and independent of total drug concentrations Rapidly absorbed; absolute bioavailability is approximately 15%. Maximum observed plasma concentrations after a single 20 mg dose in healthy volunteers are usually reached between 30 minutes and 2 hours (median 60 minutes) after oral dosing in the fasted state. A high-fat meal causes a reduction in Cmax by 18% to 50%. Enhancement of nitric oxide (NO)-induced erections in rabbits by 0.1 mg/kg vardenafil is limited by its pharmacokinetic properties (Tmax=1 h; T1/2=1.2 h), although erectile effects have been observed after 7 h. In humans, vardenafil is rapidly absorbed (Tmax approximately 40 min) and more slowly metabolized (T1/2 approximately 4 h), with an absolute bioavailability of 14.5% (vs 40% for sildenafil). Although the consumption of high-fat meals does not affect the drug's relative bioavailability, it retards intestinal absorption. Coadministration of CYP3A4 inhibitors such as ritonavir can affect hepatic metabolism. M1, an active metabolite of vardenafil, is a four-fold-less potent inhibitor of PDE5 than its parent compound, contributing approximately 7% to vardenafil's overall efficacy. PMID:15224134 Time to peak concentration: 30 minutes to 2 hours (oral dosing, fasted state) Metabolism / Metabolites Vardenafil is mainly metabolized by CYP3A4 in the liver, although CYP3A5 and CYP2C isoforms also contribute to its metabolism. The major circulating metabolite, M1 (N-desethylvardenafil), results from desethylation at the piperazine moiety of vardenafil, and has a plasma concentration of approximately 26% of that of the parent compound. M1 has a phosphodiesterase selectivity profile similar to that of vardenafil and an _in vitro_ inhibitory potency for PDE5 28% of that of vardenafil. Hepatic metabolism, via CYP3A4, with contribution from CYP3A5 and CYP2C isoforms. Major circulating metabolite, M1, results from desethylation at the piperazine moiety of vardenafil. M1 is subject to further metabolism. The plasma concentration of M1 is approximately 26% of the parent compound and accounts for 7% of total pharmacologic activity. This metabolite shows a phosphodiesterase selectivity profile similar to that of vardenafil and an in vitro inhibitory potency for PDE5 28% of that of vardenafil. Biological Half-Life Vardenafil and its primary metabolite (M1) have a terminal half-life of 4-5 hours. |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Hepatotoxicity
Despite fairly extensive use, vardenafil has not been associated with clinically apparent cases of liver injury and serum enzyme elevations during therapy are rare. The related PDE5 inhibitors, sildenafil and tadalafil have been linked to isolated, rare instances of acute liver injury and jaundice. The latency to onset ranged from a few days to 3 months and the pattern of injury was usually cholestatic. Autoimmune and immunoallergic features were not observed and all cases were self-limited without residual injury or acute liver failure. Whether vardenafil can cause a similar form of acute liver injury is unknown. Likelihood score: E* (unproven but suspected rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Interactions Vardenafil has not been studied in combination with other treatments for erectile dysfunction; use of combination erectile dysfunction medication is not recommended. Alpha-blockers, such as: Terazosin, tamsulosin, doxazosin, prazosin, alfuzosin: Use is contraindicated; co-administration can produce hypotension) Erythromycin produced a 4-fold increase in vardenafil AUC and a 3-fold increase in Cmax /when administered to healthy volunteers/. Protein Binding Approximately 95% of vardenafil and its major circulating metabolite is bound to plasma proteins. Their protein binding is reversible and independent of total drug concentrations. |
| References | |
| Additional Infomation |
Vardenafil Hydrochloride Trihydrate is the hydrochloride salt form of vardenafil, a benzenesulfonamide derivative and phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitor with vasodilatory activity. Vardenafil selectively inhibits PDE5, thus inhibiting the degradation of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) found in the smooth muscle of the corpus cavernosa and corpus spongiosum of the penis. The inhibition of cGMP degradation results in prolonged muscle relaxation, vasodilation, and blood engorgement of the corpus cavernosa, thereby prolonging penile erection.
A piperazine derivative, PHOSPHODIESTERASE 5 INHIBITOR and VASODILATOR AGENT that is used as a UROLOGICAL AGENT in the treatment of ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION. See also: Vardenafil (annotation moved to). |
| Molecular Formula |
C23H32N6O4S.HCL.3H2O
|
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
579.11
|
| Exact Mass |
578.229
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 44.88; H, 6.55; Cl, 11.52; N, 13.65; O, 18.19; S, 5.21
|
| CAS # |
330808-88-3
|
| Related CAS # |
Vardenafil hydrochloride;224785-91-5;Vardenafil dihydrochloride;224789-15-5
|
| PubChem CID |
135413545
|
| Appearance |
White to light yellow solid powder
|
| LogP |
3.636
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
5
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
11
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
8
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
38
|
| Complexity |
854
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=C1N=C(C2=CC(S(=O)(N3CCN(CC)CC3)=O)=CC=C2OCC)NN4C1=C(C)N=C4CCC.[H]Cl.[H]O[H].[H]O[H].[H]O[H]
|
| InChi Key |
NEAUGLIJDBPHAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H32N6O4S.ClH.3H2O/c1-5-8-20-24-16(4)21-23(30)25-22(26-29(20)21)18-15-17(9-10-19(18)33-7-3)34(31,32)28-13-11-27(6-2)12-14-28;;;;/h9-10,15H,5-8,11-14H2,1-4H3,(H,25,26,30);1H;3*1H2
|
| Chemical Name |
2-(2-ethoxy-5-((4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)sulfonyl)phenyl)-5-methyl-7-propylimidazo[5,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-4(1H)-one dihydrochloride trihydrate
|
| Synonyms |
BAY38-9456; BAY 38-9456; 224785-91-5; Vardenafil HCL; Vardenafil (hydrochloride); Vardenafilhydrochloride; Vardenafil, Hydrochloride Salt; Vardenafil hydrochloride [USAN]; VARDENAFIL MONOHYDROCHLORIDE;BAY-38-9456; trade names: Levitra; Staxyn; Vivanza; Vardenafil hydrochloride trihydrate; Vardenafil HCl; Levitra; Staxyn; Vivanza
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples.
Injection Formulations
Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). View More
Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] Oral Formulations
Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). View More
Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7268 mL | 8.6339 mL | 17.2679 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3454 mL | 1.7268 mL | 3.4536 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1727 mL | 0.8634 mL | 1.7268 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
|
|---|
|
|