| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
MKC-8866 (ORIN-1001; IRE1-IN-8866) is a salicylaldehyde analog that acts ass a potent, selective IRE1 RNase inhibitor with an IC50 of 0.29 μM in human vitro. MKC8866 strongly inhibits Dithiothreitol-induced X-box-binding protein 1-spliced (XBP1s) expression with an EC50 of 0.52 μM and unstresses RPMI 8226 cells with an IC50 of 0.14 μM. MKC8866 inhibits IRE1 RNase in breast cancer cells leading to the decreased production of pro-tumorigenic factors and it can inhibits prostate cancer (PCa) tumor growth.
| Targets |
IRE1 RNase (IC50 = 0.29 μM)
|
|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
All breast cancer cell lines' growth is inhibited by MKC8866 (20 μM; 6 days) [2]. Cells entering S phase are less frequently when MKC8866 (20 μM; 48 hours) is applied [2]. Under standard circumstances, MKC8866 (0.2-10 μM; 3 days) exhibits a dose-dependent inhibition of the viability of all four cell lines, with the greatest effect observed in LNCaP cells [1]. For a duration of 72 hours, MKC8866 (20 μM) is adequate to entirely prevent NSC 125973-induced XBP1 expression [1].
|
| ln Vivo |
When NSC 125973 is stopped, MKC8866 (oral; 300 mg/kg; for 28 days) decreases tumor regrowth [1].
MKC8866, strongly inhibits prostate cancer (PCa) tumor growth as monotherapy in multiple preclinical models in mice and shows synergistic antitumor effects with current PCa drugs.[1] MKC8866 strongly inhibited xenografted tumor growth in all PCa cell lines tested (Fig. 2a). XBP1s expression was significantly lower in MKC8866-treated tumors compared to controls, confirming that MKC8866 was active in mice harboring the tumors and that IRE1α activity was appropriately inhibited in vivo (Supplementary Fig. 4a). In addition, there was a decrease in PCNA expression and an increase in cleaved Caspase-3 levels, indicating that MKC8866 treatment resulted in decreased proliferation and increased apoptosis, respectively (Supplementary Fig. 4b). Removal of MKC8866 during the course of the treatment resulted in rebounding of XBP1s levels and enhanced tumor growth (Fig. 2b and Supplementary Fig. 4c), indicating the importance of sustained MKC8866 application for its growth inhibitory effects. These results show that pharmacological targeting of IRE1α exerts potent antitumor effects in preclinical mouse models of PCa.[1] There was strong synergy in tumor growth inhibition when MKC8866 was co-administered with enzalutamide. Co-administration of MKC8866 with abiraterone acetate and cabazitaxel also synergistically inhibited tumor growth. Taken together, these data demonstrate that in preclinical models MKC8866 synergizes with some of the central PCa drug regimens that are currently used in the clinic.[1] MKC8866 enhances the effectiveness of paclitaxel in vivo[2] To determine the efficacy of MKC8866 treatment in vivo, MDA-MB-231 tumor xenografts were established in athymic nude mice. Once tumors had reached a palpable size (225–250 mm3), animals were randomized into treatment groups and treated with vehicle alone, 300 mg kg−1 MKC8866 alone, 10 mg kg−1 paclitaxel alone or a combination of paclitaxel and MKC8866. Treatments in all groups were administered until tumors reached maximal size (2000 mm3) or on day 60, whichever came first. MKC8866 was well tolerated after 60 consecutive oral doses and, based on pharmacokinetic allometric scaling, systemic exposures were well above anticipated clinical therapeutic levels. Treatment with MKC8866 alone did not attenuate tumor growth compared to vehicle-only controls (Fig. 7a). Analysis of percentage XBP1 mRNA splicing in those tumors treated with MKC8866 confirmed a reduction in IRE1 RNase activity verifying on-target effect (Fig. 7b). While paclitaxel treatment reduced tumor growth, combination with MKC8866 markedly enhanced the efficacy of paclitaxel. Significantly reduced tumor growth (P ≤ 0.0001) was observed throughout the 60-day experiment in animals receiving a paclitaxel-MKC8866 combination compared to paclitaxel alone (Fig. 7c). A similar synergistic effect was observed following a paclitaxel-MKC8866 combination starting on day 14 (or ~700 mm3 tumor volume) (P ≤ 0.001) or on day 28 (or ~1300 mm3 tumor volume) (P ≤ 0.05) when compared to paclitaxel alone (Fig. 7c). Examination of XBP1 splicing in tumors revealed paclitaxel treatment increased IRE1 RNase activity, which was reduced upon combination with MKC8866 (Fig. 7d, Supplementary Fig. 5). The decrease in tumor volume observed following a combination of paclitaxel and MKC8866 also translated to an increase in survival. Mice receiving daily MKC8866 administration in combination with paclitaxel from day 1 to 60, day 14 to 60, and day 28 to 60 displayed significantly longer survival compared to those treated with paclitaxel alone (Fig. 7e). |
| Enzyme Assay |
Luciferase reporter assay[1]
LNCaP or 293T cells were cultured in six-well plates, transfected with 1 μg of pGL3-MYC luciferase reporter plasmid plus either empty vector (pCDNA3) or the pCDNA3-Flag-XBP1s plasmid of the indicated concentration for 24 h before harvest. Luciferase activity was determined using a luciferase assay system and a Wallac Victor2 1420 Multilabel counter. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell proliferation assay[2]
Cell Types: MCF7, SKBR3, MDA-MB-231 and MCF10A Cell Tested Concentrations: 20 μM Incubation Duration: 6 days Experimental Results: Proliferation was diminished in all breast cancer cell lines. Cell cycle analysis[2] Cell Types: MDA-MB-231, MCF7 and SKBR3 Cell Tested Concentrations: 20 μM Incubation Duration: 48 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: diminished number of cells entering S phase. Cell cycle analysis[1] Cell Types: LNCaP, VCaP, 22Rv1 and C4-2B Cell Tested Concentrations: 0.2, 0.5, 1, 5, 10 μM Incubation Duration: 3 days Experimental Results: Inhibited viability of all four cell lines in one dose Dependence method. Cell cycle analysis [2] Cell Types: MDA-MB-231 Cell Tested Concentrations: 20 μM Incubation Duration: 72 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Completely blocked NSC 125973-induced XBP1 expression. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: MDA-MB-231 tumor in female athymic nude mice [1]
Doses: 300 mg/kg Route of Administration: oral; continued for 28 days Experimental Results: NSC 125973 diminished tumor regeneration after drug withdrawal. In vivo MDA-MB-231 xenograft model[2] Mice were administered 10 mg kg−1 paclitaxel weekly by intravenous injection. The IRE1 inhibitor, MKC8866, was administered at a dose volume of 10 ml kg−1 from a 30 mg ml−1 suspension in 1% microcrystalline cellulose in a simple sugar at 300 mg kg−1 daily by oral gavage (Vehicle 2). Treatment groups were as follows: For Group 1, the paclitaxel vehicle was administered intravenously weekly and the MKC8866 vehicle was administered orally daily throughout the course of the study. For Groups 2–6, paclitaxel was administered weekly throughout the course of the study. In combination with paclitaxel, MKC8866 was also administered orally daily from day 1 to 28 (Group 3), from day 14 to 60 (Group 4), from day 28 to 60 (Group 5), and from day 1 to 60 (Group 6). Treatments in all groups were administered until tumors reached maximal size or day 60, whichever came first.[2] MKC8866 was administered daily for 28 days at a dose volume of 10 ml kg−1 from a 30 mg ml−1 suspension in 1% microcrystalline cellulose in a simple sugar at 300 mg kg−1 daily by oral gavage (Vehicle 2). Group 1 received paclitaxel (7.5 mg kg−1) alone while Group 2 received paclitaxel (7.5 mg kg−1) plus 300 mg kg−1 MKC8866. After palpable tumors appeared, the mice were randomly grouped and daily received either 300 mg kg−1 MKC8866 or vehicle (1% microcrystalline in 1 g ml−1 sucrose). For the combinatorial experiment of MKC8866 and enzalutamide, mice were assigned into four groups (n = 6 per group): oral gavage of 300 mg kg−1 MKC8866 every other day, oral gavage of 30 mg kg−1 enzalutamide every other day, a combination of daily gavage of either MKC8866 or enzalutamide, and daily gavage of either MKC8866 or 0.5% HP methyl cellulose with 0.1% Tween 20 as a vehicle control. The four groups (n = 6 per group) for the combination of MKC8866 and abiraterone acetate were: oral gavage of 300 mg kg−1 MKC8866 every other day, oral gavage of 20 mg kg−1 abiraterone acetate every other day, a combination of two treatments, and corresponding vehicles. The four groups (n = 6 per group) for the combination of MKC8866 and cabazitaxel were: oral gavage of 300 mg kg−1 MKC8866 every other day, intraperitoneal injections of 5 mg kg−1 cabazitaxel twice a week, a combination of two treatments, and corresponding vehicles. Tumor weight was measured in the end of experiment.[1] |
| References | |
| Additional Infomation |
IRE1 RNase Inhibitor ORIN1001 is an orally bioavailable inhibitor of the serine/threonine-protein kinase/endoribonuclease inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (inositol-requiring enzyme 1 alpha; IRE1), with potential immunoactivating, chemosensitizing and antineoplastic activities. Upon oral administration, IRE1 RNase inhibitor ORIN1001 targets and binds to the RNase domain of IRE1, thereby inhibiting the activity of IRE1. This prevents activation of the IRE1/X-Box Binding Protein 1 (XBP1) pathway, inhibits unfolded protein response (UPR) stress adaptation and prevents the production of pro-tumorigenic factors. This may inhibit tumor growth in which IRE1 is overactivated. In addition, ORIN1001 abrogates the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) through cytotoxic T-cell infiltration and depletion of immunosuppressive myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) in the TME. IRE1, an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-localized transmembrane protein containing an ER luminal stress-sensing domain and a cytoplasmic facing RNase domain, acts as a key sensor for the UPR and plays a key role in the response to and resolution of ER stress. IRE1 is involved in both protein phosphorylation and mRNA processing and degradation in response to ER stress-dependent signaling. IRE1 is frequently co-amplified with the MYC oncogene.
|
| Molecular Formula |
C18H19NO7
|
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
361.3460
|
| Exact Mass |
361.12
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 59.83; H, 5.30; N, 3.88; O, 30.99
|
| CAS # |
1338934-59-0
|
| PubChem CID |
89542346
|
| Appearance |
Light yellow to yellow solid powder
|
| LogP |
0.5
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
1
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
7
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
4
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
26
|
| Complexity |
611
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
0
|
| InChi Key |
IFDGMRMUJYGWQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H19NO7/c1-10-11-7-14(24-2)16(22)13(9-20)17(11)26-18(23)12(10)8-15(21)19-3-5-25-6-4-19/h7,9,22H,3-6,8H2,1-2H3
|
| Chemical Name |
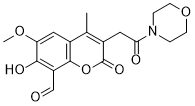
7-Hydroxy-6-methoxy-4-methyl-3-(2-morpholino-2-oxoethyl)-2-oxo-2H-chromene-8-carbaldehyde
|
| Synonyms |
ORIN1001; ORIN-1001; ORIN 1001;
MKC-8866; MKC 8866; 2H-1-Benzopyran-8-carboxaldehyde, 7-hydroxy-6-methoxy-4-methyl-3-(2-(4-morpholinyl)-2-oxoethyl)-2-oxo-; UNII-1NZ0YBP9HB;MKC8866; IRE1-IN-8866; IRE1IN8866; IRE1;
IN 8866; IRE1-IN8866; IRE1-IN 8866; IRE1IN-8866; IRE1IN 8866
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO : ~6.67 mg/mL (~18.46 mM)
|
|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples.
Injection Formulations
Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). View More
Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] Oral Formulations
Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). View More
Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7674 mL | 13.8370 mL | 27.6740 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5535 mL | 2.7674 mL | 5.5348 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2767 mL | 1.3837 mL | 2.7674 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.