
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
| Targets |
VEGFR3 (IC50 = 20 nM); Braf (IC50 = 22 nM); Raf-1 (IC50 = 6 nM); VEGFR2 (IC50 = 90 nM); PDGFRβ (IC50 = 57 nM); BrafV599E (IC50 = 38 nM); c-Kit (IC50 = 68 nM); Flt3 (IC50 = 58 nM)
|
|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
Sorafenib's IC50 values of 22 nM and 38 nM, respectively, inhibit both wild-type and V599E mutant B-Raf activity. Additionally, mVEGFR2 (Flk-1) as well as mVEGFR3, mPDGFRβ, Flt3, and c-Kit are all potently inhibited by sorafenib, with respective IC50 values of 15 nM, 20 nM, 57 nM, 58 nM, and 68 nM. Sorafenib has a 580 nM IC50 and only moderately inhibits FGFR-1. Sorafenib tosylate is ineffective against the following targets: ERK-1, MEK-1, EGFR, HER-2, IGFR-1, c-Met, PKB, PKA, cdk1/cyclinB, PKCα, PKCγ, and pim-1. In NIH 3T3 cells, sorafenib significantly reduces VEGFR2 phosphorylation with an IC50 of 30 nM, and Flt-3 phosphorylation in HEK-293 cells with an IC50 of 20 nM. In most cell lines, sorafenib potently inhibits MEK 1/2 and ERK 1/2 phosphorylation, but not in A549 or H460 cells. It has no impact on the PKB pathway's inhibition. Sorafenib has an IC50 of 0.28 μM and 2.6 μM, respectively, and prevents HAoSMC and MDA-MB-231 cells from proliferating. [1] Sorafenib also significantly inhibits the phosphorylation of eIF4E and down-regulates Mcl-1 levels in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells in a MEK/ERK-independent manner, in addition to inhibiting the RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway. With IC50 values of 6.3 μM and 4.5 μM, respectively, sorafenib inhibits the proliferation of PLC/PRF/5 and HepG2 cells and significantly induces apoptosis.[2]
|
| ln Vivo |
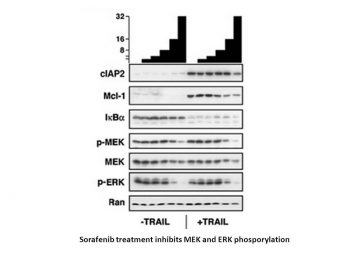
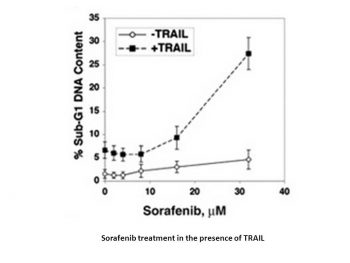
Sorafenib (60 mg/kg) administered orally exhibits no toxicity and broad spectrum, dose-dependent anti-tumor activity against a number of human tumor xenograft models, including MDA-MB-231, Colo-205, HT-29, DLD-1, NCI-H460, and A549. Sorafenib treatment significantly reduces tumor microvessel area (MVA) and microvessel density (MVD) in MDA MB-231, HT-29, and Colo-205 tumor xenografts, which is associated with its anti-tumor efficacy. However, it has no effect on MEK 1/2 phosphorylation or pERK 1/2 levels in HT-29 or MDA-MB-231 xenografts.[1] In SCID mice, sorafenib treatment results in a dose-dependent growth inhibition of PLC/PRF/5 tumor xenografts with TGIs of 49% and 78% at 10 mg/kg and 30 mg/kg, respectively. This is consistent with the inhibition of ERK and eIF4E phosphorylation, reduction of the microvessel area, and induction of tumor cell apoptosis. [2] By inhibiting NF-B mediated Mcl-1 and cIAP2 expression, sorafenib sensitizes bax-/- cells to TRAIL in a dose-dependent manner. In TRAIL-resistant HCT116 bax-/- and HT29 tumor xenografts, sorafenib (30–60 mg/kg) and TRAIL (5 mg/kg) showed dramatic efficacy. [3]
|
| Enzyme Assay |
Raf-1 (80 ng), wt BRAF (80 ng), or V599E BRAF (80 ng) are mixed with MEK-1 (1 μg) in the assay buffer (20 mM Tris (pH 8.2), 100 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, and 0.15% β-mercaptoethanol) to test the effects of the compound on different RAF kinase isoforms. Adding 25 μL of 10 μM γ-[33P]ATP (400 Ci/mol) and incubating the mixture at 32°C for 25 minutes kickstarts the RAF kinase assay (final volume of 50 μL). By filtering phosphorylated MEK-1 onto a phosphocellulose mat, radioactivity that is not bound to the protein is removed. Phosphorylated MEK-1 is then harvested. Using a β-plate counter, filter-bound radioactivity is measured after drying by microwave heating.
|
| Cell Assay |
For 72 hours, Sorafenib tosylate is infused into cells at progressively higher concentrations. The Cell TiterGlo ATP Luminescent assay kit is used to calculate the number of cells. This assay counts the number of live cells in each well by measuring the luminescent signal, which is dependent on the amount of cellular ATP.
|
| Animal Protocol |
Mice: Female NCr-nu/nu mice are used. Mice bearing 75 to 150 mg tumors are treated orally with Sorafenib (7.5 to 60 mg/kg), administered daily for 9 days. In each model, Sorafenib produces dose-dependent tumor growth inhibition with no evidence of toxicity, as measured by increased weight loss relative to control animals or drug-related lethality. In parallel to the antitumor efficacy studies, additional groups of four mice bearing 100 to 200 mg tumors are treated orally with vehicle or Sorafenib (30 to 60 mg/kg), administered daily for 5 days, which is the shortest treatment duration producing complete tumor stasis in the treated groups.
Rats: Male albino rats weighing 100 to 120 g are used for the study. Rats are weighed and randomly split into three groups following an acclimatization period. For 8 weeks, the car is given daily to Group 1 (the healthy control group; n=10). An i.p. single dose of 200 mg/kg DENA is administered to Group 2 (the DENA group; n=15). Six weeks after receiving a DENA intravenously in Group 3 (the Sorafenib group; n=12), Sorafenib is administered orally at a dose of 10 mg/kg daily for two weeks. Rats are weighed, put to sleep with ether, killed at the conclusion of the experiment (8 weeks), and their livers are removed. Fresh liver is weighed after being dried on a clean paper towel and going through two ice-cold saline washes. The liver index is calculated using the formula liver weight (g)/final body weight (g)×100. |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The administration of multiple doses for seven days resulted in a 2.5- to 7-fold accumulation compared to a single dose. Steady-state concentrations were achieved within seven days, with a peak-to-trough ratio of mean concentrations of less than 2. Mean Cmax and AUC increased less than proportionally beyond oral doses of 400 mg administered twice daily. The Tmax is approximately three hours. The mean relative bioavailability was 38–49% following the administration of oral sorafenib tablets. A high-fat meal reduced bioavailability by 29%. Following oral administration of a 100 mg dose of sorafenib, about 96% of the dose was recovered within 14 days, with 77% of the dose being excreted in feces and 19% of the dose being excreted in urine as glucuronidated metabolites. Unchanged sorafenib accounted for 51% of the dose excreted in feces. Sorafenib is widely distributed to tissues, indicating that it is lipophilic. Following oral administration of a 100 mg dose of a solution formulation of sorafenib, 96% of the dose was recovered within 14 days, with 77% of the dose excreted in feces and 19% of the dose excreted in urine as glucuronidated metabolites. Unchanged sorafenib, accounting for 51% of the dose, was found in feces but not in urine. After administration of Nexavar tablets, the mean relative bioavailability was 38-49% when compared to an oral solution. Following oral administration, sorafenib reached peak plasma levels in approximately 3 hours. With a moderate-fat meal (30% fat; 700 calories), bioavailability was similar to that in the fasted state. With a high-fat meal (50% fat; 900 calories), bioavailability was reduced by 29% compared to that in the fasted state. It is recommended that Nexavar be administered without food. Mean Cmax and AUC increased less than proportionally beyond oral doses of 400 mg administered twice daily. In vitro binding of sorafenib to human plasma proteins was 99.5%. The absorption and the basic pharmacokinetics following a single dose of sorafenib tosylate were evaluated in female CD-1 mice, male Wistar rats, and female Beagle dogs. For the determination of the absorption of sorafenib in rats, bile duct-cannulated rats (n=5/group) were used. Twenty-four hours after surgery (14)C-sorafenib tosylate was administered orally or intravenously to the rats at a dose of 5 mg/kg sorafenib. The absorption of sorafenib was almost complete in female CD-1 mice (78.6%) and male Wistar rats (79.2%). In Beagle dogs the absorption (67.6 %, calculated from AUC norm values after intravenous and oral administration) and the absolute bioavailability (59.9 %) were lower than in rodents. Maximum plasma concentrations of radioactivity between 1.5 hr and 2 hr after oral administration were observed in all species. After intravenous administration of (14)C-sorafenib tosylate to mice, rats, and dogs the elimination of the radioactivity from plasma occurred with similar terminal half-lives of 6.8, 8.8, and 7.3 hours, respectively. The terminal half-lives of radioactivity after oral administration were 6.1 hours in mice and 5.8 hours in dogs. In rats, terminal half-live after oral administration was longer (11.2 hr) than after intravenous administration. In rats, the elimination of the unchanged compound was slower (half life: 9.3 hr) than in the mice (half life: 6.5 hr) and dogs (half life:4.3 hr). The total plasma clearance in rats was 0.044 L/(hr/kg) corresponding to a blood clearance of 0.049 L/(hr/kg). In mice and dogs the total plasma clearance was 0.13 and 0.15 lL/(hr/kg) respectively. The volume of distribution at steady state ranged from 0.65 l/kg to 0.74 l/kg, depending on the species. Metabolism / Metabolites Sorafenib undergoes oxidative metabolism by CYP3A4 in the liver, as well as glucuronidation by UGT1A9 in the liver and kidneys. At steady-state, sorafenib accounts for 70-85% of the circulating analytes in plasma. About eight metabolites of sorafenib have been identified, of which five were detected in plasma. The main circulating metabolite was the pyridine N-oxide form, which comprises approximately 9–16% of the total circulating dose at steady-state: the pharmacological activity of this metabolite was comparable to the parent drug. Sorafenib undergoes oxidative metabolism by hepatic CYP3A4, as well as glucuronidation by UGT1A9. Inducers of CYP3A4 activity can decrease the systemic exposure of sorafenib. Sorafenib accounted for approximately 70-85% of the circulating analytes in plasma at steady-state. Eight metabolites of sorafenib have been identified, of which 5 have been detected in plasma. The main circulating metabolite of sorafenib, the pyridine N-oxide that comprises approximately 9-16% of circulating analytes at steady-state, showed in vitro potency similar to that of sorafenib. Sorafenib has known human metabolites that include Sorafenib and A-D-GlucuronideDISCONTINUED. Sorafenib is metabolized primarily in the liver, undergoing oxidative metabolism, mediated by CYP3A4, as well as glucuronidation mediated by UGT1A9. Sorafenib accounts for approximately 70-85% of the circulating analytes in plasma at steady- state. Eight metabolites of sorafenib have been identified, of which five have been detected in plasma. The main circulating metabolite of sorafenib in plasma, the pyridine N-oxide, shows in vitro potency similar to that of sorafenib. This metabolite comprises approximately 9-16% of circulating analytes at steady-state. Route of Elimination: Following oral administration of a 100 mg dose of a solution formulation of sorafenib, 96% of the dose was recovered within 14 days, with 77% of the dose excreted in feces, and 19% of the dose excreted in urine as glucuronidated metabolites. Half Life: 25-48 hours Biological Half-Life The mean elimination half-life of sorafenib was approximately 25 to 48 hours. After intravenous administration of (14)C-sorafenib tosylate to mice, rats, and dogs the elimination of the radioactivity from plasma occurred with similar terminal half-lives of 6.8, 8.8, and 7.3 hours, respectively. The terminal half-lives of radioactivity after oral administration were 6.1 hours in mice and 5.8 hours in dogs. In rats, terminal half-live after oral administration was longer (11.2 hr) than after intravenous administration. In rats, the elimination of the unchanged compound was slower (half life: 9.3 hr) than in the mice (half life: 6.5 hr) and dogs (half life:4.3 hr). The mean elimination half-life of sorafenib was approximately 25 to 48 hours. |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Toxicity Summary
Sorafenib interacts with multiple intracellular (CRAF, BRAF and mutant BRAF) and cell surface kinases (KIT, FLT-3, VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3, and PDGFR-ß). Several of these kinases are thought to be involved in angiogenesis, thus sorafenib reduces blood flow to the tumor. Sorafenib is unique in targeting the Raf/Mek/Erk pathway. By inhibiting these kinases, genetic transcription involving cell proliferation and angiogenesis is inhibited. Hepatotoxicity In large clinical trials of sorafenib, elevations in serum aminotransferase levels were common, occurring in up to half of patients, but values greater than 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) occurred in only 1% to 3% of treated subjects. In addition, there have been several single case reports of clinically apparent liver injury arising during sorafenib therapy which was often severe and occasionally fatal. The onset of acute liver injury ranged from a few days to 8 weeks of starting sorafenib, and the pattern of injury was typically hepatocellular with marked elevations in serum aminotransferase levels. Immunoallergic and autoimmune features were absent. Recovery was usually rapid once sorafenib was stopped, but some cases were associated with progressive liver injury and hepatic failure. Most of the reports of severe liver injury occurred in patients being treated for hepatocellular carcinoma who also had cirrhosis or in patients receiving other potentially hepatotoxic drugs31. Likelihood score: B (likely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the clinical use of sorafenib during breastfeeding. Because sorafenib is 99.5% bound to plasma proteins, the amount in milk is likely to be low. However, its half-life is 25 to 48 hours and it might accumulate in the infant. The manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding be discontinued during sorafenib therapy and for 2 weeks after the last dose. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding _In vitro_, sorafenib is 99.5% bound to human plasma proteins. Interactions Sorafenib does not appear to affect the metabolism of warfarin (a CYP2C9 substrate) in vivo; mean changes from baseline in prothrombin time (PT)/international normalized ratio (INR) did not appear to be greater in patients receiving sorafenib as compared with placebo. However, infrequent bleeding events or elevations in INR have been reported in some patients receiving concomitant therapy with warfarin and sorafenib. Potential pharmacokinetic interaction with doxorubicin and irinotecan (increased area under the serum concentration-time curve (AUC) of doxorubicin and of irinotecan and its active metabolite SN-38). The clinical importance of these findings is not known. Caution is advised. In vitro studies indicate that sorafenib inhibits glucuronidation by the uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 1A1 and 1A9 pathways; potential pharmacokinetic interaction (increased systemic exposure to UGT 1A1 or 1A9 substrates). Caution is advised when sorafenib is used concomitantly with drugs predominantly metabolized by the UGT 1A1 pathway (e.g., irinotecan, whose active metabolite SN-38 is metabolized by UGT 1A1). In vitro studies using human hepatic microsomes indicate that sorafenib inhibits CYP isoenzymes 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, and 3A4; however, sorafenib does not appear to alter exposure to dextromethorphan (a CYP2D6 substrate), midazolam (a CYP3A4 substrate), or omeprazole (a CYP2C19 substrate). The manufacturer states that it is unlikely that sorafenib will alter the metabolism of substrates of CYP isoenzymes 2C19, 2D6, or 3A4 in vivo or induce CYP isoenzymes 1A2 or 3A4. However, sorafenib may increase systemic exposure to CYP2B6 or CYP2C8 substrates; caution is advised when substrates of CYP2B6 or CYP2C8 are used concomitantly with sorafenib. For more Interactions (Complete) data for Sorafenib (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| References | |
| Additional Infomation |
Therapeutic Uses
Antineoplastic Agents; Protein Kinase Inhibitors Nexavar is indicated for the treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). /Included in US product label/ Nexavar is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally recurrent or metastatic, progressive, differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC) that is refractory to radioactive iodine treatment. /Included in US product label/ Nexavar is indicated for the treatment of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC). /Included in US product label/ Drug Warnings Palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (commonly referred to as hand-foot syndrome) and rash are common adverse effects of sorafenib, occurring in 30 and 40%, respectively, of patients receiving the drug in clinical studies, compared with 7 and 16%, respectively, of patients receiving placebo. Analysis of cumulative event rates suggests that rash and hand-foot syndrome usually are grade 1 or 2 and generally appear during the first 6 weeks of treatment with sorafenib. Management of dermatologic toxicities may include topical therapies for symptomatic relief, temporary interruption of therapy, and/or dosage modification of sorafenib; in severe or persistent cases, permanent discontinuance of sorafenib therapy may be necessary. Possible increased risk of bleeding. In clinical studies, bleeding (regardless of causality) was reported in 15.3 or 8.2% of patients receiving sorafenib or placebo, respectively. The incidences of grade 3 and 4 bleeding were 2 and 0%, respectively, in patients receiving sorafenib compared with 1.3 and 0.2%, respectively, in patients receiving placebo. Fatal hemorrhage occurred in one patient in each treatment group. Permanent discontinuance of sorafenib should be considered if any bleeding episode requires medical intervention. GI perforation, sometimes associated with apparent intra-abdominal tumor, has been reported rarely in patients receiving sorafenib. Sorafenib therapy should be discontinued if GI perforation occurs. Based on its mechanism of action and findings in animals, Nexavar may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Sorafenib caused embryo-fetal toxicities in animals at maternal exposures that were significantly lower than the human exposures at the recommended dose of 400 mg twice daily. Advise women of childbearing potential to avoid becoming pregnant while on Nexavar because of the potential hazard to the fetus. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Sorafenib (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Sorafenib decreases tumour cell proliferation _in vitro_. It attenuated tumour growth of human tumour xenografts in immunocompromised mice, reduced tumour angiogenesis, and increased tumour apoptosis in models of hepatocellular carcinoma, renal cell carcinoma, and differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Some studies suggest that sorafenib induces apoptosis in several tumour cell lines, although this effect is inconsistent across cell lines. Antiviral effects of sorafenib have been documented, as it was shown to inhibit hepatitis C viral replication _in vitro_. |
| Molecular Formula |
C21H16CLF3N4O3
|
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
464.82
|
| Exact Mass |
464.086
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 54.26; H, 3.47; Cl, 7.63; F, 12.26; N, 12.05; O, 10.33
|
| CAS # |
284461-73-0
|
| Related CAS # |
Sorafenib Tosylate;475207-59-1;Sorafenib-d3;1130115-44-4;Sorafenib-d4;1207560-07-3;Sorafenib-13C,d3;1210608-86-8
|
| PubChem CID |
216239
|
| Appearance |
white solid powder
|
| Density |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3
|
| Boiling Point |
523.3±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| Melting Point |
202-204°C
|
| Flash Point |
270.3±30.1 °C
|
| Vapour Pressure |
0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C
|
| Index of Refraction |
1.626
|
| LogP |
5.16
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
3
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
7
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
5
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
32
|
| Complexity |
646
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
0
|
| SMILES |
FC(F)(F)C1C=C(NC(NC2C=CC(=CC=2)OC2=CC=NC(C(=O)NC)=C2)=O)C=CC=1Cl
|
| InChi Key |
MLDQJTXFUGDVEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C21H16ClF3N4O3/c1-26-19(30)18-11-15(8-9-27-18)32-14-5-2-12(3-6-14)28-20(31)29-13-4-7-17(22)16(10-13)21(23,24)25/h2-11H,1H3,(H,26,30)(H2,28,29,31)
|
| Chemical Name |
4-[4-[[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbamoylamino]phenoxy]-N-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide
|
| Synonyms |
BAY 43-9006; BAY-439-006; BAY439006; BAY-439006; BAY 439006; BAY 549085; trade name: Nexavar; SFN
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: 4 mg/mL (8.61 mM) in 2% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 53% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with sonication.
Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 2.08 mg/mL (4.47 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.47 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 4: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.47 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 5: 5%DMSO+45%PEG400+50%H2O: 0.375mg/mL |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1514 mL | 10.7569 mL | 21.5137 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4303 mL | 2.1514 mL | 4.3027 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2151 mL | 1.0757 mL | 2.1514 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
Prospective, Non-interventional, Post-authorization Safety Study That Includes All Patients Diagnosed as Unresectable Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma and Treated With Sorafenib
CTID: NCT02185560
Phase: Status: Active, not recruiting
Date: 2024-11-20
The number of nuclei breaking the internal limiting membrane (ILM). A: Controlled group; B: ROP group; C: Vehicle-treated ROP group; D: Low doses sorafenib-treated ROP group; E: Middle doses sorafenib-treated ROP group; F: High dose sorafenib-treated ROP group. |
 |
 |