
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
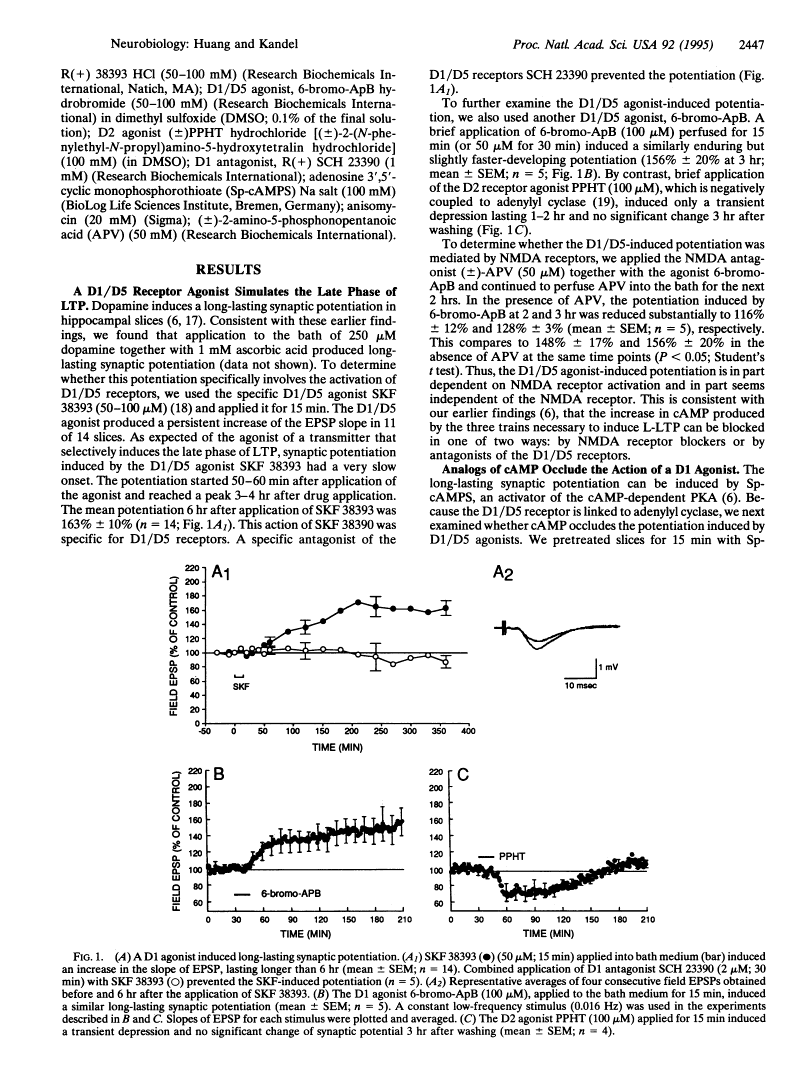
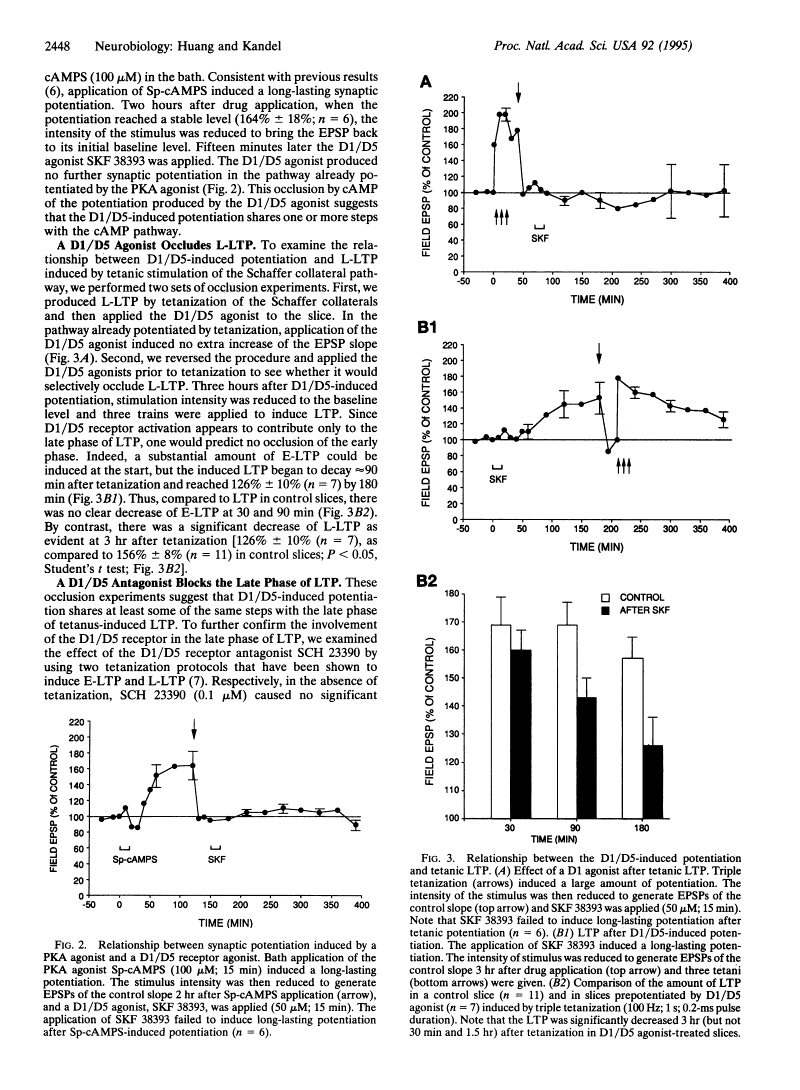
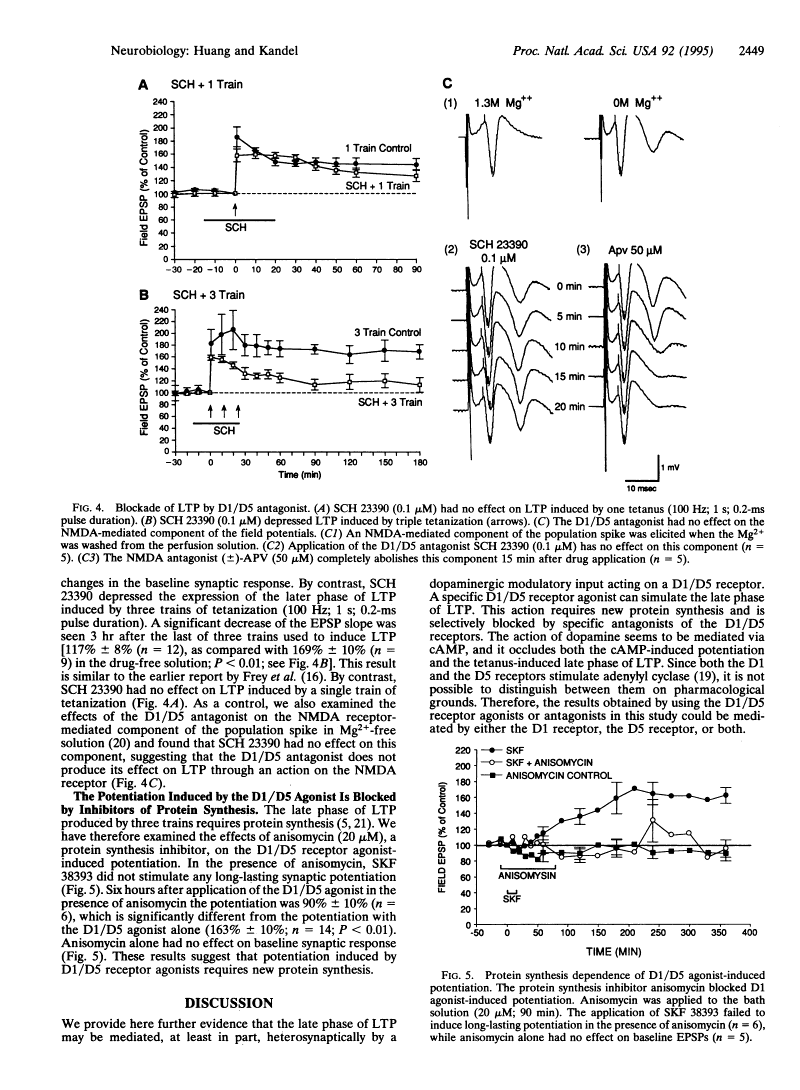
SKF 38393 HCl (SKF38393; SKF-38,393; SKF 38,393; SKF-38393A), the hydrochloride salt of SKF-38393, is a novel potent and selective dopamine D1 receptor agonist with IC50 of 110 nM, and the (+)-enantiomer is the active isomer. Desynchronization of electroencephalogram activity in rats is associated with SKF 38393-induced agonism of the D1DR. Additionally, serotonin SR-2C (5-HT1C receptor) agonism was demonstrated by SKF 38393. D5DR is triggered by SKF 38393 HCl. The intravenous administration of SKF 38393 significantly changed the activity of dopamine cells in rats treated with gallamine and locally anesthetized. Both rises and falls in the firing rate were noted in these rats.
| Targets |
dopamine D1 receptor; D5 receptor
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
In vitro activity: SKF-38393 hydrochloride causes a comparable alteration in cytomorphology and raises media cAMP levels[2].
? SKF-38393 hydrochloride (10 μmol/L; 1 hour) increases the threonine-phosphorylation of DA- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein of Mr. 32 kD (DARPP-32) in cultured GC cells[2]. The catecholamines norepinephrine and dopamine (DA) are present in the human ovary; in particular, in follicular fluid. Norepinephrine activates ovarian alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors and modulates ovarian steroidogenesis, but the significance of ovarian DA is unclear. We examined whether a DA receptor of the D1-subtype (D1-R) is present in human ovary and in cultured human granulosa luteal cells (GC). Using RT-PCR, we cloned complementary DNAs from adult human ovarian and GC messenger RNAs, which are identical to the human D1-R sequence. In ovarian sections, D1-R protein was identified (by immunohistochemistry) in granulosa cells of large antral follicles, cells of the corpus luteum, as well as in cultured GC. An immunoreactive band of approximately Mr 50,000 was found in cultured luteinized GC using the same antiserum in Western blots. The D1-R in these cells was functional, because DA, alone or in the presence of the beta-receptor antagonist propranolol, caused cellular contraction. The selective D1-R agonist SKF-38393 induced a similar change in cytomorphology and increased the levels of media cAMP. SKF-38393 failed, however, to significantly affect basal and hCG-stimulated progesterone release in vitro, indicating that the activation of the D1-R was not directly linked to synthesis of progesterone, the major steroid of human GC. Estradiol synthesis likewise was not affected. Using RT-PCR and immunohistochemistry, we found that GC express DA- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein of Mr 32,000 (DARPP-32), a protein typically associated with neurons bearing the D1-R. In cultured GC, DA and SKF-38393 induced increased threonine-phosphorylation of DARPP-32, even in the presence of propranolol but not in the presence of D1-R antagonist SCH-23390. Taken together, the presence of DA and a functional DA receptor and DARPP-32 indicate that a novel, physiological regulatory pathway involving DA exists in the human ovary [2]. |
||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Enzyme Assay |
SKF 38393 hydrochloride is an agonist of D1 with IC50 of 110 nM.
Iodinated SCH 23390, 125I-SCH 23982 (DuPont-NEN), was examined using quantitative autoradiography for its potency, selectivity, and anatomical and neuronal localization of binding to the dopamine D1 receptor in rat brain sections. 125I-SCH 23982 bound to D1 sites in the basal ganglia with very high affinity (Kd values of 55-125 pM), specificity (70-85% of binding was displaced by 5 microM cis-flupenthixol), and in a saturable manner (Bmax values of 65-176 fmol/mg protein). Specific 125I-SCH 23982 binding was displaced by the selective D1 antagonists SCH 23390 (IC50 = 90 pM) and cis-flupenthixol (IC50 = 200 pM) and the D1 agonist SKF 38393 (IC50 = 110 nM) but not by D2-selective ligands (I-sulpiride, LY 171555) or the S2 antagonist cinanserin. Compared with 3H-SCH 23390, the 5- to 10-fold greater affinity for the D1 site and 50-fold greater specific radioactivity of 125I-SCH 23982 makes it an excellent radioligand for labeling the D1 receptor. The concentrations of D1 sites were greatest in the medial substantia nigra and exceeded by over 50% the concentration of D1 sites in the lateral substantia nigra, caudoputamen, nucleus accumbens, olfactory tubercle, and entopeduncular nucleus. Lower concentrations of D1 sites were present in the internal capsule, dorsomedial frontal cortex, claustrum, and layer 6 of the neocortex. D1 sites were absent in the ventral tegmental area. Intrastriatal injections of the axon-sparing neurotoxin, quinolinic acid, depleted by 87% and by 46-58% the concentrations of displaceable D1 sites in the ipsilateral caudoputamen and medial and central pars reticulata of the substantia nigra, respectively. No D1 sites were lost in the lateral substantia nigra. Destruction of up to 94% of the mesostriatal dopaminergic projection with 6-hydroxydopamine did not reduce D1 binding nor, with one exception, increase striatal or nigral D1 receptor concentrations. 125I-SCH 23982 selectively labels D1 binding sites on striatonigral neurons with picomolar affinity, and these neurons contain the majority of D1 sites in rat brain[1]. |
||
| Cell Assay |
Cell Line: GC cells
Concentration: 10 μmol/L Incubation Time: 1 hour Result: Induced increased threonine-phosphorylation of DA- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein of Mr 32 kD (DARPP-32) in cultured GC cells. Western blotting [2] Western blotting was performed as previously described, with minor modifications. In brief, cells were harvested, frozen, thawed, homogenized in 62.5 mmol/L Tris-HCl buffer (pH 6.8) containing 10% sucrose and 2% SDS, sonicated, and heated (95 C for 5 min) in the presence of 10% mercaptoethanol. Samples (15 μg/lane) were separated electrophoretically on 10% or 12.5% SDS-polyacrylamide gels (SDS-PAGE). Proteins were transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes and probed with the same D1-R antiserum used for immunohistochemistry (1:1,000 dilution, incubation overnight at 4 C). In addition, a well-characterized monoclonal phospho-DARPP-32 specific antibody was used (1:500) to examine whether treatment of GC (for 1 h, in 2 cases, also 24 h) with DA (1 and 10 μmol/L) or SKF-38393 (1 and 10 μmol/L, RBI, Biotrend, Cologne, Germany, diluted in medium without serum) changed the phosphorylation of DARPP-32. For control purposes, the β-receptor antagonist propranolol (10 μmol/L) or the D1-R antagonist SCH-23390 (10 μmol/L, RBI) were added to the cells treated with DA or SKF-38393 (used at 1 μm). Cell morphology was monitored and documented. Immunoreactivity was detected using peroxidase-labeled antisera (1:3,000) and enhanced chemiluminescence, as described. In some cases, the blots were digitized, and integrated optical densities of the bands were determined using an edited version of the program NIH Image, as described previously. Immunoprecipitation experiments [2] Immunoprecipitation experiments were carried out to examine whether SKF-38393 (100 μmol/L, diluted in medium without serum) treatment of cultured GC (1 day after isolation) for 1 h increased threonine phosphorylation of DARPP-32. Media were removed, and cells were solubilized in buffer, containing 10 mmol/L NaH2PO4, 150 mmol/L NaCl, 2 mmol/L EDTA, 1% Triton X-100, 0.25% SDS, 1% sodium deoxycholate, and 2 mmol/L phenylmethanesulfonylfluoride. For immunoprecipitation, we used magnetic beads labeled with antimouse IgG and magnetic separation. The beads were first incubated with normal mouse serum (5% in PBS containing 10 mmol/L EGTA, 250 mmol/L saccharose, and 0.1% BSA) and were then labeled with 2 μL of the well-characterized monoclonal antibody directed against bovine DARPP-32, which recognizes primate DARPP-32 and which was used for immunocytochemistry, as well. Subsequently, beads were incubated with 150 μL GC cell lysate for 1 h at room temperature and then for 30 min at 4 C. After magnet separation, pellets were washed several times and used for SDS-PAGE, as described. Blots were developed using a monoclonal antibody against phospho-threonine (1:100); and, in some cases, they were evaluated densitometrically. Progesterone and estradiol measurements [2] The release of progesterone and estradiol into the culture medium by GC incubated for 6 h with SKF-38393 (10μ mol/L) in the absence or presence of hCG (10 IU/mL) was examined using triplicate wells for each treatment (n = 3). Samples were analyzed using commercial enzyme immunoassays, following the instructions of the manufacturer. Intraassay coefficients of variation ranged between 5–8%, and interassay coefficients of variation did not exceed 10%. All incubation and pipetting steps and the calculations of hormone concentrations were carried out in a fully automated immunodiagnos-tic analyzer. Results were corrected for small changes in cellular protein. ANOVA and t test were used to evaluate the results. Determination of cAMP [2] The levels of cAMP in the media of GC, 1 day after isolation, were examined after incubation for 3 or 6 h with SKF-38393 (1–100μ mol/L) in the presence of the phosphodiesterase inhibitor isobutylmethylxanthine (1 mmol/L). In a pilot study, SKF-38393 (at a concentration of 1 μmol/L) caused a small, but not statistically significant, increase in cAMP (20% over basal levels). Therefore, for three independent additional experiments, a higher SKF-38393 concentration (100 μmol/L) was used. These samples were measured using an enzyme immunoassay (R&D Systems), according to the instructions of the manufacturer. The sensitivity of the assay was 0.5 pmol/mL, and the intraassay coefficient of variability was smaller than 10%. To correct for small differences in cell density, cAMP results were expressed per microgram of cellular protein. Student’s t test was used to evaluate data. |
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References |
|
||
| Additional Infomation |
A selective D1 dopamine receptor agonist used primarily as a research tool.
Iodinated SCH 23390, 125I-SCH 23982 (DuPont-NEN), was examined using quantitative autoradiography for its potency, selectivity, and anatomical and neuronal localization of binding to the dopamine D1 receptor in rat brain sections. 125I-SCH 23982 bound to D1 sites in the basal ganglia with very high affinity (Kd values of 55-125 pM), specificity (70-85% of binding was displaced by 5 microM cis-flupenthixol), and in a saturable manner (Bmax values of 65-176 fmol/mg protein). Specific 125I-SCH 23982 binding was displaced by the selective D1 antagonists SCH 23390 (IC50 = 90 pM) and cis-flupenthixol (IC50 = 200 pM) and the D1 agonist SKF-38393 (IC50 = 110 nM) but not by D2-selective ligands (I-sulpiride, LY 171555) or the S2 antagonist cinanserin. Compared with 3H-SCH 23390, the 5- to 10-fold greater affinity for the D1 site and 50-fold greater specific radioactivity of 125I-SCH 23982 makes it an excellent radioligand for labeling the D1 receptor. The concentrations of D1 sites were greatest in the medial substantia nigra and exceeded by over 50% the concentration of D1 sites in the lateral substantia nigra, caudoputamen, nucleus accumbens, olfactory tubercle, and entopeduncular nucleus. Lower concentrations of D1 sites were present in the internal capsule, dorsomedial frontal cortex, claustrum, and layer 6 of the neocortex. D1 sites were absent in the ventral tegmental area. Intrastriatal injections of the axon-sparing neurotoxin, quinolinic acid, depleted by 87% and by 46-58% the concentrations of displaceable D1 sites in the ipsilateral caudoputamen and medial and central pars reticulata of the substantia nigra, respectively. No D1 sites were lost in the lateral substantia nigra. Destruction of up to 94% of the mesostriatal dopaminergic projection with 6-hydroxydopamine did not reduce D1 binding nor, with one exception, increase striatal or nigral D1 receptor concentrations. 125I-SCH 23982 selectively labels D1 binding sites on striatonigral neurons with picomolar affinity, and these neurons contain the majority of D1 sites in rat brain. [1] Parkinson's disease (PD) is characterized by progressive degeneration of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons. Several factors such as inhibition of the mitochondrial respiration, generation of hydroxyl radicals and reduced free radical defense mechanisms causing oxidative stress, have been postulated to contribute to the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons. 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) treated animals is a useful experimental model of PD, exhibiting most of the clinical features, as well as the main biochemical and pathologic symptoms of the disease. In the present study, we have examined a dopaminergic (D1) receptor agonist, SKF-38393 HCl (SKF) for its possible neuroprotective action against MPTP-induced insults on dopaminergic neurons. MPTP is converted by monoamine oxidase-B (MAO-B) to its neurotoxic metabolite 1-methyl-4-phenyl-pyridinium (MPP+), which is then taken up into the dopaminergic neurons. SKF-38393 had no effects either on total or monoamine oxidase B in the striatum. SKF-38393 blocked the MPTP-induced depletion of glutathione and attenuated MPTP-induced depletion of dopamine. Furthermore, it enhanced the activity of superoxide dismutase and hence mimicked the action of selegiline. The results of these studies are interpreted to suggest that SKF-38393 may prove a valuable drug in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. [3] The present study was undertaken to better assess the role of dopamine on exocytosis. Since direct activation of adenylate cyclase (e.g., with forskolin) enhances neurotransmitter release it was of interest to see whether the activation of D1-type dopamine receptors, which are positively coupled to adenylate cyclase, could also modulate the molecular machinery underlying the fusion of synaptic vesicles and the release of neurotransmitter. To answer this question we have looked at the effect of the D1-type dopamine receptor agonist SKF-38393 on the spontaneous release of glutamate from cultured rat hippocampal neurons. SKF-38393 enhanced the frequency but not the amplitude of tetrodotoxin-resistant excitatory postsynaptic currents which argues for a presynaptic locus of D1 action. This effect was blocked by the D1-dopaminergic receptor antagonist SCH-23390 and the protein kinase A inhibitors H-7 and Rp-cAMP whereas pertussis toxin failed to affect the dopaminergic response. In addition, carbachol and Ruthenium Red also stimulated exocytosis but did not occlude the SKF-38393-induced modulation. These results indicate that SKF-38393 presynaptically enhances the release of glutamate via a pertussis toxin-insensitive and protein kinase A-dependent mechanism, which most likely involves D1-type dopamine receptors. Our results underline the importance of protein kinase A as potent modulator of synaptic transmission and suggest that high concentrations of dopamine can greatly enhance the release of glutamate in the hippocampus. [4] |
| Molecular Formula |
C16H18CLNO2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
291.77
|
|
| Exact Mass |
291.102
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 65.86; H, 6.22; Cl, 12.15; N, 4.80; O, 10.97
|
|
| CAS # |
62717-42-4
|
|
| Related CAS # |
SKF 38393 hydrobromide; 20012-10-6; (R)-SKF 38393 hydrochloride; 81702-42-3; 62751-59-1 (R-isomer); 67287-49-4; 62717-42-4 (HCl)
|
|
| PubChem CID |
147514
|
|
| Appearance |
Light yellow to khaki solid powder
|
|
| LogP |
3.506
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
4
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
3
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
1
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
20
|
|
| Complexity |
291
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
Cl[H].O([H])C1=C(C([H])=C2C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(C3C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C=3[H])C2=C1[H])O[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
YEWHJCLOUYPAOH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C16H17NO2.ClH/c18-15-8-12-6-7-17-10-14(13(12)9-16(15)19)11-4-2-1-3-5-11;/h1-5,8-9,14,17-19H,6-7,10H2;1H
|
|
| Chemical Name |
5-phenyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-3-benzazepine-7,8-diol;hydrochloride
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (7.13 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4274 mL | 17.1368 mL | 34.2736 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6855 mL | 3.4274 mL | 6.8547 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3427 mL | 1.7137 mL | 3.4274 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
 |
|---|
 |
 |