
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
SB269970 HCl (SB 269970; GR125743; GR-125743; SB-269970), the hydrochloride salt form of SB-269970, is a novel and potent 5-HT7 receptor antagonist with antianxiety-like effects. It shows >50-fold selectivity for 5-HT7 over other receptors and inhibits 5-HT7 with a pKi of 8.3.
| Targets |
5-HT7 Receptor ( pKi = 8.3 nM )
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
|
||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Enzyme Assay |
SB269970 an antagonist of the 5-HT7 receptor with pKi of 8.3, exhibits >50-fold selectivity against other receptors.
|
||
| Cell Assay |
1. The presence of 5-HT(7) receptor mRNA and protein in 5-HT neurons suggests that this receptor may act as a 5-HT autoreceptor. In this study, the effect of the 5-HT(7) receptor antagonist, SB-269970 ((R)-1-[3-hydroxy phenyl)sulfonyl]-2-[2-(4-methyl-1-piperidinyl)ethyl]pyrrolidine), was investigated on 5-HT release in the guinea-pig and rat cortex and the rat dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN), using the techniques of in vitro [(3)H]-5-HT release or fast cyclic voltammetry, respectively. 2. Cortical slices were loaded with [(3)H]-5-HT and release was evoked by electrical stimulation. 5-CT inhibited the evoked release of [(3)H]-5-HT in a concentration-dependent manner. SB-269970 had no significant effect on [(3)H]-5-HT release while the 5-HT(1B) receptor antagonist, SB-224289 significantly potentiated [(3)H]-5-HT release. In addition, SB-269970 was unable to attenuate the 5-CT-induced inhibition of release while SB-224289 produced a rightward shift of the 5-CT response, generating estimated pK(B) values of 7.8 and 7.6 at the guinea-pig and rat terminal 5-HT autoreceptors respectively. 3. Rat DRN slices were electrically stimulated and the evoked 5-HT efflux detected by voltammetric analysis. 8-OH-DPAT inhibited evoked 5-HT efflux and was fully reversed by WAY 100635. SB-269970 had no effect on either 5-HT efflux per se or 8-OH-DPAT-induced inhibition of 5-HT efflux. In addition, 5-CT inhibited 5-HT efflux in a concentration-dependent manner. SB-269970 was unable to attenuate the 5-CT-induced inhibition of 5-HT efflux. 4. In conclusion, we were unable to provide evidence to suggest a 5-HT autoreceptor role for 5-HT(7) receptors. However, investigations with more selective 5-HT(7) receptor agonists are needed to confirm the data reported here.[2]
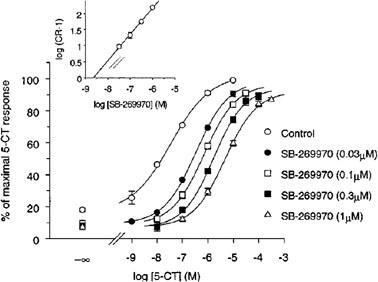
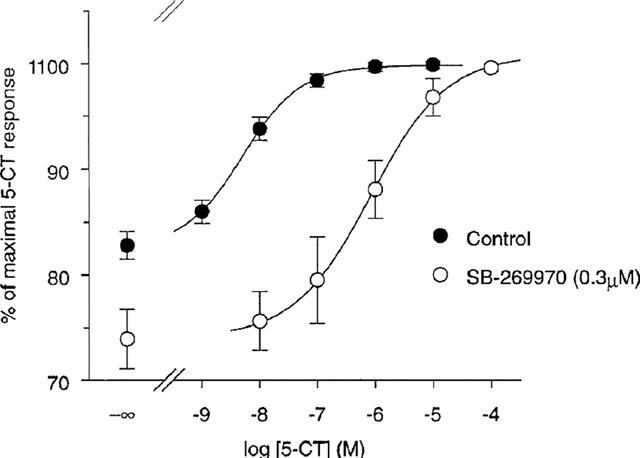
The novel 5-HT(7) receptor antagonist, SB-269970-A, potently displaced [(3)H]-5-CT from human 5-HT(7(a)) (pK(i) 8.9+/-0.1) and 5-HT(7) receptors in guinea-pig cortex (pK(i) 8.3+/-0.2). 5-CT stimulated adenylyl cyclase activity in 5-HT(7(a))/HEK293 membranes (pEC(50) 7.5+/-0.1) and SB-269970-A (0.03 - 1 microM) inhibited the 5-CT concentration-response with no significant alteration in the maximal response. The pA(2) (8.5+/-0.2) for SB-269970-A agreed well with the pK(i) determined from [(3)H]-5-CT binding studies. 5-CT-stimulated adenylyl cyclase activity in guinea-pig hippocampal membranes (pEC(50) of 8.4+/-0.2) was inhibited by SB-269970-A (0.3 microM) with a pK(B) (8.3+/-0.1) in good agreement with its antagonist potency at the human cloned 5-HT(7(a)) receptor and its binding affinity at guinea-pig cortical membranes. 5-HT(7) receptor mRNA was highly expressed in human hypothalamus, amygdala, thalamus, hippocampus and testis. SB-269970-A was CNS penetrant (steady-state brain : blood ratio of ca. 0.83 : 1 in rats) but was rapidly cleared from the blood (CLb=ca. 140 ml min(-1) kg(-1)). [1] |
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References | |||
| Additional Infomation |
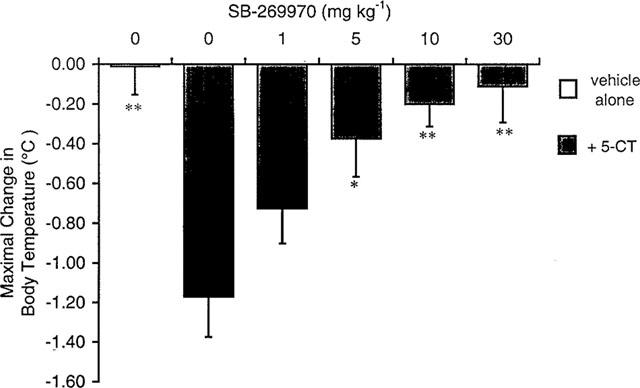
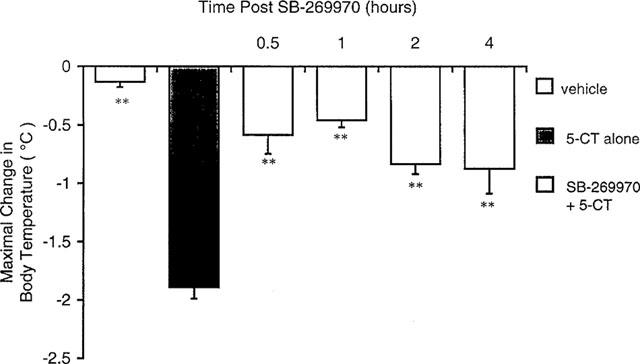
The aim of the present study was to examine the effect of the selective 5-HT7 receptor antagonist SB 269970 (0.25-20 mg/kg) in the behavioral tests commonly used for predicting anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like activity. Diazepam and imipramine were used as standard drugs. SB 269970 (in one medium dose of 0.5 or 1 mg/kg) exerted a specific antianxiety-like effect in the Vogel drinking test in rats, in the elevated plus-maze test in rats and in the four-plate test in mice. Moreover, SB 269970 (in one medium dose of 5 or 10 mg/kg) showed antidepressant-like activity in the forced swimming and the tail suspension tests in mice. At the same time, the tested compound at doses of 1-20 mg/kg did not change the spontaneous locomotor activity of mice. The potential anxiolytic and antidepressant effects produced by SB 269970 were weaker than those of the reference drugs employed. It is noteworthy that the active doses of SB 269970 were devoid of any visible motor side-effects. In conclusion, the results of our studies indicate that 5-HT7 receptor antagonists may play a role in the therapy of both anxiety and depression.[5]
Using conflict drinking and forced swimming tests in rats, we examined the anxiolytic- and the antidepressant-like activity, respectively, of (2R)-1-[(3-hydroxyphenyl)sulfonyl]-2-[2-(4-methyl-1-piperidinyl)ethyl]-pyrrolidine (SB 269970), a selective 5-HT(7) receptor antagonist, after its intrahippocampal administration. SB 269970 at doses of 0.3, 1 and 3 mug showed an anticonflict effect which was weaker than that of diazepam (40 mug), whereas SB 269970 at doses of 3 and 10 mug had marked anti-immobility action comparable to that of imipramine (0.1 mug). Importantly, the anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like activity of SB 269970 seemed to be specific, since that agent - when given by the same route in doses effective in either model - affected neither the shock threshold, nor the non-punished water consumption, nor the exploratory activity of rats. The obtained results indicate that the hippocampus is one of the neuroanatomical structures involved in the potential anxiolytic and, in particular, antidepressant activity of SB 269970.[6] |
| Molecular Formula |
C18H29CLN2O3S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
388.95
|
|
| Exact Mass |
388.159
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 55.58; H, 7.52; Cl, 9.11; N, 7.20; O, 12.34; S, 8.24
|
|
| CAS # |
261901-57-9
|
|
| Related CAS # |
SB-269970; 201038-74-6
|
|
| PubChem CID |
11957684
|
|
| Appearance |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| LogP |
4.425
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
2
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
5
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
5
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
25
|
|
| Complexity |
497
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
OC1=CC=CC(S(=O)(N2[C@@H](CCN3CCC(C)CC3)CCC2)=O)=C1.[H]Cl
|
|
| InChi Key |
XQCJOYZLWFNDIO-PKLMIRHRSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H28N2O3S.ClH/c1-15-7-11-19(12-8-15)13-9-16-4-3-10-20(16)24(22,23)18-6-2-5-17(21)14-18;/h2,5-6,14-16,21H,3-4,7-13H2,1H3;1H/t16-;/m1./s1
|
|
| Chemical Name |
3-[(2R)-2-[2-(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl)ethyl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]sulfonylphenol;hydrochloride
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.43 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.43 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: 30% Propylene glycol , 5% Tween 80 , 65% D5W: 30mg/mL Solubility in Formulation 4: 10 mg/mL (25.71 mM) in PBS (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with ultrasonication. |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5710 mL | 12.8551 mL | 25.7102 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5142 mL | 2.5710 mL | 5.1420 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2571 mL | 1.2855 mL | 2.5710 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
 |
|---|
 |
 |
 |
|---|
 |