
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
Doxorubicin HCl (formerly known as Adriamycin; FI 106; Adriblastina; DOXOCELL; Doxolem; NSC-123127 etc.) is an anthracycline antibiotic agent with anticancer activity. It causes DNA damage and apoptosis in tumor cells and inhibits DNA topoisomerase II. The use of it as an antineoplastic agent was authorized. Doxorubicin, the hydroxylated congener of daunorubicin, is isolated from Streptomyces peucetius var. caesius. By intercalating between base pairs in the DNA helix, doxorubicin inhibits the synthesis of proteins by preventing DNA replication. Furthermore, topoisomerase II is inhibited by doxorubicin.
| Targets |
Topoisomerase I (IC50 = 0.8 μM); Topoisomerase II (IC50 = 2.67 μM); Daunorubicins/Doxorubicins; HIV-1; DNA topoisomerase II (induces DNA double-strand breaks) [5][9]
Histone eviction from chromatin [5] |
|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
Doxorubicin, an antibiotic anthracycline, is widely believed to exhibit its anti-tumor activity on two basic levels: it modifies DNA and generates free radicals to cause DNA damage that causes cancer cells to undergo apoptosis. Doxorubicin inhibits DNA topoisomerase II (TOP2) and can intercalate into DNA strands to prevent DNA synthesis. When cells are multiplying quickly and expressing a lot of TOP2, doxorubicin works best. Additionally, doxorubicin can cause apoptosis by releasing cytochrome c from the mitochondria, ceramide (which activates p53 or other downstream pathways like JNK), the degradation of Akt by serine threonine proteases, an increase in the production of FasL (death receptor Fas/CD95 ligand) mRNA, and an increase in free radical production.[2]
Pre-treatment with GSNO (nitrosoglutathione) results in increased protein glutathionylation and doxorubicin accumulation in the nucleus of the doxorubicin-resistant breast cancer cell line MCF7/Dx, which in turn suppresses resistance.[3] Doxorubicin increased expression of cyclin G2 (CycG2) and phosphorylation of proteins in the ATM, ATM and Rad3-related (ATR) signaling pathways are responsible for induced G2/M checkpoint arrest.[5] Doxorubicin inhibits AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which can be further sensitized by pre-inhibition of AMPK. This results in SIRT1 dysfunction, p53 accumulation, and increased cell death in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) and cardiomyocytes.[6] Doxorubicin causes a noticeable heat shock response, and in neuroblastoma cells, it increases the apoptotic effect by either inhibiting or silencing heat shock proteins. When nanomolar Doxorubicin is administered to neuroblastoma cells, it results in a dose-dependent over-ubiquitination of a particular set of proteins without any detectable proteasome inhibition. Additionally, it causes a decrease in the activity of ubiquitinated enzymes like lactate dehydrogenase and α-enolase, whose protein ubiquitination patterns resemble those of the proteasome inhibitor Bortezomib, suggesting that Doxorubicin may also cause protein damage. [8] - Doxorubicin shows potent cytotoxicity against MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells (IC50 = 0.1 μM) and MCF-7 cells (IC50 = 0.05 μM) after 72h exposure [4] - Induces senescence in human cardiac progenitor cells via p53/p21 pathway activation (SA-β-gal+ cells increase to 80% at 0.5 μM) [1] - Synergistic effect with Bcl-2 siRNA in multidrug-resistant NCI/ADR-RES cells (combination index=0.3 at 50 nM) [4] - Generates ROS in H9c2 cardiomyocytes (2-fold increase at 1 μM) [3] |
| ln Vivo |
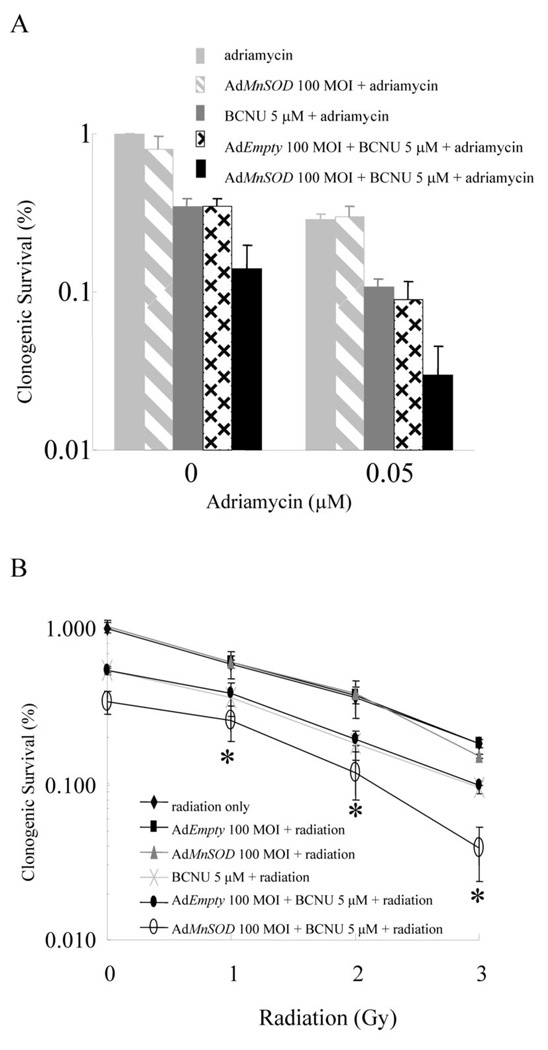
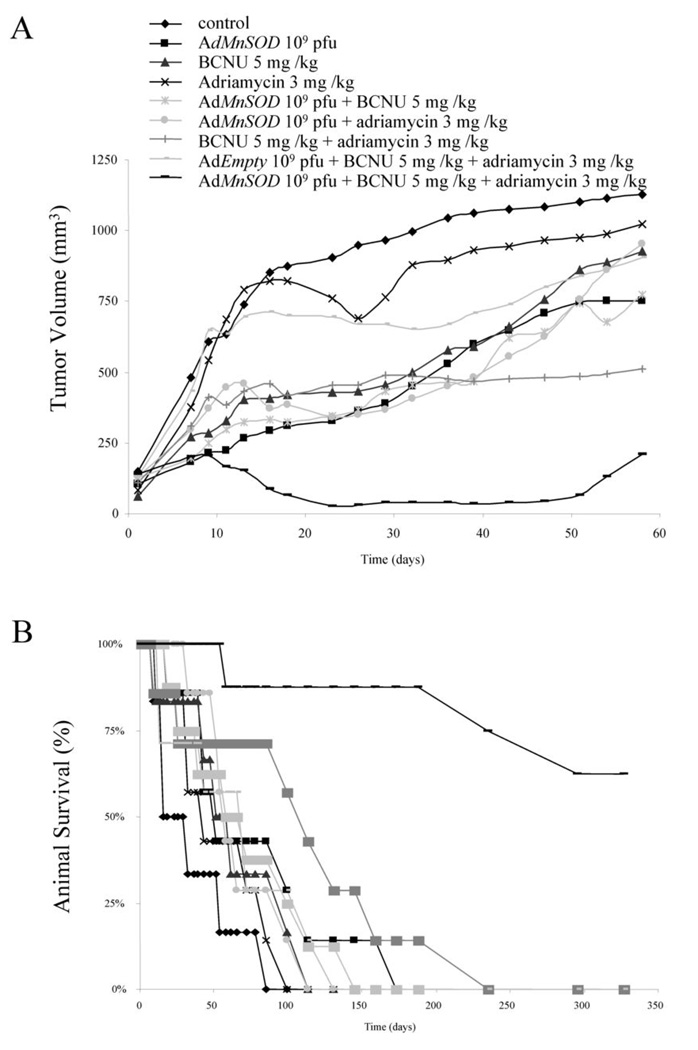
In vivo, the most effective combination for reducing the volumes of MB231 tumors and extending mouse survival is doxorubicin plus 1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea (BCNU) in conjunction with adenoviral MnSOD (AdMnSOD).[1]
Doxorubicin is indispensable in the treatment of solid tumors in childhood, soft tissue sarcomas, Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphomas, osteosarcomas, Kaposi's sarcoma, and breast and oesophageal carcinomas, despite the fact that its use is restricted by the toxic side effects, both acute and chronic.[2] - Doxorubicin (5 mg/kg weekly × 4, i.v.) reduces tumor volume by 70% in MDA-MB-231 xenograft mice [7] - Magnetic nanoparticle-loaded formulation (3 mg/kg, i.v.) increases tumor drug concentration 5-fold vs free drug [7] - Cumulative dose (15 mg/kg) induces chronic cardiotoxicity in rats: LVEF decrease 40%, fibrosis area 25% [2] |
| Enzyme Assay |
Purified human DNA topoisomerase I was assayed quantitatively by enzyme titrations with supercoiled pHC624 DNA in the presence of 0-2.0 microM doxorubicin. Supercoiled and relaxed DNAs were resolved by agarose gel electrophoresis in the presence of ethidium bromide, and the percentage of conversion of supercoiled DNA to relaxed DNA was quantified by scanning microdensitometry. The inhibition of DNA topoisomerase I activity was measured at varying concentrations of doxorubicin. Doxorubicin inhibited enzyme activity at an IC50 value (the concentration required to inhibit 50% of the total activity) of 0.8 microM. Similar inhibition was observed for daunomycin, a structurally related anthracycline antitumor drug. These results indicate that anthracyclines inhibit human DNA topoisomerase I activity at concentrations that cause DNA damage and cytotoxicity in vivo [11].
- Topoisomerase II decatenation assay: Kinetoplast DNA incubated with enzyme and Doxorubicin (0.1-10 μM) for 30 min at 37°C. DNA breaks visualized by agarose gel electrophoresis [5] - Caspase-3 activity assay: Cell lysates treated with Doxorubicin (1 μM) incubated with DEVD-pNA substrate. Cleavage measured at 405 nm [1] |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Culture[7]
LS141 primary human cell line was derived from a patient with high-grade retroperitoneal dedifferentiated liposarcoma and the MPNST cells were derived from a patient with a high-grade peripheral nerve sheath tumor of the thigh. These were grown in RPMI1640 supplemented with 15% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum plus penicillin and streptomycin.[7] Colony Assays [7] MPNST cells were treated with doxorubicin, flavopiridol, or the combination of the two drugs together in sequence. MPNST cells were chosen given that LS141 (and other CDK4 dependent) cells are exquisitely sensitive to CDK4 inhibition in vitro, thus making combination studies uninterruptable. MPNST cells were plated, in triplicate, at a density of 1000 cells/100 mm2 per plate. Twenty-four hours after plating, cells were treated for 24 hours with the IC50 of doxorubicin (D, 15 nM), flavopiridol (F, 150 nM), drug free media (control), or a combination of the two drugs, either concomitantly or sequentially for 24 hours each. After treatment, drug-containing medium was removed and cells were allowed to grow for 10 days to form colonies. The resulting colonies were stained with 0.01% crystal violet for 30 minutes and colonies counted using an automated colony counter. Results are presented as the percentage of untreated controls and the statistical significance of the experimental results was determined by the two-sided t test. - Apoptosis assay: Cells stained with Annexin V/PI after 48h Doxorubicin treatment (0.1-5 μM). Quantified by flow cytometry [4] - ROS measurement: H9c2 cells loaded with DCFH-DA, treated with Doxorubicin (0.5-5 μM). Fluorescence read at 488/525 nm [3] - Senescence assay: SA-β-gal staining performed after 72h exposure to 0.5 μM Doxorubicin. Blue-stained cells counted microscopically [1] |
| Animal Protocol |
Female athymic nude mice injected s.c. with MB231 cells; 3 mg/kg/day; Delivered intratumorly
Female athymic nude mice injected s.c. with MB231 cells In vivo studies LS141 xenografts were established by directly implanting into severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice. Once tumors reached 100 mm3 , groups of five mice were treated with the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of flavopiridol (9 mg/kg), doxorubicin (0.9 mg/kg), or doxorubicin (0.7 mg/kg) followed by flavopiridol (7 mg/kg) at selected time points (1, 4 and 7 hours). In addition, one set of animals was treated in reverse order of flavopiridol followed by doxorubicin, administered 7 hours apart. All treatments were administered in intraperitoneal fashion, twice weekly, for a total of 5 treatments. Tumors were measured every 2 to 3 days with calipers, and tumor volumes were calculated by the formula π/ 6 × (large diameter) × (small diameter)2. Tumor volume was compared between groups of mice at various points in time based on the experiment and the statistical significance of the experimental results was determined by the two-sided t test. Given the aggressive morbidity of the tumors, animal survival data could not be estimated. Toxicity was monitored by weight loss. These studies were done in accordance with the Principles of Laboratory Animal Care, under an IACUC-approved protocol. - Xenograft model: MDA-MB-231 cells implanted subcutaneously in nude mice. Doxorubicin (5 mg/kg in saline) administered i.v. weekly × 4. Tumors measured biweekly [7] - Cardiotoxicity model: Rats injected i.p. with Doxorubicin (2.5 mg/kg cumulative dose weekly × 6). Echocardiography performed pre/post treatment [2] - Biodistribution: Tumor-bearing mice injected with 99mTc-labeled liposomal Doxorubicin (3 mg/kg). Organs harvested at 24h for gamma counting [10] |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Following a 10 mg/m2 administration of liposomal doxorubicin in patients with AIDS-related Kaposi's Sarcoma, the Cmax and AUC values were calculated to be 4.12 ± 0.215 μg/mL and 277 ± 32.9 μg/mL•h respectively. Approximately 40% of the dose appears in the bile in 5 days, while only 5% to 12% of the drug and its metabolites appear in the urine during the same time period. In urine, <3% of the dose was recovered as doxorubicinol over 7 days. The steady-state distribution volume of doxorubicin ranges from 809 L/m2 to 1214 L/m2. The plasma clearance of doxorubicin ranges from 324 mL/min/m2 to 809 mL/min/m2 by metabolism and biliary excretion. Sexual differences in doxorubicin were also observed, with men having a higher clearance compared to women (1088 mL/min/m2 versus 433 mL/min/m2). Following the administration of doses ranging from 10 mg/m2 to 75 mg/m2 of doxorubicin hydrochloride, the plasma clearance was estimated to be 1540 mL/min/m2 in children greater than 2 years of age and 813 mL/min/m2 in infants younger than 2 years of age. Nonencapsulated doxorubicin hydrochloride is not stable in gastric acid, and animal studies indicate that the drug undergoes little, if any, absorption from the GI tract. The drug is extremely irritating to tissues and, therefore, must be administered iv. Following iv infusion of a single 10- or 20-mg/sq m dose of liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride in patients with AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma, average peak plasma doxorubicin (mostly bound to liposomes) concentrations are 4.33 or 10.1 ug/mL, respectively, following a 15-minute infusion and 4.12 or 8.34 ug/mL, respectively, following a 30-minute infusion. Following iv infusion over 15 minutes of a 40-mg/sq m dose of liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride in adults with AIDS-related Kaposi's, peak plasma concentrations averaged 20.1 ug/mL. Nonencapsulated (conventional) doxorubicin hydrochloride exhibits linear pharmacokinetics; PEG-stabilized liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride also exhibits dose-proportional, linear pharmacokinetics over a dosage range of 10-20 mg/sq m. The pharmacokinetics of liposomally encapsulated doxorubicin at a dose of 50 mg/sq m have been reported to be nonlinear. At a dose of 50 mg/sq m, a longer elimination half-life and lower clearance compared to those observed with a 20 mg/sq m dose are expected, with greater-than-proportional increases in area under the plasma concentration-time curve. Encapsulation of doxorubicin hydrochloride in PEG-stabilized (Stealth) liposomes substantially alters the pharmacokinetics of the drug relative to conventional iv formulations (ie, nonencapsulated drug), with resultant decreased distribution into the peripheral compartment, increased distribution into Kaposi's lesions, and decreased plasma clearance. Doxorubicin administered as a conventional injection is widely distributed in the plasma and in tissues. As early as 30 seconds after iv administration, doxorubicin is present in the liver, lungs, heart, and kidneys. Doxorubicin is absorbed by cells and binds to cellular components, particularly to nucleic acids. The volume of distribution of doxorubicin hydrochloride administered iv as a conventional injection is about 700-1100 L/sq m. Nonencapsulated doxorubicin is approximately 50-85% bound to plasma proteins... Doxorubicin hydrochloride administered iv as the liposomally encapsulated drug distributes into Kaposi's sarcoma lesions to a greater extent than into healthy skin. Following iv administration of a single 20-mg/sq m dose of liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride, doxorubicin concentrations in Kaposi's sarcoma lesions were 19 (range: 3-53)-fold higher than those observed in healthy skin; however, blood concentrations in the lesions or in healthy skin were not considered. In addition, distribution of doxorubicin into Kaposi's sarcoma lesions following iv administration of liposomally encapsulated drug was 5.2-11.4 times greater than that following iv administration of comparable doses of a conventional (nonencapsulated) injection. The mechanism by which liposomal encapsulation enhances doxorubicin distribution into Kaposi's sarcoma lesions has not been elucidated fully, but similar PEG-stabilized liposomes containing colloidal gold as a marker have been shown to enter Kaposi's sarcoma-like lesions in animals. Extravasation of the liposomes also may occur by passage of the particles through endothelial cell gaps present in Kaposi's sarcoma. Once within the lesions, the drug presumably is released locally as the liposomes degrade and become permeable in situ. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for DOXORUBICIN (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Doxorubicin is capable of undergoing 3 metabolic routes: one-electron reduction, two-electron reduction, and deglycosidation. However, approximately half of the dose is eliminated from the body unchanged. The two-electron reduction is the major metabolic pathway of doxorubicin. In this pathway, doxorubicin is reduced to doxorubicinol, a secondary alcohol, by various enzymes, including Alcohol dehydrogenase [NADP(+)], Carbonyl reductase [NADPH] 1, Carbonyl reductase [NADPH] 3, and Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3. The one-electron reduction is facilitated by several oxidoreductase, both cytosolic and mitochondrial, to form a doxirubicin-semiquinone radical. These enzymes include mitochondrial and cystolic NADPH dehydrogenates, xanthine oxidase, and nitric oxide synthases. This semiquinone metabolite can be re-oxidized to doxorubicin, although with the concurrent formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and hydrogen peroxide. It is the ROS generating through this pathway that contributes most to the doxorubicin-related adverse effects, particularly cardiotoxicity, rather than through doxorubicin semiquinone formation. Deglycosidation is a minor metabolic pathway, since it only accounts for 1 to 2% of doxorubicin metabolism. Under the catalysis of cytoplasmic NADPH quinone dehydrogenase, xanthine oxidase, NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase, doxorubicin can either be reduced to doxorubicin deoxyaglycone or hydrolyzed to doxorubicin hydroxyaglycone. Nonencapsulated doxorubicin is metabolized by NADPH-dependent aldoketoreductases to the hydrophilic 13-hydroxyl metabolite doxorubicinol, which exhibits antineoplastic activity and is the major metabolite; these reductases are present in most if not all cells, but particularly in erythrocytes, liver, and kidney. Although not clearly established, doxorubicinol also appears to be the moiety responsible for the cardiotoxic effects of the drug. Undetectable or low plasma concentrations (ie, 0.8-26.2 ng/mL) of doxorubicinol have been reported following iv administration of a single 10- to 50-mg/sq m dose of doxorubicin hydrochloride as a PEG-stabilized liposomal injection; it remains to be established whether such liposomally encapsulated anthracyclines are less cardiotoxic than conventional (nonencapsulated) drug, and the usual precautions for unencapsulated drug currently also should be observed for the liposomal preparation. Substantially reduced or absent plasma concentrations of the usual major metabolite of doxorubicin observed with the PEG-stabilized liposomal injection suggests that either the drug is not released appreciably from the liposomes as they circulate or that some doxorubicin may be released but that the rate of doxorubicinol elimination greatly exceeds the release rate; doxorubicin hydrochloride encapsulated in liposomes that have not been PEG-stabilized is metabolized to doxorubicinol. Other metabolites, which are therapeutically inactive, include the poorly water-soluble aglycones, doxorubicinone (adriamycinone) and 7-deoxydoxorubicinone (17-deoxyadriamycinone), and conjugates. The aglycones are formed in microsomes by NADPH-dependent, cytochrome reductase-mediated cleavage of the amino sugar moiety. The enzymatic reduction of doxorubicin to 7-deoxyaglycones is important to the cytotoxic effect of the drug since it results in hydroxyl radicals that cause extensive cell damage and death. With nonencapsulated doxorubicin, more than 20% of the total drug in plasma is present as metabolites as soon as 5 minutes after a dose, 70% in 30 minutes, 75% in 4 hours, and 90% in 24 hours. ... At least 6 metabolites have been identified, the principal one being adriamycinol. This product results from redn of the keto group on C13 by an enzyme found in leukocytes and erythrocytes, and presumably in malignant tissues. Doxorubicin is converted to doxorubicinol, to aglycones, and to other derivatives For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for DOXORUBICIN (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Doxorubicin is capable of undergoing 3 metabolic routes: one-electron reduction, two-electron reduction, and deglycosidation. However, approximately half of the dose is eliminated from the body unchanged. Two electron reduction yields doxorubicinol, a secondary alcohol. This pathway is considered the primary metabolic pathway. The one electron reduction is facilitated by several oxidoreductases to form a doxirubicin-semiquinone radical. These enzymes include mitochondrial and cystolic NADPH dehydrogenates, xanthine oxidase, and nitric oxide synthases. Deglycosidation is a minor metabolic pathway (1-2% of the dose undergoes this pathway). The resultant metabolites are deoxyaglycone or hydroxyaglycone formed via reduction or hydrolysis respectively. Enzymes that may be involved with this pathway include xanthine oxidase, NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase, and cytosolic NADPH dehydrogenase. Route of Elimination: 40% of the dose appears in bile in 5 days. 5-12% of the drug and its metabolites appears in urine during the same time period. <3% of the dose recovered in urine was doxorubicinol. Half Life: Terminal half life = 20 - 48 hours. Biological Half-Life The terminal half-life of doxorubicin ranges from 20 hours to 48 hours. The distribution half-life of doxorubicin is approximately 5 minutes. For the liposomal formulation, the first-phase and second-phase half-lives were calculated to be 4.7 ± 1.1 and 52.3 ± 5.6 hours respectively for a 10 mg/m2 of doxorubicin in patients with AIDS-Related Kaposi’s Sarcoma. Plasma concentrations of nonencapsulated doxorubicin and its metabolites decline in a biphasic or triphasic manner. In the first phase of the triphasic model, nonencapsulated doxorubicin is rapidly metabolized, presumably by a first-pass effect through the liver. It appears that most of this metabolism is completed before the entire dose is administered. In the triphasic model, nonencapsulated doxorubicin and its metabolites are rapidly distributed into the extravascular compartment with a plasma half-life of approximately 0.2-0.6 hours for doxorubicin and 3.3 hours for its metabolites. This is followed by relatively prolonged plasma concentrations of doxorubicin and its metabolites, probably resulting from tissue binding. During the second phase, the plasma half-life of nonencapsulated doxorubicin is 16.7 hours and that of its metabolites is 31.7 hours. In the biphasic model, the initial distribution t1/2 has been reported to average about 5-10 minutes, and the terminal elimination t1/2 has been reported to average about 30 hours. Plasma concentrations of liposomally encapsulated doxorubicin hydrochloride appear to decline in a biphasic manner. Following iv administration of a single 10- to 40-mg/sq m dose of doxorubicin hydrochloride as a liposomal injection in patients with AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma, the initial plasma half-life (t1/2 alpha) of doxorubicin averaged 3.76-5.2 hours while the terminal elimination half-life (t1/2 beta) averaged 39.1-55 hours. The initial distribution half-life of approximately 5 minutes suggests rapid tissue uptake of doxorubicin, while its slow elimination from tissues is reflected by a terminal half-life of 20 to 48 hours. Plasma T/2 of Adriamycin is about 17 hr in patient, whereas that of its metabolites is about 32 hr. - Plasma t₁/₂ = 20-48 h in humans, Vd = 25 L/kg [11] - 90% plasma protein binding [11] - Major metabolites: Doxorubicinol (active), aglycones [9] - Biliary excretion >60% [9] |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
The chemotherapeutic agent doxorubicin (DOX) is associated with a dose-dependent cardiotoxicity that can eventuate into heart failure. This study aimed to characterize the onset and degree of cardiotoxicity in rats receiving 10 mg/kg DOX administered as a single intraperitoneal injection (DOX1), 10 daily intraperitoneal injections of 1 mg/kg (DOX2), or in 5 weekly intraperitoneal injections of 2 mg/kg (DOX3). Transthoracic echocardiography measurements were recorded every week to characterize the onset and degree of cardiotoxicity in the 3 groups. An 80% mortality rate was observed at day 28 in DOX1, whereas DOX2 and DOX3 reached 80% mortality at days 107 and 98, respectively. Fractional shortening decreased by 30% at week 2 in DOX1, 55% at week 13 in DOX2, and 42% at week 13 in DOX3. In addition, cardiac function clearly differed between DOX1 and DOX3, whereas DOX2 and DOX3 were similar. These findings indicate that administration of the dose over the course of days (DOX2) or weeks (DOX3) results in a better survival rate and more classic signs of DOX-induced dilated cardiomyopathy, albeit with later onset, as compared with a single 10 mg/kg bolus injection of DOX.[J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2007 Jul;46(4):20-32.]
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Most sources consider breastfeeding to be contraindicated during maternal antineoplastic drug therapy, especially anthracyclines such as doxorubicin. It might be possible to breastfeed safely during intermittent therapy with an appropriate period of breastfeeding abstinence; however, the high levels and persistence of the active metabolite doxorubicinol in milk make defining an appropriate abstinence interval difficult. Some have suggested a breastfeeding abstinence period of 5 to 10 days after a dose. More recent pharmacokinetic modeling using a worst-case scenario suggests that 13 days would be required to minimize both systemic and gut toxicity after the colostral phase. Chemotherapy may adversely affect the normal microbiome and chemical makeup of breastmilk. Women who receive chemotherapy during pregnancy are more likely to have difficulty nursing their infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants A woman was diagnosed with B-cell lymphoma at 27 weeks of pregnancy. Labor was induced at 34 4/7 weeks and treatment was begun with a standard regimen of rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone in unspecified doses on a 21-day cycle, starting on day 2 postpartum. She pumped and discarded her milk and fed her infant donor milk for the first 10 days of each cycle and then breastfed her infant for the remaining 10 days before the next treatment cycle. The 10-day period of breastfeeding abstinence was determined by using about 3 half-lives of vincristine. After completion of 4 cycles of chemotherapy, her infant was reportedly healthy and developing without any complications. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk A study of adolescent males who had received chemotherapy for childhood malignancies found that having received doxorubicin was associated with elevated serum prolactin concentrations. A woman diagnosed with Hodgkin's lymphoma during the second trimester of pregnancy received 3 rounds of chemotherapy during the third trimester of pregnancy and resumed chemotherapy 4 weeks postpartum. Milk samples were collected 15 to 30 minutes before and after chemotherapy for 16 weeks after restarting. The regimen consisted of doxorubicin 40 mg, bleomycin 16 units, vinblastine 9.6 mg and dacarbazine 600 mg, all given over a 2-hour period every 2 weeks. The microbial population and metabolic profile of her milk were compared to those of 8 healthy women who were not receiving chemotherapy. The breastmilk microbial population in the patient was markedly different from that of the healthy women, with increases in Acinetobacter sp., Xanthomonadacae and Stenotrophomonas sp. and decreases in Bifidobacterium sp. and Eubacterium sp. Marked differences were also found among numerous chemical components in the breastmilk of the treated woman, most notably DHA and inositol were decreased. A telephone follow-up study was conducted on 74 women who received cancer chemotherapy at one center during the second or third trimester of pregnancy to determine if they were successful at breastfeeding postpartum. Only 34% of the women were able to exclusively breastfeed their infants, and 66% of the women reported experiencing breastfeeding difficulties. This was in comparison to a 91% breastfeeding success rate in 22 other mothers diagnosed during pregnancy, but not treated with chemotherapy. Other statistically significant correlations included: 1. mothers with breastfeeding difficulties had an average of 5.5 cycles of chemotherapy compared with 3.8 cycles among mothers who had no difficulties; and 2. mothers with breastfeeding difficulties received their first cycle of chemotherapy on average 3.4 weeks earlier in pregnancy. Of the 62 women who received a doxorubicin-containing regimen, 39 had breastfeeding difficulties. - Cardiotoxicity: Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) decrease >10% at cumulative dose >400 mg/m² [9] - Myelosuppression: Nadir at 10-14 days (WBC <2000 cells/mm³) [11] - LD50 = 10 mg/kg in mice (single i.v. dose) [6] - Hepatotoxicity: ALT increase 3-fold at 15 mg/kg cumulative dose [2] |
| References |
[1]. Cancer Res. 2009 May 15;69(10):4294-300. [2]. Food Chem Toxicol. 2010 Jun;48(6):1425-38. [3]. Biochem J. 2011 Dec 1;440(2):175-83. [4]. Br J Cancer. 2011 Mar 15;104(6):957-67. [5]. J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 29;287(27):22838-53. [6]. J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 9;287(11):8001-12. [7]. Clin Cancer Res. 2012 May 1;18(9):2638-47. [8]. FEBS J. 2012 Jun;279(12):2182-91. [9]. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009 May;9(5):338-50. |
| Additional Infomation |
Doxorubicin Hydrochloride (Adriamycin) can cause cancer according to an independent committee of scientific and health experts. It can cause developmental toxicity and male reproductive toxicity according to state or federal government labeling requirements.
Adriamycin hydrochloride appears as orange-red thin needles. Aqueous solutions yellow-orange at acid pHs, orange-red at neutral pHs, and violet blue over pH 9. (NTP, 1992) Doxorubicin hydrochloride is an anthracycline. Doxorubicin hydrochloride (liposomal) is an antineoplastic prescription medicine approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of certain types of cancer, including ovarian cancer, multiple myeloma, and AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma. Kaposi sarcoma is caused by infection with human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8). HHV-8 infection can be an opportunistic infection (OI) of HIV. Doxorubicin Hydrochloride is the hydrochloride salt of doxorubicin, an anthracycline antibiotic with antineoplastic activity. Doxorubicin, isolated from the bacterium Streptomyces peucetius var. caesius, is the hydroxylated congener of daunorubicin. Doxorubicin intercalates between base pairs in the DNA helix, thereby preventing DNA replication and ultimately inhibiting protein synthesis. Additionally, doxorubicin inhibits topoisomerase II which results in an increased and stabilized cleavable enzyme-DNA linked complex during DNA replication and subsequently prevents the ligation of the nucleotide strand after double-strand breakage. Doxorubicin also forms oxygen free radicals resulting in cytotoxicity secondary to lipid peroxidation of cell membrane lipids; the formation of oxygen free radicals also contributes to the toxicity of the anthracycline antibiotics, namely the cardiac and cutaneous vascular effects. Antineoplastic antibiotic obtained from Streptomyces peucetius. It is a hydroxy derivative of DAUNORUBICIN. See also: Doxorubicin (has active moiety). Drug Indication Celdoxome pegylated liposomal is indicated in adults: as monotherapy for patients with metastatic breast cancer , where there is an increased cardiac risk. or treatment of advanced ovarian cancer in women who have failed a first-line platinum-based chemotherapy regimen. in combination with bortezomib for the treatment of progressive multiple myeloma in patients who have received at least one prior therapy and who have already undergone or are unsuitable for bone marrow transplant. for treatment of AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) in patients with low CD4 counts (< 200 CD4 lymphocytes/mm3) and extensive mucocutaneous or visceral disease. Celdoxome pegylated liposomal may be used as first-line systemic chemotherapy, or as second line chemotherapy in AIDS-KS patients with disease that has progressed with, or in patients intolerant to, prior combination systemic chemotherapy comprising at least two of the following agents: a vinca alkaloid, bleomycin and standard doxorubicin (or other anthracycline). Caelyx pegylated liposomal is indicated: as monotherapy for patients with metastatic breast cancer , where there is an increased cardiac risk; for treatment of advanced ovarian cancer in women who have failed a first-line platinum-based chemotherapy regimen; in combination with bortezomib for the treatment of progressive multiple myeloma in patients who have received at least one prior therapy and who have already undergone or are unsuitable for bone marrow transplant; for treatment of AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) in patients with low CD4 counts ( Myocet liposomal, in combination with cyclophosphamide, is indicated for the first-line treatment of metastatic breast cancer in adult women. Treatment of breast and ovarian cancer . Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma Doxorubicin is a deoxy hexoside, an anthracycline, an anthracycline antibiotic, an aminoglycoside, a member of tetracenequinones, a member of p-quinones, a primary alpha-hydroxy ketone and a tertiary alpha-hydroxy ketone. It has a role as an Escherichia coli metabolite. It is a conjugate base of a doxorubicin(1+). It derives from a hydride of a tetracene. Doxorubicin hydrochloride (liposomal) is an antineoplastic prescription medicine approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of certain types of cancer, including ovarian cancer, multiple myeloma, and AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma. Kaposi sarcoma is caused by infection with human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8). HHV-8 infection can be an opportunistic infection (OI) of HIV. Doxorubicin is a cytotoxic anthracycline antibiotic isolated from cultures of Streptomyces peucetius var. caesius along side with daunorubicin, another cytotoxic agent, in 1970. Although they both have aglyconic and sugar moieties, doxorubicin's side chain terminates with a primary alcohol group compared to the methyl group of daunorubicin. Although its detailed molecular mechanisms have yet to be understood, doxorubicin is generally thought to exert its effect through DNA intercalation, which eventually leads to DNA damage and the generation of reactive oxygen species. Thanks to its efficacy and broad effect, doxorubicin was approved by the FDA in 1974 to treat a variety of cancer, including but not limited to breast, lung, gastric, ovarian, thyroid, non-Hodgkin’s and Hodgkin’s lymphoma, multiple myeloma, sarcoma, and pediatric cancers. However, one of the major side effects of doxorubicin is cardiotoxicity, which excludes patients with poor heart function and requires treatment termination once the maximally tolerated cumulative dose is reached. Doxorubicin is an Anthracycline Topoisomerase Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of doxorubicin is as a Topoisomerase Inhibitor. Doxorubicin has been reported in Talaromyces aculeatus, Hamigera fusca, and other organisms with data available. Doxorubicin is an anthracycline antibiotic with antineoplastic activity. Doxorubicin, isolated from the bacterium Streptomyces peucetius var. caesius, is the hydroxylated congener of daunorubicin. Doxorubicin intercalates between base pairs in the DNA helix, thereby preventing DNA replication and ultimately inhibiting protein synthesis. Additionally, doxorubicin inhibits topoisomerase II which results in an increased and stabilized cleavable enzyme-DNA linked complex during DNA replication and subsequently prevents the ligation of the nucleotide strand after double-strand breakage. Doxorubicin also forms oxygen free radicals resulting in cytotoxicity secondary to lipid peroxidation of cell membrane lipids; the formation of oxygen free radicals also contributes to the toxicity of the anthracycline antibiotics, namely the cardiac and cutaneous vascular effects. Doxorubicin is only found in individuals that have used or taken this drug. It is antineoplastic antibiotic obtained from Streptomyces peucetius. It is a hydroxy derivative of daunorubicin. [PubChem]Doxorubicin has antimitotic and cytotoxic activity through a number of proposed mechanisms of action: Doxorubicin forms complexes with DNA by intercalation between base pairs, and it inhibits topoisomerase II activity by stabilizing the DNA-topoisomerase II complex, preventing the religation portion of the ligation-religation reaction that topoisomerase II catalyzes. Antineoplastic antibiotic obtained from Streptomyces peucetius. It is a hydroxy derivative of DAUNORUBICIN. See also: Doxorubicin Hydrochloride (has salt form); Zoptarelin Doxorubicin (is active moiety of); Zoptarelin Doxorubicin Acetate (is active moiety of). Drug Indication Doxorubicin is indicated for the treatment of neoplastic conditions like acute lymphoblastic leukemia, acute myeloblastic leukemia, Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma, metastatic breast cancer, metastatic Wilms’ tumor, metastatic neuroblastoma, metastatic soft tissue and bone sarcomas, metastatic ovarian carcinoma, metastatic transitional cell bladder carcinoma, metastatic thyroid carcinoma, metastatic gastric carcinoma, and metastatic bronchogenic carcinoma. Doxorubicin is also indicated for use as a component of adjuvant therapy in women with evidence of axillary lymph node involvement following resection of primary breast cancer. For the liposomal formulation, doxorubicin is indicated for the treatment of ovarian cancer that has progressed or recurred after platinum-based chemotherapy, AIDS-Related Kaposi's Sarcoma after the failure of prior systemic chemotherapy or intolerance to such therapy, and multiple myeloma in combination with bortezomib in patients who have not previously received bortezomib and have received at least one prior therapy. FDA Label Zolsketil pegylated liposomal is a medicine used to treat the following types of cancer in adults: ⢠breast cancer that has spread to other parts of the body in patients at risk of heart problems. Zolsketil pegylated liposomal is used on its own for this disease; ⢠advanced ovarian cancer in women whose previous treatment including a platinum-based cancer medicine has stopped working; ⢠multiple myeloma (a cancer of the white blood cells in the bone marrow), in patients with progressive disease who have received at least one other treatment in the past and have already had, or are unsuitable for, a bone marrow transplantation. Zolsketil pegylated liposomal is used in combination with bortezomib (another cancer medicine); ⢠Kaposi's sarcoma in patients with AIDS who have a very damaged immune system. Kaposi's sarcoma is a cancer that causes abnormal tissue to grow under the skin, on moist body surfaces or on internal organs. Zolsketil pegylated liposomal contains the active substance doxorubicin and is a âhybrid medicine'. This means that it is similar to a âreference medicine' containing the same active substance called Adriamycin. However, in Zolsketil pegylated liposomal the active substance is enclosed in tiny fatty spheres called liposomes, whereas this is not the case for Adriamycin. Caelyx pegylated liposomal is indicated: as monotherapy for patients with metastatic breast cancer , where there is an increased cardiac risk; for treatment of advanced ovarian cancer in women who have failed a first-line platinum-based chemotherapy regimen; in combination with bortezomib for the treatment of progressive multiple myeloma in patients who have received at least one prior therapy and who have already undergone or are unsuitable for bone marrow transplant; for treatment of AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) in patients with low CD4 counts ( Myocet liposomal, in combination with cyclophosphamide, is indicated for the first-line treatment of metastatic breast cancer in adult women. Treatment of breast and ovarian cancer . Mechanism of Action Generally, doxorubicin is thought to exert its antineoplastic activity through 2 primary mechanisms: intercalation into DNA and disrupt topoisomerase-mediated repairs and free radicals-mediated cellular damages. Doxorubicin can intercalate into DNA through the anthraquinone ring, which stabilizes the complex by forming hydrogen bonds with DNA bases. Intercalation of doxorubicin can introduce torsional stress into the polynucleotide structure, thus destabilizing nucleosome structures and leading to nucleosome eviction and replacement. Additionally, the doxorubicin-DNA complex can interfere with topoisomerase II enzyme activity by preventing relegation of topoisomerase-mediated DNA breaks, thus inhibiting replication and transcription and inducing apoptosis. Moreover, doxorubicin can be metabolized by microsomal NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase into a semiquinone radical, which can be reoxidized in the presence of oxygen to form oxygen radicals. Reactive oxygen species have been known to cause cellular damage through various mechanisms, including lipid peroxidation and membrane damage, DNA damage, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. Although free radicals generated from this pathway can be deactivated by catalase and superoxide dismutase, tumor and myocardial cells tend to lack these enzymes, thus explaining doxorubicin's effectiveness against cancer cells and tendency to cause cardiotoxicity. Doxorubicin hydrochloride is an antineoplastic antibiotic with pharmacologic actions similar to those of daunorubicin. Although the drug has anti-infective properties, its cytotoxicity precludes its use as an anti-infective agent. The precise and/or principal mechanism(s) of the antineoplastic action of doxorubicin is not fully understood. It appears that the cytotoxic effect of the drug results from a complex system of multiple modes of action related to free radical formation secondary to metabolic activation of the doxorubicin by electron reduction, intercalation of the drug into DNA, induction of DNA breaks and chromosomal aberrations, and alterations in cell membranes induced by the drug. Evidence from in vitro studies in cells treated with doxorubicin suggests that apoptosis (programmed cell death) also may be involved in the drug's mechanism of action. These and other mechanisms (chelation of metal ions to produce drug-metal complexes) also may contribute to the cardiotoxic effects of the drug. Doxorubicin undergoes enzymatic 1- and 2-electron reduction to the corresponding semiquinone and dihydroquinone. 7-Deoxyaglycones are formed enzymatically by 1-electron reduction, and the resulting semiquinone free radical reacts with oxygen to produce the hydroxyl radical in a cascade of reactions; this radical may lead to cell death by reacting with DNA, RNA, cell membranes, and proteins. The dihydroquinone that results from 2-electron reduction of doxorubicin also can be formed by the reaction of 2 semiquinones. In the presence of oxygen, dihydroquinone reacts to form hydrogen peroxide, and in its absence, loses its sugar and gives rise to the quinone methide, a monofunctional alkylating agent with low affinity for DNA. The contribution of dihydroquinone and the quinone methide to the cytotoxicity of doxorubicin is unclear. Experimental evidence indicates that doxorubicin forms a complex with DNA by intercalation between base pairs, causing inhibition of DNA synthesis and DNA-dependent RNA synthesis by the resulting template disordering and steric obstruction. Doxorubicin also inhibits protein synthesis. Doxorubicin is active throughout the cell cycle including the interphase. Several anthracycline-induced effects may contribute to the development of cardiotoxicity. In animals, anthracyclines cause a selective inhibition of cardiac muscle gene expression for ?-actin, troponin, myosin light-chain 2, and the M isoform of creatine kinase, which may result in myofibrillar loss associated with anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity. Other potential causes of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity include myocyte damage from calcium overload, altered myocardial adrenergic function, release of vasoactive amines, and proinflammatory cytokines. Limited data indicate that calcium-channel blocking agents (eg, prenylamine) or beta-adrenergic blocking agents may prevent calcium overload ... It has been suggested that the principal cause of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity is associated with free radical damage to DNA. Anthracyclines intercalate DNA, chelate metal ions to produce drug-metal complexes, and generate oxygen free radicals via oxidation-reduction reactions. Anthracyclines contain a quinone structure that may undergo reduction via NADPH-dependent reactions to produce a semiquinone free radical that initiates a cascade of oxygen-free radical generation. It appears that the metabolite, doxorubicinol, may be the moiety responsible for cardiotoxic effects, and the heart may be particularly susceptible to free-radical injury because of relatively low antioxidant concentrations. ... Chelation of metal ions, particularly iron, by the drug results in a doxorubicin-metal complex that catalyzes the generation of reactive oxygen free radicals, and the complex is a powerful oxidant that can initiate lipid peroxidation in the absence of oxygen free radicals. This reaction is not blocked by free-radical scavengers, and probably is the principal mechanism of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity. The effect of doxorubicin on reactive oxygen metb in rat heart was investigated. It produced oxygen radicals in heart homogenate, sarcoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, and cytosol, the major sites of cardiac damage. Superoxide prodn in heart sarcosomes and the mitochondrial fraction was incr. Apparently, free radical formation by doxorubicin, which occurs in the same myocardial compartments that are subject to drug-induced tissue injury, may damage the heart by exceeding the oxygen radical detoxifying capacity of cardiac mitochondria and sarcoplasmic reticulum. - Anthracycline antibiotic that intercalates DNA and inhibits topoisomerase II [9] - FDA black box warning for cardiotoxicity [9] - Clinical applications: Breast cancer, lymphoma, sarcoma [9] - Resistance mechanisms: P-gp efflux, glutathione conjugation [8] |
| Molecular Formula |
C27H29NO11.HCL
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
579.98
|
|
| Exact Mass |
579.15
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 55.91; H, 5.21; Cl, 6.11; N, 2.42; O, 30.34
|
|
| CAS # |
25316-40-9
|
|
| Related CAS # |
25316-40-9 (Doxorubicin HCl); 23214-92-8
|
|
| PubChem CID |
443939
|
|
| Appearance |
Red to orange solid powder
|
|
| Boiling Point |
810.3ºC at 760 mmHg
|
|
| Melting Point |
216ºC
|
|
| Flash Point |
443.8ºC
|
|
| Vapour Pressure |
9.64E-28mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| Source |
Streptomyces peucetius var. Caesius
|
|
| LogP |
1.503
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
7
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
12
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
5
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
40
|
|
| Complexity |
977
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
6
|
|
| SMILES |
Cl[H].O([C@@]1([H])C([H])([H])[C@@]([H])([C@@]([H])([C@]([H])(C([H])([H])[H])O1)O[H])N([H])[H])[C@]1([H])C2C(=C3C(C4C(=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C=4C(C3=C(C=2C([H])([H])[C@@](C(C([H])([H])O[H])=O)(C1([H])[H])O[H])O[H])=O)OC([H])([H])[H])=O)O[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
MWWSFMDVAYGXBV-RUELKSSGSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C27H29NO11.ClH/c1-10-22(31)13(28)6-17(38-10)39-15-8-27(36,16(30)9-29)7-12-19(15)26(35)21-20(24(12)33)23(32)11-4-3-5-14(37-2)18(11)25(21)34;/h3-5,10,13,15,17,22,29,31,33,35-36H,6-9,28H2,1-2H3;1H/t10-,13-,15-,17-,22+,27-;/m0./s1
|
|
| Chemical Name |
(7S,9S)-7-[(2R,4S,5S,6S)-4-amino-5-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-6,9,11-trihydroxy-9-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-4-methoxy-8,10-dihydro-7H-tetracene-5,12-dione;hydrochloride
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment (e.g. under nitrogen), avoid exposure to moisture and light. |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.75 mg/mL (4.74 mM) (saturation unknown) in 5% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 50% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.59 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.59 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7242 mL | 8.6210 mL | 17.2420 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3448 mL | 1.7242 mL | 3.4484 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1724 mL | 0.8621 mL | 1.7242 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
Treatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children
CTID: NCT00400946
Phase: Phase 3 Status: Completed
Date: 2024-11-27
 |
|---|
 |