
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
Betaxolol (Betoptima; Kerlone; Betoptic; Kerlon; SL-75212 HCl; ALO-140102) is a β1 adrenergic receptor antagonist/blocker with antihypertensive effects. It is applied to the management of glaucoma and hypertension. With an IC50 of 6 μM, betaxolol inhibits the β1 adrenergic receptor.
| Targets |
Beta1 Adrenergic Receptor
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
|
||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Cell Assay |
Dissociated cortical cells from 16–18-day-old fetal rats are grown in 35 mm dishes in DMEM supplemented with L-glutamine (4 mM), glucose (6 g/L), penicillin (100 U/mL), streptomycin (100 μg/mL), and 10% hormonal supplemented medium that contains sodium selenite (0.3 μM), progesterone (0.2 μM), putrescine (600 μM), transferrin (1 mg/mL), insulin (250 μg/mL), putrescine (600 μM), progesterone (0.2 μM), and estradiol (0.1 pM). After that, the cultures are moved to a culture medium without hormone supplements. After adding L-glutamate, the mixture is incubated under normoxic conditions for an additional 4 hours. L-glutamate and betaxolol are added to the cultures simultaneously. In anoxic conditions, 95% N2/5% CO2 for 5 hours at 37 °C, are applied to the cultures in other experiments. Anoxia occurs first, and then bexolol. Next, the cells are swapped out for normoxic ones (95% O2/5% CO2) for three hours in order to achieve reoxygenation. Measuring the release of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) into the supernatant of cell cultures following hypoxia/reoxygenation or glutamate exposure is a useful method for evaluating cellular injury. By monitoring NADH metabolism for two minutes at 340 nm, LDH activity is measured spectrophotometrically.
|
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Absorption of an oral dose is complete. There is a small and consistent first-pass effect resulting in an absolute bioavailability of 89% ± 5% that is unaffected by the concomitant ingestion of food or alcohol. Metabolism / Metabolites Primarily hepatic. Approximately 15% of the dose administered is excreted as unchanged drug, the remainder being metabolites whose contribution to the clinical effect is negligible. Biological Half-Life 14-22 hours |
||
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Hepatotoxicity
Betaxolol therapy has been associated with a low rate of mild-to-moderate elevations of serum aminotransferase levels which are usually asymptomatic and transient and resolve even with continuation of therapy. There have been no well documented cases of clinically apparent, acute liver injury attributable to betaxolol. Thus, hepatotoxicity due to betaxolol must be very rare, if it occurs at all. Most commonly used beta-blockers have been linked to rare instances of clinically apparent liver injury, typically with onset within 2 to 12 weeks, a hepatocellular pattern of liver enzyme elevations, rapid recovery on withdrawal, and little evidence of hypersensitivity (rash, fever, eosinophilia) or autoantibody formation. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Because of its relatively extensive excretion into breastmilk and minimal reported experience during breastfeeding, other beta-blocking agents may be preferred for systemic use, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. Ophthalmic use of betaxolol by the mother should pose little risk to the breastfed infant, although some guidelines state that gel formulations are preferred over solutions. To substantially diminish the amount of drug that reaches the breastmilk after using eye drops, place pressure over the tear duct by the corner of the eye for 1 minute or more, then remove the excess solution with an absorbent tissue. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants A study of mothers taking beta-blockers during nursing found a numerically, but not statistically significant increased number of adverse reactions in those taking any beta-blocker. Although the ages of infants were matched to control infants, the ages of the affected infants were not stated. None of the mothers were taking betaxolol. Beta-adrenergic blocking drugs with breastmilk excretion characteristics similar to betaxolol have caused adverse effects in breastfed newborns. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information on the effects of beta-blockade or betaxolol during normal lactation was not found as of the revision date. A study in 6 patients with hyperprolactinemia and galactorrhea found no changes in serum prolactin levels following beta-adrenergic blockade with propranolol. Protein Binding 50% |
||
| References | |||
| Additional Infomation |
Betaxolol is a propanolamine that is 3-aminopropane-1,2-diol in which the hydrogen of the primary hydoxy is substituted by a 4-[2-(cyclopropylmethoxy)ethyl]phenyl group and one of the hydrogens attached to the amino group is substituted by isopropyl. It is a selective beta1-receptor blocker and is used in the treatment of glaucoma as well as hypertension, arrhythmias, and coronary heart disease. It is also used to reduce non-fatal cardiac events in patients with heart failure. It has a role as a beta-adrenergic antagonist, an antihypertensive agent and a sympatholytic agent.
A cardioselective beta-1-adrenergic antagonist with no partial agonist activity. Betaxolol is a beta-Adrenergic Blocker. The mechanism of action of betaxolol is as an Adrenergic beta-Antagonist. Betaxolol is a cardioselective beta-blocker used in the treatment of hypertension. Betaxolol has not been linked to instances of clinically apparent drug induced liver injury. Betaxolol is a racemic mixture and selective beta-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist with antihypertensive and anti-glaucoma activities and devoid of intrinsic sympathomimetic activity. Betaxolol selectively and competitively binds to and blocks beta-1 adrenergic receptors in the heart, thereby decreasing cardiac contractility and rate. This leads to a reduction in cardiac output and lowers blood pressure. When applied topically in the eye, this agent reduces aqueous humor secretion and lowers the intraocular pressure (IOP). In addition, betaxolol prevents the release of renin, a hormone secreted by the kidneys that causes constriction of blood vessels. A cardioselective beta-1-adrenergic antagonist with no partial agonist activity. See also: Betaxolol Hydrochloride (has salt form). Drug Indication For the management of hypertension. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Betaxolol selectively blocks catecholamine stimulation of beta(1)-adrenergic receptors in the heart and vascular smooth muscle. This results in a reduction of heart rate, cardiac output, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and possibly reflex orthostatic hypotension. Betaxolol can also competitively block beta(2)-adrenergic responses in the bronchial and vascular smooth muscles, causing bronchospasm. Pharmacodynamics Betaxolol is a competitive, beta(1)-selective (cardioselective) adrenergic antagonist. Betaxolol is used to treat hypertension, arrhythmias, coronary heart disease, glaucoma, and is also used to reduce non-fatal cardiac events in patients with heart failure. Activation of beta(1)-receptors (located mainly in the heart) by epinephrine increases the heart rate and the blood pressure, and the heart consumes more oxygen. Drugs such as betaxolol that block these receptors therefore have the reverse effect: they lower the heart rate and blood pressure and hence are used in conditions when the heart itself is deprived of oxygen. They are routinely prescribed in patients with ischemic heart disease. In addition, beta(1)-selective blockers prevent the release of renin, which is a hormone produced by the kidneys which leads to constriction of blood vessels. Betaxolol is lipophilic and exhibits no intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA) or membrane stabilizing activity. |
| Molecular Formula |
C18H29NO3
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
307.43
|
|
| Exact Mass |
307.21
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 70.32; H, 9.51; N, 4.56; O, 15.61
|
|
| CAS # |
63659-18-7
|
|
| Related CAS # |
Betaxolol hydrochloride; 63659-19-8; Levobetaxolol hydrochloride; 116209-55-3; Betaxolol-d5; 1189957-99-0; 63659-18-7; 93221-48-8 (S-isomer free base); 116209-55-3 (S-isomer HCl)
|
|
| PubChem CID |
2369
|
|
| Appearance |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| Density |
1.067 g/cm3
|
|
| Boiling Point |
448ºC at 760 mmHg
|
|
| Melting Point |
61-63°C
|
|
| Flash Point |
224.7ºC
|
|
| LogP |
2.784
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
2
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
4
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
11
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
22
|
|
| Complexity |
286
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
O(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1[H])OC([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])N([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])O[H])C([H])([H])C1([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
NWIUTZDMDHAVTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H29NO3/c1-14(2)19-11-17(20)13-22-18-7-5-15(6-8-18)9-10-21-12-16-3-4-16/h5-8,14,16-17,19-20H,3-4,9-13H2,1-2H3
|
|
| Chemical Name |
1-[4-[2-(cyclopropylmethoxy)ethyl]phenoxy]-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propan-2-ol
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.13 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.13 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.13 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2528 mL | 16.2639 mL | 32.5277 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6506 mL | 3.2528 mL | 6.5055 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3253 mL | 1.6264 mL | 3.2528 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT01660620 | Completed | Drug: topical betaxolol Drug: Betaxolol |
Development of Side Effects From Betaxolol |
Smith-Kettlewell Eye Research Institute |
April 2011 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00061542 | Completed | Drug: BETOPTIC S (betaxolol HCl) Drug: Timolol Gel-forming Solution (TGFS) |
Glaucoma Ocular Hypertension |
Alcon Research | January 2003 | Phase 3 |
| NCT02617459 | Completed | Drug: Levobetaxolol eye drops Drug: Betaxolol eye drops |
Primary Open-angle Glaucoma Ocular Hypertension |
Zhaoke (Guangzhou) Ophthalmology Pharmaceutical Ltd. |
January 4, 2019 | Phase 3 |
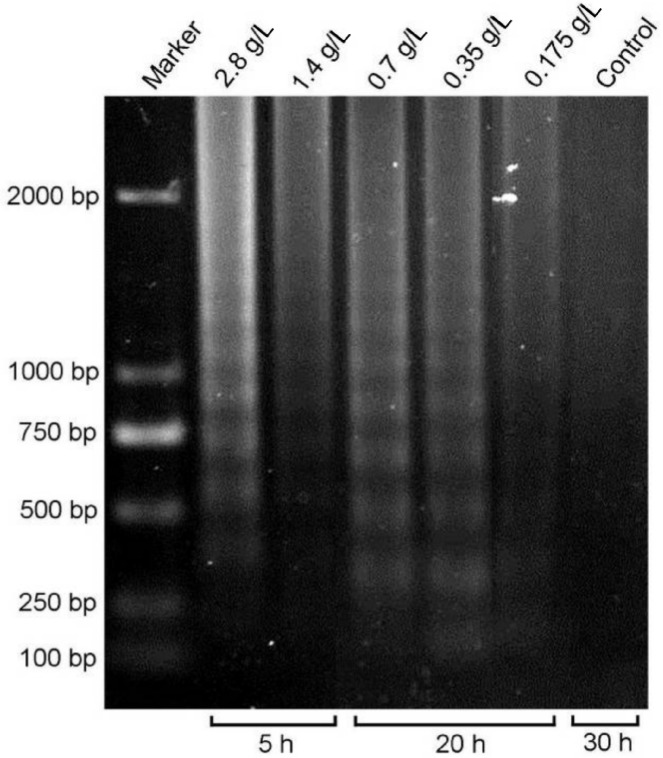 Effect of betaxolol on the DNA fragmentation of HCE cells.Int J Ophthalmol. 2014; 7(1): 14–21. Effect of betaxolol on the DNA fragmentation of HCE cells.Int J Ophthalmol. 2014; 7(1): 14–21. |
|---|
 |
|