
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g | |||
| Other Sizes |
Purity: ≥98%
Atomoxetine HCl (formerly LY139603; LY-139603; Tomoxetine; Strattera; Tomoxetina; Tomoxetinum), the hydrochloride salt of Atomoxetine, is a potent and selective norepinephrine (NE) transporter/reuptate inhibitor that has been used for treating attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). It has a Ki of 5 nM for norepinephrine (NE) transporter/reuptate inhibition, and it has 290- and 15-fold lower affinity for human 5-HT and DA transporters, respectively. The treatment of ADHD with atomoxetine has received approval.
| Targets |
Norepinephrine (NE) transporter ( Ki = 5 nM ); 5-HT ( Ki = 77 nM )
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
|
||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Enzyme Assay |
Atomoxetine, a neuroactive drug, is approved for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). It is primarily known as a high affinity blocker of the noradrenaline transporter, whereby its application leads to an increased level of the corresponding neurotransmitter in different brain regions. However, the concentrations used to obtain clinical effects are much higher than those which are required to block the transporter system. Thus, off-target effects are likely to occur. In this way, we previously identified atomoxetine as blocker of NMDA receptors. As many psychotropic drugs give rise to sudden death of cardiac origin, we now tested the hypothesis whether atomoxetine also interacts with voltage-gated sodium channels of heart muscle type in clinically relevant concentrations. Electrophysiological experiments were performed by means of the patch-clamp technique at human heart muscle sodium channels (hNav1.5) heterogeneously expressed in human embryonic kidney cells. Atomoxetine inhibited sodium channels in a state- and use-dependent manner. Atomoxetine had only a weak affinity for the resting state of the hNav1.5 (Kr: ∼ 120 µM). The efficacy of atomoxetine strongly increased with membrane depolarization, indicating that the inactivated state is an important target. A hallmark of this drug was its slow interaction. By use of different experimental settings, we concluded that the interaction occurs with the slow inactivated state as well as by slow kinetics with the fast-inactivated state. Half-maximal effective concentrations (2-3 µM) were well within the concentration range found in plasma of treated patients. Atomoxetine also interacted with the open channel. However, the interaction was not fast enough to accelerate the time constant of fast inactivation. Nevertheless, when using the inactivation-deficient hNav1.5_I408W_L409C_A410W mutant, we found that the persistent late current was blocked half maximal at about 3 µM atomoxetine. The interaction most probably occurred via the local anesthetic binding site. Atomoxetine inhibited sodium channels at a similar concentration as it is used for the treatment of ADHD. Due to its slow interaction and by inhibiting the late current, it potentially exerts antiarrhythmic properties[2].
|
||
| Cell Assay |
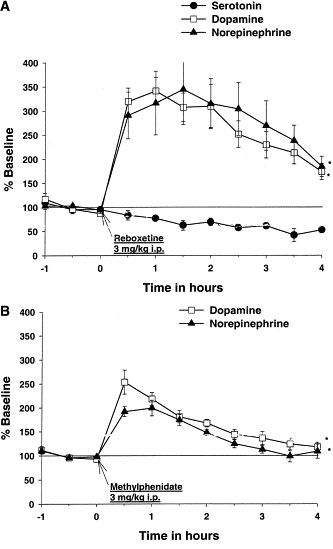
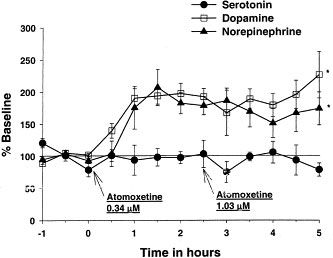
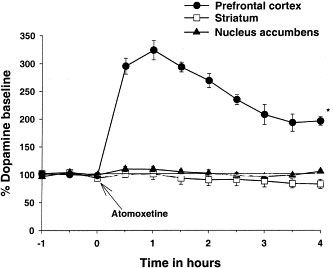
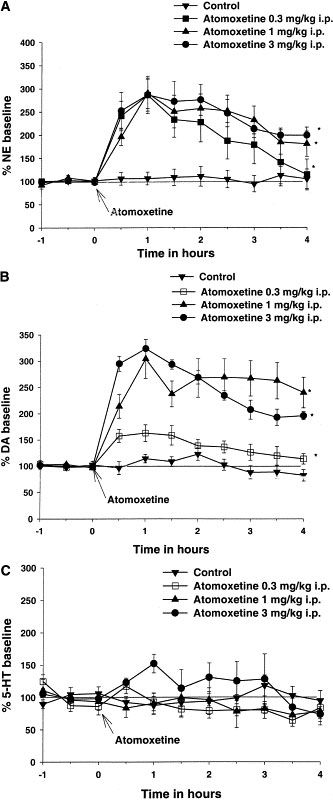
The selective norepinephrine (NE) transporter inhibitor atomoxetine (formerly called tomoxetine or LY139603) has been shown to alleviate symptoms in Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). We investigated the mechanism of action of atomoxetine in ADHD by evaluating the interaction of atomoxetine with monoamine transporters, the effects on extracellular levels of monoamines, and the expression of the neuronal activity marker Fos in brain regions. Atomoxetine inhibited binding of radioligands to clonal cell lines transfected with human NE, serotonin (5-HT) and dopamine (DA) transporters with dissociation constants (K(i)) values of 5, 77 and 1451 nM, respectively, demonstrating selectivity for NE transporters. In microdialysis studies, atomoxetine increased extracellular (EX) levels of NE in prefrontal cortex (PFC) 3-fold, but did not alter 5-HT(EX) levels. Atomoxetine also increased DA(EX) concentrations in PFC 3-fold, but did not alter DA(EX) in striatum or nucleus accumbens. In contrast, the psychostimulant methylphenidate, which is used in ADHD therapy, increased NE(EX) and DA(EX) equally in PFC, but also increased DA(EX) in the striatum and nucleus accumbens to the same level. The expression of the neuronal activity marker Fos was increased 3.7-fold in PFC by atomoxetine administration, but was not increased in the striatum or nucleus accumbens, consistent with the regional distribution of increased DA(EX). We hypothesize that the atomoxetine-induced increase of catecholamines in PFC, a region involved in attention and memory, mediates the therapeutic effects of atomoxetine in ADHD. In contrast to methylphenidate, atomoxetine did not increase DA in striatum or nucleus accumbens, suggesting it would not have motoric or drug abuse liabilities[3].
|
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Absorption The pharmacokinetic profile of atomoxetine is highly dependent on cytochrome P450 2D6 genetic polymorphisms of the individual. A large fraction of the population (up to 10% of Caucasians and 2% of people of African descent and 1% of Asians) are poor metabolizers (PMs) of CYP2D6 metabolized drugs. These individuals have reduced activity in this pathway resulting in 10-fold higher AUCs, 5-fold higher peak plasma concentrations, and slower elimination (plasma half-life of 21.6 hours) of atomoxetine compared with people with normal CYP2D6 activity. Atomoxetine is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with absolute bioavailability of about 63% in extensive metabolizers (EMs) and 94% in poor metabolizers (PMs). Mean maximal plasma concentrations (Cmax) are reached approximately 1 to 2 hours after dosing with a maximal concentration of 350 ng/ml with an AUC of 2 mcg.h/ml. Route of Elimination Atomoxetine is excreted primarily as 4-hydroxyatomoxetine-O-glucuronide, mainly in the urine (greater than 80% of the dose) and to a lesser extent in the feces (less than 17% of the dose). Only a small fraction (less than 3%) of the atomoxetine dose is excreted as unchanged atomoxetine, indicating extensive biotransformation. Volume of Distribution The reported volume of distribution of oral atomoxetine was 1.6-2.6 L/kg. The steady-state volume of distribution of intravenous atomoxetine was approximately 0.85 L/kg. Clearance The clearance rate of atomoxetine depends the CYP2D6 genetic polymorphisms of the individual and can range of 0.27-0.67 L.h/kg. Steady-state volume of distribution (intravenous administration): 8.5 L/kg. Atomexetine distributes primarily into total body water; volume of distribution is similar across patient weight range after normalizing for body weight. Atomoxetine is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with absolute bioavailability of about 63% in extensive metabolizers and 94% in poor metabolizers. Maximal plasma concentrations (Cmax) are reached approximately 1 to 2 hours after dosing. /MILK/ Atomoxetine and/or its metabolites are distributed into milk in rats; it is not known whether the drug is distributed into milk in humans. View More... Atomoxetine has high aqueous solubility and biological membrane permeability that facilitates its rapid and complete absorption after oral administration. Absolute oral bioavailability ranges from 63 to 94%, which is governed by the extent of its first-pass metabolism. Three oxidative metabolic pathways are involved in the systemic clearance of atomoxetine: aromatic ring-hydroxylation, benzylic hydroxylation and N-demethylation. Aromatic ring-hydroxylation results in the formation of the primary oxidative metabolite of atomoxetine, 4-hydroxyatomoxetine, which is subsequently glucuronidated and excreted in urine. The formation of 4-hydroxyatomoxetine is primarily mediated by the polymorphically expressed enzyme cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2D6. This results in two distinct populations of individuals: those exhibiting active metabolic capabilities (CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers) and those exhibiting poor metabolic capabilities (CYP2D6 poor metabolizers) for atomoxetine. The oral bioavailability and clearance of atomoxetine are influenced by the activity of CYP2D6; nonetheless, plasma pharmacokinetic parameters are predictable in extensive and poor metabolizer patients. After single oral dose, atomoxetine reaches maximum plasma concentration within about 1-2 hours of administration. In extensive metabolizers, atomoxetine has a plasma half-life of 5.2 hours, while in poor metabolizers, atomoxetine has a plasma half-life of 21.6 hours. The systemic plasma clearance of atomoxetine is 0.35 and 0.03 L/h/kg in extensive and poor metabolizers, respectively. Correspondingly, the average steady-state plasma concentrations are approximately 10-fold higher in poor metabolizers compared with extensive metabolizers. Upon multiple dosing there is plasma accumulation of atomoxetine in poor metabolizers, but very little accumulation in extensive metabolizers. The volume of distribution is 0.85 L/kg, indicating that atomoxetine is distributed in total body water in both extensive and poor metabolizers. Atomoxetine is highly bound to plasma albumin (approximately 99% bound in plasma). Although steady-state concentrations of atomoxetine in poor metabolizers are higher than those in extensive metabolizers following administration of the same mg/kg/day dosage, the frequency and severity of adverse events are similar regardless of CYP2D6 phenotype.Atomoxetine administration does not inhibit or induce the clearance of other drugs metabolized by CYP enzymes. In extensive metabolizers, potent and selective CYP2D6 inhibitors reduce atomoxetine clearance; however, administration of CYP inhibitors to poor metabolizers has no effect on the steady-state plasma concentrations of atomoxetine. PMID:15910008 Metabolism / Metabolites Atomoxetine undergoes biotransformation primarily through the cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) enzymatic pathway. People with reduced activity in the CYP2D6 pathway (also known as poor metabolizers or PMs) have higher plasma concentrations of atomoxetine compared with people with normal activity (also known as extensive metabolizers, or EMs). For PMs, the AUC of atomoxetine at steady-state is approximately 10-fold higher and Cmax is about 5-fold greater than for EMs. The major oxidative metabolite formed regardless of CYP2D6 status is 4-hydroxy-atomoxetine, which is rapidly glucuronidated. 4-Hydroxyatomoxetine is equipotent to atomoxetine as an inhibitor of the norepinephrine transporter, but circulates in plasma at much lower concentrations (1% of atomoxetine concentration in EMs and 0.1% of atomoxetine concentration in PMs). In individuals that lack CYP2D6 activity, 4-hydroxyatomoxetine is still the primary metabolite, but is formed by several other cytochrome P450 enzymes and at a slower rate. Another minor metabolite, N-Desmethyl-atomoxetine is formed by CYP2C19 and other cytochrome P450 enzymes, but has much less pharmacological activity than atomoxetine and lower plasma concentrations (5% of atomoxetine concentration in EMs and 45% of atomoxetine concentration in PMs). Atomoxetine is metabolized primarily through the CYP2D6 enzymatic pathway. People with reduced activity in this pathway (PMs) have higher plasma concentrations of atomoxetine compared with people with normal activity (EMs). For PMs, AUC of atomoxetine is approximately 10-fold and Css, max is about 5-fold greater than EMs. Laboratory tests are available to identify CYP2D6 PMs. The major oxidative metabolite formed, regardless of CYP2D6 status, is 4-hydroxyatomoxetine, which is glucuronidated. 4-Hydroxyatomoxetine is equipotent to atomoxetine as an inhibitor of the norepinephrine transporter but circulates in plasma at much lower concentrations (1% of atomoxetine concentration in extensive metabolizers (EMs) and 0.1% of atomoxetine concentration in PMs). 4-Hydroxyatomoxetine is primarily formed by CYP2D6, but in PMs, 4-hydroxyatomoxetine is formed at a slower rate by several other cytochrome P450 enzymes. N-Desmethylatomoxetine is formed by CYP2C19 and other cytochrome P450 enzymes, but has substantially less pharmacological activity compared with atomoxetine and circulates in plasma at lower concentrations (5% of atomoxetine concentration in EMs and 45% of atomoxetine concentration in poor metabolizers (PMs)). The role of the polymorphic cytochrome p450 2D6 (CYP2D6) in the pharmacokinetics of atomoxetine hydrochloride [(-)-N-methyl-gamma-(2-methylphenoxy)benzenepropanamine hydrochloride; LY139603] has been documented following both single and multiple doses of the drug. In this study, the influence of the CYP2D6 polymorphism on the overall disposition and metabolism of a 20-mg dose of (14)C-atomoxetine was evaluated in CYP2D6 extensive metabolizer (EM; n = 4) and poor metabolizer (PM; n = 3) subjects under steady-state conditions. Atomoxetine was well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and cleared primarily by metabolism with the preponderance of radioactivity being excreted into the urine. In EM subjects, the majority of the radioactive dose was excreted within 24 hr, whereas in PM subjects the majority of the dose was excreted by 72 hr. The biotransformation of atomoxetine was similar in all subjects undergoing aromatic ring hydroxylation, benzylic oxidation, and N-demethylation with no CYP2D6 phenotype-specific metabolites. The primary oxidative metabolite of atomoxetine was 4-hydroxyatomoxetine, which was subsequently conjugated forming 4-hydroxyatomoxetine-O-glucuronide. Due to the absence of CYP2D6 activity, the systemic exposure to radioactivity was prolonged in PM subjects (t(1/2) = 62 hr) compared with EM subjects (t(1/2) = 18 hr). In EM subjects, atomoxetine (t(1/2) = 5 hr) and 4-hydroxyatomoxetine-O-glucuronide (t(1/2) = 7 hr) were the principal circulating species, whereas atomoxetine (t(1/2) = 20 hr) and N-desmethylatomoxetine (t(1/2) = 33 hr) were the principal circulating species in PM subjects. Although differences were observed in the excretion and relative amounts of metabolites formed, the primary difference observed between EM and PM subjects was the rate at which atomoxetine was biotransformed to 4-hydroxyatomoxetine. PMID:12485958 Atomoxetine is excreted primarily as 4-hydroxyatomoxetine-O-glucuronide, mainly in the urine (greater than 80% of the dose) and to a lesser extent in the feces (less than 17% of the dose). Only a small fraction of the Strattera dose is excreted as unchanged atomoxetine (less than 3% of the dose), indicating extensive biotransformation. Atomoxetine is primarily metabolized by the CYP2D6 pathway to 4-hydroxyatomoxetine. 4-Hydroxyatomoxetine is equipotent to atomoxetine as an inhibitor of the norepinephrine transporter but circulates in plasma at much lower concentrations (1% of atomoxetine concentration in EMs and 0.1% of atomoxetine concentration in PMs). Half Life: 5 hours The plasma elimination half life in normal (extensive) metabolizers is about 5 hours. In person who are poor metabolizers (7% of whites and 2% of blacks), the drug plasma levels are much higher and the plasma elimination half life is 24 hours. Mean apparent plasma clearance of atomoxetine after oral administration in adult extensive metabolizers (EMs) is 0.35 L/hr/kg and the mean half-life is 5.2 hours. Following oral administration of atomoxetine to poor metabolizers (PMs), mean apparent plasma clearance is 0.03 L/hr/kg and mean half-life is 21.6 hours. For PMs, AUC of atomoxetine is approximately 10-fold and Css, max is about 5-fold greater than EMs. The elimination half-life of 4-hydroxyatomoxetine is similar to that of N-desmethylatomoxetine (6 to 8 hours) in EM subjects, while the half-life of N-desmethylatomoxetine is much longer in PM subjects (34 to 40 hours). ... In extensive metabolizers, atomoxetine has a plasma half-life of 5.2 hours, while in poor metabolizers, atomoxetine has a plasma half-life of 21.6 hours. ... PMID:15910008 ... Twenty-one cytochrome P450 2D6 extensive metabolizer patients participated in these single-dose and steady-state pharmacokinetic evaluations. Atomoxetine was rapidly absorbed, with peak plasma concentrations occurring 1 to 2 hours after dosing. Half-life averaged 3.12 and 3.28 hours after a single dose and at steady state, respectively. ... |
||
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Toxicity Summary
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Atomoxetine, as Strattera, is indicated for the treatment of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: Atomoxetine increased the risk of suicidal ideation in short-term studies in children or adolescents with ADHD. Symptoms accompanying acute and chronic overdoses of atomoxetine include gastrointestinal symptoms, somnolence, dizziness, tremor, abnormal behavior, hyperactivity, agitation, and signs and symptoms consistent with mild to moderate sympathetic nervous system activation (e.g., tachycardia, blood pressure increased, mydriasis, dry mouth). Less commonly, there have been reports of QT prolongation and mental changes, including disorientation and hallucinations. Atomoxetine may cause clinically significant hepatotoxicity either by metabolic idiosyncrasy or by inducing autoimmune hepatitis. There have been fatalities reported involving a mixed ingestion overdose of Strattera and at least one other drug. Sudden deaths, stroke, and myocardial infarction have been reported in both children and adults with structural cardiac abnormalities or other serious heart problems. ANIMAL STUDIES: The median lethal oral dose of atomoxetine hydrochloride in animals was estimated to be 25 mg/kg for cats, >37.5 mg/kg for dogs, and 0.190 mg/kg in rats and mice. Premonitory signs of toxicity following single oral doses of atomoxetine in animals included mydriasis and reduced pupillary light reflex, mucoid stools, salivation, vomiting, ataxia, tremors, myoclonic jerking, and convulsions. Chronic toxicity studies of up to 1 year were conducted in adult rats and dogs. There was no major target organ toxicity observed in dogs given oral doses up to 16 mg/kg/day or in rats given atomoxetine in the diet at time-weighted average doses up to 47 mg/kg/day. These doses are 4-5 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in adults. Mild hepatic effects, characterized by mottling and pallor of the liver, increased relative liver weights, hepatocellular vacuolation, and slightly increased serum ALT values, occurred in male rats given time weighted average doses >/= 14 mg/kg/day. No hepatic effects were observed in dogs. Clinical signs of mydriasis, reduced pupillary light reflex, emesis, and tremors were observed in dogs, and these effects were minimal in adult dogs given >/= 8 mg/kg/day. No evidence of drug-associated teratogenicity or retarded fetal development was produced in rabbits or rats administered atomoxetine hydrochloride throughout organogenesis at oral doses up to 100 mg/kg/day and 150 mg/kg/day (13 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in adults). In a rat fertility study, decreased pup weight and survival was observed, predominantly during the first week postpartum following maternal dietary atomoxetine timeweighted average doses of 23 mg/kg/day or higher. Atomoxetine hydrochloride was negative in a battery of genotoxicity studies that included a reverse point mutation assay (Ames Test), an in vitro mouse lymphoma assay, a chromosomal aberration test in Chinese hamster ovary cells, an unscheduled DNA synthesis test in rat hepatocytes, and an in vivo micronucleus test in mice. However, there was a slight increase in the percentage of Chinese hamster ovary cells with diplochromosomes, suggesting endoreduplication (numerical aberration). Atomoxetine hydrochloride was not carcinogenic in rats and mice when given in the diet for 2 years at time-weighted average doses up to 47 and 458 mg/kg/day, respectively. The precise mechanism by which atomoxetine produces its therapeutic effects in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is unknown, but is thought to be related to selective inhibition of the pre-synaptic norepinephrine transporter, as determined through in-vitro studies. Atomoxetine appears to have minimal affinity for other noradrenergic receptors or for other neurotransmitter transporters or receptors. Hepatotoxicity Atomoxetine has been linked to serum aminotransferase elevations in a small proportion of patients (~0.5%). More importantly, there have been several reports of clinically apparent acute liver injury due to atomoxetine. The onset of injury was within 3 to 12 weeks of starting the medication. The typical pattern of serum enzyme elevations was hepatocellular with marked increases in serum aminotransferase levels (often >20 times upper limit of normal) and clinical features that resembled acute viral hepatitis. Most cases have been self-limited, but instances of acute liver failure sometimes requiring emergency liver transplantation have been reported. Immunoallergic features were not found, but several patients with acute injury had antinuclear antibody and at least one patient had other features that resembled autoimmune hepatitis (with typical liver histology and high levels of immunoglobulins in serum). Likelihood score: C (probable cause of clinically apparent liver injury). View More
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
Exposure Routes Atomoxetine is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with absolute bioavailability of about 63% in EMs and 94% in PMs. Drugs that elevate gastric pH (magnesium hydroxide/aluminum hydroxide, omeprazole) have no effect on atomoxetine bioavailability. Absorption is minimally affected by food. Symptoms The most commonly reported symptoms accompanying acute and chronic overdoses are somnolence, agitation, hyperactivity, abnormal behavior, and gastrointestinal symptoms. Treatment An airway should be established. Monitoring of cardiac and vital signs is recommended, along with appropriate symptomatic and supportive measures. Gastric lavage may be indicated if performed soon after ingestion. Activated charcoal may be useful in limiting absorption. Because atomoxetine is highly protein-bound, dialysis is not likely to be useful in the treatment of overdose. (L1712) L1712: RxList: The Internet Drug Index (2009). http://www.rxlist.com/ Interactions Strattera should be administered with caution to patients being treated with systemically-administered (oral or intravenous) albuterol (or other beta2 agonists) because the action of albuterol on the cardiovascular system can be potentiated resulting in increases in heart rate and blood pressure. Albuterol (600 mcg iv over 2 hours) induced increases in heart rate and blood pressure. These effects were potentiated by atomoxetine (60 mg BID for 5 days) and were most marked after the initial coadministration of albuterol and atomoxetine. However, these effects on heart rate and blood pressure were not seen in another study after the coadministration with inhaled dose of albuterol (200-800 ug) and atomoxetine (80 mg QD for 5 days) in 21 healthy Asian subjects who were excluded for poor metabolizer status. The manufacturer states that atomoxetine is contraindicated in patients currently receiving or having recently received (i.e., within 2 weeks) monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor therapy. In addition, at least 2 weeks should elapse after discontinuing atomoxetine before initiating MAO inhibitor therapy. Severe, potentially fatal, reactions (including hyperthermia, rigidity, myoclonus, autonomic instability with possible rapid fluctuations of vital signs, and mental status changes that include extreme agitation progressing to delirium and coma) have been reported in patients receiving other drugs that affect brain monoamine concentrations concomitantly with MAO inhibitor therapy. Protein Binding At therapeutic concentrations, 98.7% of plasma atomoxetine is bound to protein, with 97.5% of that being bound to albumin, followed by alpha-1-acid glycoprotein and immunoglobulin G. |
||
| References |
|
||
| Additional Infomation |
Atomoxetine hydrochloride is the hydrochloride salt of atomoxetine. It has a role as an antidepressant and an adrenergic uptake inhibitor. It contains an atomoxetine.
Atomoxetine Hydrochloride is the hydrochloride salt of atomoxetine, a phenoxy-3-propylamine derivative and selective non-stimulant, norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor with cognitive-enhancing activity. Although its precise mechanism of action is unknown, atomoxetine appears to selectively inhibit the pre-synaptic norepinephrine transporter, resulting in inhibition of the presynaptic reabsorption of norepinephrine and prolongation of norepinephrine activity in the synaptic cleft. The effect on cognitive brain function may result in improved attention and decreased impulsivity and activity levels. A propylamine derivative and selective ADRENERGIC UPTAKE INHIBITOR that is used in the treatment of ATTENTION DEFICIT HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER. See also: Atomoxetine (has active moiety). Drug Indication Treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) |
| Molecular Formula |
C17H22CLNO
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
291.82
|
|
| Exact Mass |
291.138
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 69.97; H, 7.60; Cl, 12.15; N, 4.80; O, 5.48
|
|
| CAS # |
82248-59-7
|
|
| Related CAS # |
Atomoxetine; 83015-26-3; Atomoxetine-d5 hydrochloride
|
|
| PubChem CID |
54840
|
|
| Appearance |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| Boiling Point |
389ºC at 760 mmHg
|
|
| Melting Point |
167-169ºC
|
|
| Flash Point |
164.1ºC
|
|
| LogP |
4.917
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
2
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
2
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
6
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
20
|
|
| Complexity |
237
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
[C@H](C1C=CC=CC=1)(CCNC)OC1C=CC=CC=1C.Cl
|
|
| InChi Key |
LUCXVPAZUDVVBT-UNTBIKODSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H21NO.ClH/c1-14-8-6-7-11-16(14)19-17(12-13-18-2)15-9-4-3-5-10-15;/h3-11,17-18H,12-13H2,1-2H3;1H/t17-;/m1./s1
|
|
| Chemical Name |
(3R)-N-methyl-3-(2-methylphenoxy)-3-phenylpropan-1-amine;hydrochloride
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.57 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.57 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.57 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 4: 8.33 mg/mL (28.54 mM) in PBS (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with ultrasonication (<60°C). |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4268 mL | 17.1338 mL | 34.2677 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6854 mL | 3.4268 mL | 6.8535 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3427 mL | 1.7134 mL | 3.4268 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
Comparison of Lisdexamfetamine Dimesylate With Atomoxetine HCl in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Subjects With an Inadequate Response to Methylphenidate
CTID: NCT01106430
Phase: Phase 3 Status: Completed
Date: 2021-06-11
 |
|---|
  |
 |