
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
Vortioxetine HBr (formerly AA21004, Lu-AA21004, AA21004; Lu AA21004), the hydrobromide salt of Vortioxetine which is a marketed and atypical antidepressant, is an orally bioactive and multimodal serotonergic agent with potential anti-depressive activity. It has IC50 values of 15 nM, 33 nM, 3.7 nM, 19 nM, and 1.6 nM for 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT3A, 5-HT7 receptor, and SERT, respectively. In 2013, the FDA approved the atypical antidepressant vortioxetine for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) in adults. One such "serotonin modulator and stimulator" is vortioxetine.
| Targets |
sPLA2 ( Ki = 15 nM ); 5-HT3A Receptor ( Ki = 3.7 nM ); 5-HT7 Receptor ( Ki = 19 nM ); SERT ( Ki = 1.6 nM )
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
|
||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Enzyme Assay |
Vortioxetine (Compound 5m) is a multimodal serotonergic agent that inhibits SERT with values of 1.6 nM, 33 nM, 3.7 nM, 19 nM, and 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, and 5-HT7 receptors, respectively. Vortioxetine exhibits strong suppression of SERT as well as antagonistic effects at 5-HT3A and 5-HT7 receptors, partial agonist effects at 5-HT1B receptors, and agonistic effects at 5-HT1A receptors.
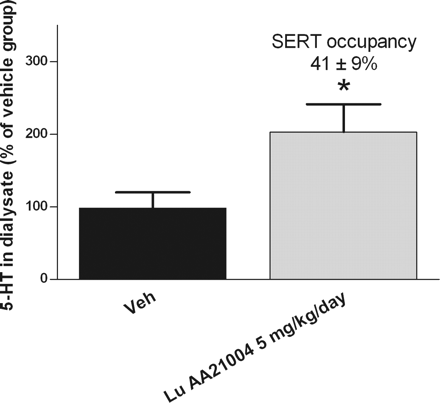
Compound 5m (Lu AA21004) was the lead compound, displaying high affinity for recombinant human 5-HT(1A) (K(i) = 15 nM), 5-HT(1B) (K(i) = 33 nM), 5-HT(3A) (K(i) = 3.7 nM), 5-HT(7) (K(i) = 19 nM), and noradrenergic β(1) (K(i) = 46 nM) receptors, and SERT (K(i) = 1.6 nM). Compound 5m displayed antagonistic properties at 5-HT(3A) and 5-HT(7) receptors, partial agonist properties at 5-HT(1B) receptors, agonistic properties at 5-HT(1A) receptors, and potent inhibition of SERT.[1] Ex vivo SERT and 5-HT3 receptor occupancy assays[2] Brains from mice treated with vehicle, fluoxetine, or vortioxetine (1 h after acute administration or 24 h after the 14th or 21st injection) were flash frozen, sectioned coronally using a cryostat, and then mounted on slides and frozen until use. Slices were 20 μm thick, and began at approximately +1.2 mm anterior from bregma for SERT receptor occupancy or −2.7 mm posterior from bregma for 5-HT3 receptor occupancy determination (Franklin and Paxinos, 2008). Slides were stored for at least 24 h at −20 °C before use in autoradiography experiments. |
||
| Cell Assay |
Vortioxetine is a partial h5-HT1B receptor agonist that, in a whole-cell cAMP-based assay, has an EC50 of 460 nM and an intrinsic activity of 22%. In vitro whole-cell cAMP assay, vortioxetine binds to the r5-HT7 receptor with a Kivalue of 200 nM and is a functional antagonist at the r5-HT7 receptor with an IC50 of 2 μM.
Assessment of SERT occupancy[2] Slides were incubated at room temperature for 60 min in buffer (50 mM Tris–HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, pH = 7.4) containing 4.5 nM [3H]-escitalopram. Nonspecific binding was determined using 1 μM escitalopram. Slides were washed briefly in cold buffer, dried, and exposed in a Beta imager for 16 h. The region of interest (ROI) for the SERT assay included the lateral and medial septum, the nucleus accumbens and the olfactory tubercle. An example image of the ROI for the SERT assay can be found in Supplementary Fig. 2A. Assessment of 5-HT3 receptor occupancy[2] Slides were preincubated for 5 min in a buffer consisting of 50 mM Tris and 150 mM NaCl. Slides were dried under a stream of air for 30–45 min. Subsequently, slides were incubated at room temperature for 60 min in buffer (50 mM Tris–HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, pH = 7.4) containing 1 nM [3H]LY278584. Nonspecific binding was determined using 1 μM ondansetron. Slides were washed briefly in cold buffer, dried, and exposed in a Beta imager for 24 h. The ROI for the 5-HT3 receptor occupancy assay consisted of the hippocampus. An example image for the 5-HT3 receptor occupancy assay can be found in Supplementary Fig. 2B. |
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Amounts of vortioxetine in milk appear to be low. If vortioxetine is required by the mother, it is not a reason to discontinue breastfeeding. However, until more data are available, vortioxetine should be used with careful infant monitoring during breastfeeding. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Three lactating mothers were taking vortioxetine for depression, two were taking 10 mg once daily and one was taking 20 mg once daily. All mothers were exclusively breastfeeding their infants aged 1, 2 and 6 months of age. No mothers reported any unusual behavior in their infants. A woman who was taking a vortioxetine dose of 76.1 mcg/kg daily partially breastfed her infant. She did not observe any adverse effects in her infant. A postpartum Japanese woman with depression was taking vortioxetine 20 mg zolpidem 10 mg, duloxetine 20 mg, rebamipide 100 mg and the Asian herbal medicine Kami-kihi-tou 2.5 grams daily. She partially (over 50%) breastfed her infant for 3 months. The infant had no detectable drug-related adverse effects on routine follow-up at 1, 3, 5, 7 and 9-months postpartum. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Vortioxetine has caused hyperprolactinemia and galactorrhea in some patients. An observational study looked at outcomes of 2859 women who took an antidepressant during the 2 years prior to pregnancy. Compared to women who did not take an antidepressant during pregnancy, mothers who took an antidepressant during all 3 trimesters of pregnancy were 37% less likely to be breastfeeding upon hospital discharge. Mothers who took an antidepressant only during the third trimester were 75% less likely to be breastfeeding at discharge. Those who took an antidepressant only during the first and second trimesters did not have a reduced likelihood of breastfeeding at discharge. The antidepressants used by the mothers were not specified. A retrospective cohort study of hospital electronic medical records from 2001 to 2008 compared women who had been dispensed an antidepressant during late gestation (n = 575) to those who had a psychiatric illness but did not receive an antidepressant (n = 1552) and mothers who did not have a psychiatric diagnosis (n = 30,535). Women who received an antidepressant were 37% less likely to be breastfeeding at discharge than women without a psychiatric diagnosis, but no less likely to be breastfeeding than untreated mothers with a psychiatric diagnosis. None of the mothers were taking vortioxetine. In a study of 80,882 Norwegian mother-infant pairs from 1999 to 2008, new postpartum antidepressant use was reported by 392 women and 201 reported that they continued antidepressants from pregnancy. Compared with the unexposed comparison group, late pregnancy antidepressant use was associated with a 7% reduced likelihood of breastfeeding initiation, but with no effect on breastfeeding duration or exclusivity. Compared with the unexposed comparison group, new or restarted antidepressant use was associated with a 63% reduced likelihood of predominant, and a 51% reduced likelihood of any breastfeeding at 6 months, as well as a 2.6-fold increased risk of abrupt breastfeeding discontinuation. Specific antidepressants were not mentioned. |
||
| References |
|
||
| Additional Infomation |
Vortioxetine hydrobromide is a hydrobromide obtained by combining vortioxetine with one molar equivalent of hydrobromic acid. Used for treatment of major depressive disorder. It has a role as an antidepressant, an anxiolytic drug, a serotonergic antagonist and a serotonergic agonist. It contains a vortioxetine(1+).
Vortioxetine Hydrobromide is a hydrobromide salt form of vortioxetine, a serotonin (5-HT) modulator and stimulator (SMS), with antidepressant activity. Vortioxetine inhibits the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine from the synaptic cleft and acts variably as a serotonin receptor agonist (5-HT1A), partial agonist (5-HT1B) or antagonist (5-HT3, 5-HT1D and 5-HT7). It is not clear how this agent's purported multimodal mechanism of action contributes to its antidepressant effect; however, it is presumed to increase the synaptic availability of serotonin and norepinephrine. A piperazine derivative that acts as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor, as a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, and 5-HT1A receptor agonist. It is used for the treatment of anxiety and depression. See also: Vortioxetine (has active moiety). Drug Indication Treatment of major depressive episodes in adults. |
| Molecular Formula |
C18H22N2S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
379.36
|
|
| Exact Mass |
378.076
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 56.99; H, 6.11; Br, 21.06; N, 7.38; S, 8.45
|
|
| CAS # |
960203-27-4
|
|
| Related CAS # |
Vortioxetine; 508233-74-7; Vortioxetine-d8 hydrobromide
|
|
| PubChem CID |
56843850
|
|
| Appearance |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| LogP |
5.216
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
2
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
3
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
3
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
22
|
|
| Complexity |
316
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
Br.S(C1C(C)=CC(C)=CC=1)C1C(N2CCNCC2)=CC=CC=1
|
|
| InChi Key |
VNGRUFUIHGGOOM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H22N2S.BrH/c1-14-7-8-17(15(2)13-14)21-18-6-4-3-5-16(18)20-11-9-19-10-12-20;/h3-8,13,19H,9-12H2,1-2H3;1H
|
|
| Chemical Name |
1-[2-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)sulfanylphenyl]piperazine;hydrobromide
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.59 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.59 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.59 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 4: 15% Captisol, pH 9: 10 mg/mL |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6360 mL | 13.1801 mL | 26.3602 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5272 mL | 2.6360 mL | 5.2720 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2636 mL | 1.3180 mL | 2.6360 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
 |
|---|
|
|