
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
Trichostatin A (also called TSA) is a novel, potent and specific inhibitor of histone deacetylase (HDAC) with potential anticancer activity. Its IC50 value for HDAC inhibition is 1.8 nM. Additionally, at low nanomolar concentrations, it reversibly and noncompetivively inhibits HDAC in both fractionated cell nuclear extracts and cultured mammalian cells. It possesses cytostatic and differentiating qualities as an antifungal antibiotic agent. A study looking at TSA's impact on human breast cancer cell lines found that TSA significantly increased histone H4 hyperacetylation and inhibited the proliferation of breast carcinoma cell lines (IC50 124.4 ± 120.4 nM) compared to all other cell lines (IC50 2.4 ± 0.5 nM).
| Targets |
HDAC ( IC50 = 1.8 nM )
|
|
|---|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
|
|
| ln Vivo |
|
|
| Enzyme Assay |
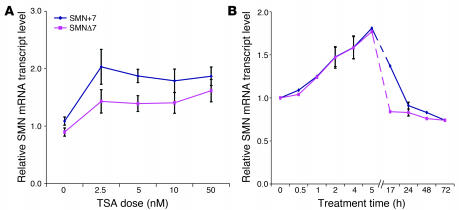
Each of the following breast cancer cell lines is used to prepare total cellular extracts: MCF-7, T-47D, ZR-75-1, BT-474, MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-453, CAL 51, or SK-BR-3. A 20 μL crude cell extract (~2.5 ×105 cells) is incubated for 60 minutes at 25 °C with 1 μL (~1.5 × 106 cpm) of [3H]acetyl-labeled histone H4 peptide substrate (NH2-terminal residues 2–20) that has been acetylated with [3H]acetic acid, sodium salt (3.7 GBq/mmol) by an in vitro incorporation method. These conditions are followed by different concentrations of Trichostatin A in 0.1% (v/v) ethanol or 0.1% (v/v) ethanol as vehicle control. Scintillation counting is used to quantify the released [3H]acetate after each 200 μL reaction is extracted with 600 μL of ethyl acetate and quenched with 50 μL of 1 M HCl/0.16 M acetic acid. In order to fit inhibition data to the appropriate dose-response curve, IC50 values are graphically determined using nonlinear regression.
|
|
| Cell Assay |
For 72 hours, cells are cultivated in a 96-well plate at a density of 1×103 cells per well using 100 μL of full-dose DMEM, either with or without the HDAC inhibitor Trichostatin A. With a CCK-8 cell proliferation kit, the WST-8 assay is used to quantify cytotoxicity. A microplate reader is used to measure the absorbance at 450 nm. Three separate experiments are conducted, and each experiment is run in triplicate.
|
|
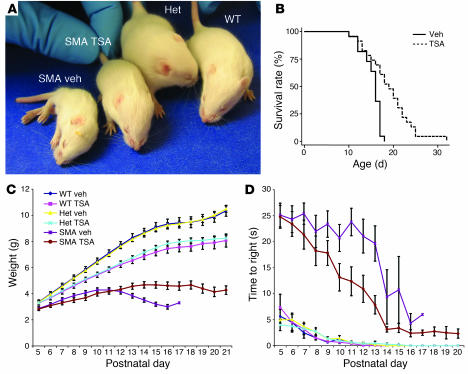
| Animal Protocol |
|
|
| References | ||
| Additional Infomation |
Trichostatin A is an antibiotic antifungal agent, a trichostatin and a hydroxamic acid. It has a role as a bacterial metabolite, a geroprotector and an EC 3.5.1.98 (histone deacetylase) inhibitor. It is functionally related to a (R)-trichostatic acid.
trichostatin A has been reported in Streptomyces, Streptomyces sioyaensis, and other organisms with data available. Trichostatin A is a natural derivative of dienohydroxamic acid isolated from species of the bacterial genus Streptomyces. Trichostatin A (TSA) reversibly and specifically inhibits histone deacetylases, resulting in hyperacetylation of core histones which modulate chromatin structure. The increase in histone acetylation promotes selective gene transcription and the inhibition of tumor growth. This agent is a potent inducer of tumor cell growth arrest, differentiation and apoptosis in a variety of transformed cells in culture and in tumor-bearing animals. (NCI04) |
| Molecular Formula |
C17H22N2O3
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
302.4
|
|
| Exact Mass |
302.163
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 67.53; H, 7.33; N, 9.26; O, 15.87
|
|
| CAS # |
58880-19-6
|
|
| Related CAS # |
122292-85-7 (S-isomer); 58880-19-6 (R-isomer)
|
|
| PubChem CID |
444732
|
|
| Appearance |
White to light yellow solid powder
|
|
| Density |
1.1±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| Melting Point |
141-143ºC
|
|
| Index of Refraction |
1.578
|
|
| LogP |
2.77
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
2
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
4
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
6
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
22
|
|
| Complexity |
447
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
O=C(C1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1[H])N(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])[C@]([H])(C([H])([H])[H])/C(/[H])=C(/C(/[H])=C(\[H])/C(N([H])O[H])=O)\C([H])([H])[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
RTKIYFITIVXBLE-QEQCGCAPSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H22N2O3/c1-12(5-10-16(20)18-22)11-13(2)17(21)14-6-8-15(9-7-14)19(3)4/h5-11,13,22H,1-4H3,(H,18,20)/b10-5+,12-11+/t13-/m1/s1
|
|
| Chemical Name |
(2E,4E,6R)-7-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethyl-7-oxohepta-2,4-dienamide
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: 2.5 mg/mL (8.27 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with sonication.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.27 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: 2.5 mg/mL (8.27 mM) in 5% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 50% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. Solubility in Formulation 4: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.27 mM) (saturation unknown) in 5% DMSO + 95% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 5: 1% DMSO+30% polyethylene glycol+1% Tween 80, pH 4: 6mg/mL |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3069 mL | 16.5344 mL | 33.0688 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6614 mL | 3.3069 mL | 6.6138 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3307 mL | 1.6534 mL | 3.3069 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
  |