
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
Purity: ≥98%
Sunitinib Malate (formerly also known as SU11248 Malate; trade nameSutent)) is a potent, orally bioavailable and multi-targeted RTK (receptor tyrosine kinase) inhibitor with potent anticancer activities. In cell-free assays, it inhibits c-Kit in addition to VEGFR2 (Flk-1) and PDGFRβ, with IC50s of 80 nM and 2 nM, respectively. On January 26, 2006, the FDA approved it for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma and gastrointestinal stromal tumor that was resistant to imatinib. The malate salt of an indolinone-based tyrosine kinase inhibitor with possible anti-tumor properties is called sunitinib malate. Sunitinib inhibits angiogenesis and cell proliferation by blocking the tyrosine kinase activities of VEGFR2, PDGFRb, and c-kit.
| Targets |
VEGFR2 (IC50 = 80 nM); PDGFRβ (IC50 = 2 nM)
|
|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
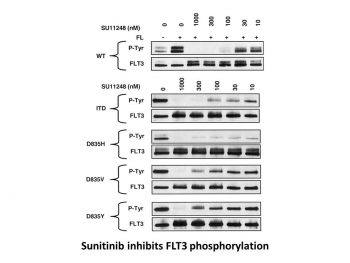
Sunitinib inhibits FLT-3 and Kit with considerable potency.[1] With a Ki of 9 nM and 8 nM, respectively, sunitinib is a strong ATP-competitive inhibitor of VEGFR2 (Flk1) and PDGFRβ. It provides >10-fold greater selectivity for VEGFR2 and PDGFR than FGFR-1, EGFR, Cdk2, Met, IGFR-1, Abl, and src. With IC50 values of 10 nM and 10 nM, respectively, sunitinib inhibits the phosphorylation of VEGFR2 in response to VEGF and PDGFRβ in response to PDGF in serum-starved NIH-3T3 cells expressing VEGFR2 or PDGFRβ. Sunitinib has an IC50 of 40 nM for VEGF-induced proliferation of serum-starved HUVECs and an IC50 of 39 nM and 69 nM for PDGF-induced proliferation of NIH-3T3 cells overexpressing PDGFRβ or PDGFRβ, respectively.[2] With an IC50 of 250 nM, 50 nM, and 30 nM, respectively, sunitinib inhibits the phosphorylation of wild-type FLT3, FLT3-ITD, and FLT3-Asp835. With IC50 values of 8 nM and 14 nM, respectively, sunitinib suppresses the growth of MV4;11 and OC1-AML5 cells and, in a dose-dependent fashion, triggers apoptosis.[3]
|
| ln Vivo |
Sunitinib (20–80 mg/kg/day) exhibits broad and potent dose-dependent anti-tumor activity against a variety of tumor xenograft models, including HT-29, A431, Colo205, H-460, SF763T, C6, A375, or MDA-MB-435. This is consistent with the significant and selective inhibition of VEGFR2 or PDGFR phosphorylation and signaling in vivo. Six out of eight mice receiving 80 mg/kg/day of sunitinib for 21 days experience complete tumor regression, and 110 days after the end of the treatment, there is no regrowth of the tumor.Tumors that do not completely regress after the first round of treatment can still be successfully treated with sunitinib in a second round. Tumor MVD significantly decreases with sunitinib treatment, with SF763T glioma tumors reduced by approximately 40%. Tumor size remains unchanged, but luciferase-expressing PC-3M xenografts treated with SU11248 completely inhibits further tumor growth.[2] Treatment with sunitinib (20 mg/kg/day) increases survival in the FLT3-ITD bone marrow engraftment model and significantly suppresses the growth subcutaneous MV4;11 (FLT3-ITD) xenografts.[3]
|
| Enzyme Assay |
Sunitinib's IC50 values against PDGFRβ and VEGFR2 (Flk-1) are ascertained by employing glutathione S-transferasefusion proteins that encompass the entire RTK cytoplasmic domain. In order to measure the trans-phosphorylation activity of VEGFR2 (Flk-1) and PDGFRβ, biochemical tyrosine kinase assays are carried out in 96-well microtiter plates that have been precoated (20 μg/well in PBS) and incubated with the peptide substrate poly-Glu,Tyr (4:1) for an entire night at 4 °C. Adding 1-5% (w/v) BSA to PBS blocks excess protein binding sites. The cells of insects infected with baculovirus produce purified GST-fusion proteins. The microtiter wells are then filled with GST-VEGFR2 and GST-PDGFRβ in a 2 × concentration kinase dilution buffer that contains 40 μM NaVO4, 50 mM NaCl, 100 mM HEPES, and 0.02% (w/v) BSA. 50 ng/mL is the final enzyme concentration for GST-VEGFR2 or GST-PDGFRβ. To create a range of inhibitor concentrations suitable for every enzyme, 25 μL of diluted Sunitinib is then added to each reaction well. A solution of MnCl2 is mixed with varying concentrations of ATP to start the kinase reaction. The final concentration of MnCl2 is 10 mM, and the final ATP concentrations span the Km for the enzyme. After allowing the plates to sit at room temperature for five to fifteen minutes, the reaction is halted by adding EDTA. After that, TBST is used to wash the plates three times. After adding rabbit polyclonal antiphosphotyrosine antisera at a 1:10,000 dilution to the wells in TBST containing 0.025% (w/v) nonfat dry milk, 0.5% (w/v) BSA, and 100 μM NaVO4, the wells are incubated at 37 °C for one hour. After three TBST washes, the plates are inoculated with goat anti-rabbit antisera conjugated with horseradish peroxidase (1:10,000 dilution in TBST). The plates are cleaned three times with TBST after an hour of incubation at 37 °C. Once 2,2′-azino-di-[3-ethylbenzthiazoline sulfonate] has been added as substrate, the amount of phosphotyrosine in each well is quantified.
|
| Cell Assay |
The cells are starved for an entire night in a medium containing 0.1% FBS before FL (50 ng/mL; FLT3-WT cells only) and sunitinib are added. After 48 hours of culture, proliferation is assessed using trypan blue cell viability assays or the Alamar Blue assay. Apoptosis is quantified using Western blotting 24 hours after Sunitinib addition in order to identify caspase-3 levels or poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage.
|
| Animal Protocol |
Mice: The mice used are female nu/nu (8–12 weeks old, 25 g). In short, on day 0, mice receive a subcutaneous injection of 3-5×106 tumor cells into the hind flank region. Once the tumors have grown to the indicated average size, the mice bearing the tumors are treated daily with SU11248 administered orally as a carboxymethyl cellulose suspension or as a citrate buffered (pH 3.5) solution. Tumor growth is assessed using tumor volume measurements taken twice a week. When tumors in animals receiving vehicle treatment reach an average size of 1000 mm3 or are determined to negatively impact the animals' quality of life, studies are usually stopped.
Rats: There are forty 200–230 g female Sprague-Dawley rats used. Five to ten animals per group are fed freely. Under 2% isoflurane gas anesthesia, 1×104 Walker 256 cells are injected into the left abdominal mammary fat pad. Rats are weighed every day, and they are gavaged with 30 mg/kg of sunitinib malate or 5 mg/kg of figolimod in olive oil. Calipers are used to measure the tumours. Before the tumors become ulcerated, the animals are put to sleep and killed with an intracardiac injection of ketamine (50 mg/mL). Rats are dissected to look for intestinal, liver, kidney, or lung metastases.
|
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Absorption Maximum plasma concentrations (Cmax) of sunitinib are generally observed between 6 and 12 hours (Tmax) following oral administration. Food has no effect on the bioavailability of sunitinib. Sunitinib may be taken with or without food. The pharmacokinetics were similar in healthy volunteers and in the solid tumor patient populations tested, including patients with GIST and RCC. Route of Elimination Sunitinib is metabolized primarily by the cytochrome P450 enzyme, CYP3A4, to produce its primary active metabolite, which is further metabolized by CYP3A4. Elimination is primarily via feces. In a human mass balance study of [14C]sunitinib, 61% of the dose was eliminated in feces, with renal elimination accounting for 16% of the administered dose. Volume of Distribution 2230 L (apparent volume of distribution, Vd/F) Clearance 34 - 62 L/h [Total oral clearance] Following oral administration, peak plasma concentrations of sunitinib generally occur within 6-12 hours. Food has no effect on bioavailability of sunitinib. Steady-state concentrations of sunitinib and its primary active metabolite are achieved within 10 to 14 days. By Day 14, combined plasma concentrations of sunitinib and its active metabolite ranged from 62.9 - 101 ng/mL. No significant changes in the pharmacokinetics of sunitinib or the primary active metabolite were observed with repeated daily administration or with repeated cycles in the dosing regimens tested. View More
Sunitinib and its primary active metabolite are 95 and 90% bound to human plasma proteins in vitro, respectively.
Metabolism / Metabolites Sunitinib is metabolized primarily by the cytochrome P450 enzyme, CYP3A4, to produce its primary active metabolite, which is further metabolized by CYP3A4. Sunitinib is metabolized principally by cytochrome P-450 (CYP) isoenzyme 3A4 to several metabolites. The main circulating metabolite, an N-desethyl derivative, has been shown to be equipotent to sunitinib in biochemical and cellular assays; this metabolite accounts for approximately 23-37% of total plasma concentrations of the drug and also is metabolized by CYP3A4. Sunitinib and its primary active metabolite were the major drug-related compounds identified in plasma, urine, and feces, representing 91.5%, 86.4% and 73.8% of radioactivity in pooled samples, respectively. Biological Half-Life Following administration of a single oral dose in healthy volunteers, the terminal half-lives of sunitinib and its primary active metabolite are approximately 40 to 60 hours and 80 to 110 hours, respectively. Following oral administration of a single dose in healthy volunteers, the terminal half-life of sunitinib or its primary active metabolite is approximately 40-60 or 80-110 hours, respectively. |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the clinical use of sunitinib during breastfeeding. Because sunitinib and its metabolite are over 90% bound to plasma proteins, the amount in milk is likely to be low. However, one of its metabolites has a half-life of up to 110 hours, and might accumulate in the infant. The manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding be discontinued during sunitinib therapy and for at least 4 weeks after the last dose. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. |
| References | |
| Additional Infomation |
Sunitinib Malate is the orally bioavailable malate salt of an indolinone-based tyrosine kinase inhibitor with potential antineoplastic activity. Sunitinib blocks the tyrosine kinase activities of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2), platelet-derived growth factor receptor b (PDGFRb), and c-kit, thereby inhibiting angiogenesis and cell proliferation. This agent also inhibits the phosphorylation of Fms-related tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3), another receptor tyrosine kinase expressed by some leukemic cells.
An indole and pyrrole derivative that inhibits VEGFR-2 and PDGFR BETA RECEPTOR TYROSINE KINASES. It is used as an antineoplastic agent for the treatment of GASTROINTESTINAL STROMAL TUMORS, and for treatment of advanced or metastatic RENAL CELL CARCINOMA. See also: Sunitinib (has active moiety). Drug Indication Gastrointestinal stromal tumour (GIST)Sutent is indicated for the treatment of unresectable and/or metastatic malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumour (GIST) in adults after failure of imatinib mesilate treatment due to resistance or intolerance. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma (MRCC)Sutent is indicated for the treatment of advanced/metastatic renal cell carcinoma (MRCC) in adults. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours (pNET)Sutent is indicated for the treatment of unresectable or metastatic, well-differentiated pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours with disease progression in adults. Experience with Sutent as first-line treatment is limited (see section 5. 1). |
| Molecular Formula |
C26H33FN4O7
|
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
532.56
|
| Exact Mass |
532.233
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 58.64; H, 6.25; F, 3.57; N, 10.52; O, 21.03
|
| CAS # |
341031-54-7
|
| Related CAS # |
Sunitinib;557795-19-4; Sunitinib Malate;341031-54-7;Sunitinib-d10;1126721-82-1;Sunitinib-d4;1126721-79-6; 342641-94-5; 1275588-72-1 (mesylate) ; 1126641-10-8; 1327155-72-5 (HCl); 1221149-36-5 (acetate); 1332306-95-2 (oxalate)
|
| PubChem CID |
6456015
|
| Appearance |
Yellow solid powder
|
| Density |
1.3600 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
|
| Boiling Point |
156 °C(lit.)
|
| Melting Point |
189-191°C
|
| Flash Point |
163 °F
|
| Index of Refraction |
n20/D 1.455(lit.)
|
| LogP |
2.77
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
6
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
9
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
10
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
38
|
| Complexity |
765
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
1
|
| SMILES |
FC1C([H])=C([H])C2=C(C=1[H])/C(/C(N2[H])=O)=C(\[H])/C1=C(C([H])([H])[H])C(C(N([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])=O)=C(C([H])([H])[H])N1[H].O([H])[C@]([H])(C(=O)O[H])C([H])([H])C(=O)O[H]
|
| InChi Key |
LBWFXVZLPYTWQI-IPOVEDGCSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H27FN4O2.C4H6O5/c1-5-27(6-2)10-9-24-22(29)20-13(3)19(25-14(20)4)12-17-16-11-15(23)7-8-18(16)26-21(17)28;5-2(4(8)9)1-3(6)7/h7-8,11-12,25H,5-6,9-10H2,1-4H3,(H,24,29)(H,26,28);2,5H,1H2,(H,6,7)(H,8,9)/b17-12-;/t;2-/m.0/s1
|
| Chemical Name |
N-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-5-[(Z)-(5-fluoro-2-oxo-1H-indol-3-ylidene)methyl]-2,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxamide;(2S)-2-hydroxybutanedioic acid
|
| Synonyms |
sunitinib; SU-11248; SU 11248; Sutent; SU011248 L-malate salt; PHA-290940AD; sunitinib L-malate; Sunitinib malate [USAN]; SU010398; SU11248; SU011248; trade name: Sutent
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.69 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.69 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.69 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 4: 4% DMSO+30% PEG 300+ddH2O: 2mg/mL Solubility in Formulation 5: 10 mg/mL (18.78 mM) in 100 mM citrate buffer (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; Need ultrasonic and adjust pH to 5 with HCl. |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8777 mL | 9.3886 mL | 18.7772 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3755 mL | 1.8777 mL | 3.7554 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1878 mL | 0.9389 mL | 1.8777 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT03541902 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Cabozantinib Drug: Sunitinib Malate |
Renal Cell Carcinoma Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma |
M.D. Anderson Cancer Center | May 15, 2018 | Phase 2 |
| NCT00329043 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: LHRH Agonist Drug: Sunitinib Malate |
Prostate Cancer | M.D. Anderson Cancer Center | May 2006 | Phase 2 |
| NCT00381641 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Sunitinib Drug: Sunitinib Malate |
Recurrent Thyroid Gland Carcinoma Refractory Thyroid Gland Carcinoma |
National Cancer Institute (NCI) |
August 8, 2006 | Phase 2 |
| NCT05687123 | Recruiting | Drug: Lutetium Lu 177 Dotatate Drug: Sunitinib Malate |
Metastatic Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor Pancreatic Neoplasm |
National Cancer Institute (NCI) |
January 6, 2024 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05678673 | Recruiting | Drug: Nivolumab Drug: Sunitinib Malate |
Non-Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma |
Exelixis | January 1, 2023 | Phase 3 |
|
 |