
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
SC79 is a novel, potent, selective, cell-permeable, and brain-penetrable activator of Akt phosphorylation with the potential to be used to enhance Akt activity in various physiological and pathological conditions, e.g. to prevent progressive neuronal death in neurological diseases. By interacting with the PH domain of Akt, SC79 inhibits the translocation of the Akt-PH (pleckstrin homology) domain and promotes Akt phosphorylation by upstream protein kinases. The cytosolic activation of Akt by SC79 is sufficient to recapitulate the primary cellular function of Akt signaling, resulting in increased neuronal survival, in a hippocampal neuronal culture system and a mouse model for ischemic stroke.
| Targets |
Akt
|
|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
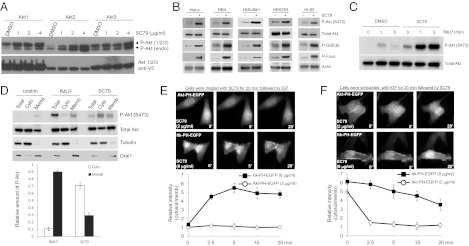
Synthetic Compound SC79 Suppresses PHAKT-GFP Plasma Membrane Translocation but Enhances Akt Phosphorylation and Activation in the Cytosol.
SC79 Enhances Phosphorylation of all Three Akt Isoforms and Elevates Akt Activation in Multiple Cell Types.
SC79 Specifically Enhances Akt Phosphorylation and Activation in both Receptor Tyrosine Kinase- and GPCR-Mediated Signaling.
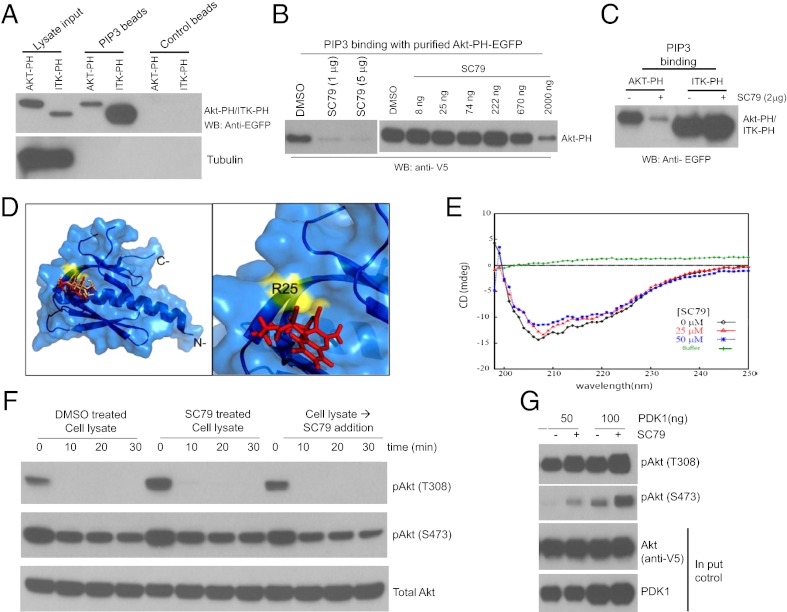
SC79 Directly Binds to Akt and Converts It to an Active Conformation More Amenable to Be Phosphorylated by Upstream Kinases.
SC79 Reduces Neuronal Excitotoxicity and Prevents Stroke-Induced Neuronal Death. [1]
In HEK293, HeLa, HL60, NB4 and HsSulton (B cells) cells, SC79 reduces PHAKTM-GFP plasma membrane translocation and increases the phosphorylation of all three Akt isoforms. SC79 lessens neuronal excitotoxicity and stops the death of neurons brought on by stroke.[1] SC79 increases MitoSox-positive cells' ability to produce superoxide while decreasing the proliferation of BRAT1 knockdown cells.[2] |
| ln Vivo |
In the mouse model of permanent focal cerebral ischemia, SC79 (0.04 mg/g, i.p.) activates Akt in the cytosol and mimics the main cellular function of Akt signaling, increasing neuronal survival. [1]
To ascertain whether SC79 can lead to Akt hyperactivation and prevent glutamate-mediated neurotoxicity in intact organisms, an ischemic stroke model was used. Researchers subjected mice to middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO), which elicits substantial cell death in the area of the occlusion. Most clinical symptoms of stroke, such as paralysis, aphasia, visual disturbance, and memory loss, are caused by neuronal death elicited by oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD), which is a result of lack of blood flow. Stroke-initiated OGD in affected brain regions induces a dramatic elevation of glutamate in the synaptic clefts that, in turn, causes massive excitotoxicity-elicited neuronal cell death (27, 28). Akt was identified as a potential target for treating stroke-induced neuronal death (29–32). Consistently, i.p. pretreatment with SC79 in mice effectively prevented stroke-induced Akt deactivation (Fig. 4 C and D). Consequently, it provided protection from excitotoxicity-induced brain damage in both the cortical area and striatum. The effect of SC79 was potent, with a single dose of SC79, 0.04 mg/g of body weight (equivalent to 0.5 μM), reducing the neocortical lesion size by 35% 24 h after MCAO and more than 40% 1 wk after MCAO (Fig. 4E). More drastic effect was observed when SC79 was injected multiple times (Fig. 4F).[1] Rats were treated with SC79 (a selective Akt activator which is cell and BBB permeable) 0.05 mg/kg × 3 i.p. or vehicle i.p. perioperatively. After one hour of MCAO and two hours of reperfusion, the transfer coefficient (Ki) of 14C-α-aminoisobutyric acid (14C-AIB, molecular weight 104 Da) and the volume of 3H-dextran (molecular weight 70,000 Da) distribution were determined to measure the degree of BBB disruption. At the same time point, the size of infarction was determined using tetrazolium staining. In an additional group of rats, a higher dose of SC79 (0.5 mg/kg × 3) was administered to determine the size of infarct. Administration of SC79 increased the Ki in the ischemic-reperfused cortex (IR-C, +32%, p < 0.05) as well as in the contralateral cortex (CC, +35%, p < 0.05) when compared with the untreated animals with MCAO/reperfusion. The volume of dextran distribution was not significantly changed by SC79. SC79 treatment significantly produced a decrease in the percentage of cortical infarct out of total cortical area (12.7 ± 1.7% vs 6.9 ± 0.9%, p < 0.001). Increasing the dose of SC79 by ten times did not significantly affect the size of cortical infarct. Contrary to our hypothesis, our data demonstrated that SC79 decreased the size of the infarct in the ischemic-reperfused cortex despite an increase in BBB disruption. Our data suggest the importance of activation of Akt for neuronal survival in the early stage of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion within the therapeutic window and that the mechanism of neuroprotection may not be related to the BBB effects of SC79. [3] Researchers report here that the Akt activator SC79 protects hepatocytes from TNF-α-induced apoptosis and protects mice from d-galactosamine (d-Gal)/lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced TNF-α-mediated liver injury and damage. SC79 not only enhances the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) prosurvival signaling in response to TNF-α stimulation, but also increases the expression of cellular FLICE (FADD-like IL-1β-converting enzyme)-inhibitory protein L and S (FLIPL/S), which consequently inhibits the activation of procaspase-8. Furthermore, pretreatment of the PI3K/Akt inhibitor LY294002 reverses all the SC79-induced hepatoprotective effects. These results strongly indicate that SC79 protects against TNF-α-induced hepatocyte apoptosis and suggests that SC79 is likely a promising therapeutic agent for ameliorating the development of liver injury. NEW & NOTEWORTHY SC79 protects hepatocytes from TNF-α-mediated apoptosis and mice from Gal/LPS-induced liver injury and damage. Cytoprotective effects of SC79 against TNF-α act through both AKT-mediated activation of NF-κB and upregulation of FLIPL/S. [5] Previous studies have demonstrated that activation of Akt may alleviate early brain injury (EBI) following subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). This study is undertaken to determine whether iron metabolism is involved in the beneficial effect of Akt activation after SAH. Therefore, we used a novel molecule, SC79, to activate Akt in an experimental Sprague-Dawley rat model of SAH. Rats were randomly divided into four groups as follows: sham, SAH, SAH + vehicle, SAH + SC79. The results confirmed that SC79 effectively enhanced the defense against oxidative stress and alleviated EBI in the temporal lobe after SAH. Interestingly, we found that phosphorylation of Akt by SC79 reduced cell surface transferrin receptor-mediated iron uptake and promoted ferroportin-mediated iron transport after SAH. As a result, SC79 administration diminished the iron content in the brain tissue. Moreover, the impaired Fe-S cluster biogenesis was recovered and loss of the activities of the Fe-S cluster-containing enzymes were regained, indicating that injured mitochondrial functions are restored to healthy levels. These findings suggest that disrupted iron homeostasis could contribute to EBI and Akt activation may regulate iron metabolism to relieve iron toxicity, further protecting neurons from EBI after SAH. [6] |
| Enzyme Assay |
Hela cells are serum starved for 1 hr and treated with IGF (100ng/mL) or SC79 (4 μg/mL) for 30 minutes. Protease inhibitors are added to the lysis buffer, which contains 250 mM sucrose, 20 mM HEPES, 10 mM KCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EDTA, and 1 mM EGTA. Multiple passes of a 25G needle are made with the cells, which are then placed on ice for 20 minutes. At this point, the entire cell lysate is collected. Centrifuging cell lysates at 100,000 g for 30 minutes. The cytosolic fraction is obtained by collecting supernatant. The pellet, which represents the membrane fraction, is washed in lysis buffer. SDS-PAGE is used to separate the total cell lysate, cytosolic, and membrane fractions. Western blotting is then used to check for the presence of phospho-Akt (S473), total Akt, tubulin (a cytosolic marker), and Orai1 (a membrane marker).
Screening for inhibitors of Akt plasma membrane translocation. To validate our cell based assay for high throughput screening, we first conducted a pilot screening using a bioactive compound library (approximately 3000 compounds). The screening was performed at the Institute for Chemistry and Cell Biology (ICCB) at Harvard Medical School. Every step of the experiment was handled in a high throughput mode (Figure S3). Based on our preliminary data, we incubated cells which have been serum-starved (0.1% serum) for overnight with chemical compounds for 30 min before inducing PHAkt-GFP membrane translocation with IGF. Our goal is to identify compounds which directly inhibit PtdIns(3,4,5)P3/Akt signaling pathway. Thus, we chose to use short incubation time to exclude compounds which indirectly block GFP-PH membrane translocation (e.g. via affecting transcription or translation). From the pilot screening, we identified 21 positive hit compounds (Figure S4 and Table S1). As expected, several known PI3 kinase inhibitors and compounds that nonspecifically inhibit PI3 kinase activity were identified as positive hit compounds, validating our strategy and method for high throughput screening. We then carried out the high throughput screening using several synthetic compound libraries. The ICCB compounds are from a variety of sources including commercial libraries, and libraries that result from diversity-oriented organic synthesis (DOS), known bioactive compounds, and historic collections of compounds resulting from different synthetic strategies. When ICCB purchased compound libraries, they selected collections that are enriched for complex heterocyclic compounds and compounds of higher molecular weight (an average mw of ~350-400 Daltons) because these types of compounds are more likely to provide interesting hits in high throughput screens. In addition, they sought to minimize the number of potentially “bad” compounds, those with groups that might make them unstable or toxic. In particular, they eliminated unstable imines, compounds with free carboxyl groups, and compounds with building block elements that might chelate metals. Table S2 is a list of libraries used for current screening, which include more than 60,000 synthetic compounds. The high throughput screening was performed twice to minimize the number of false positive hit compounds. From the first screening, we identified about 446 positive hit compounds and 125 of them were confirmed in the second screening (Table S3 and Figure S5). We later found that 25 of the positive compounds could generate auto-florescence and their effect on PH-Akt membrane translocation was in fact of the result of the greatly enhanced background florescence (Table S3) [1] Confirmation of the positive hits by time-lapse fluorescent imaging. In this study, more than 60,000 chemical compounds were screened and it is difficult to titrate the optimal concentration of each compound. The compound stocks were stored at 5 mg/ml in DMSO. In our screen, 100 nl of compound stock was transferred into a 50 µl assay volume, resulting in a final concentration of 20 µM for a compound of 500 Daltons. This is a generally utilized concentration at ICCB. One potential problem of our screening assay is that the transferred compounds may not be able to diffuse evenly in each well due to the relatively short incubation time. Thus, the effect of some positive hit compounds on PH-Akt membrane translocation could be result of very high local concentration. In order to select the most potent compounds for further characterization, we conducted dose-ranging experiments using live cells cultured in 35-mm plate. The initial 125 positive hit compounds identified after the second screening (Figure S5) were purchased from several companies. The fresh stock solution was freshly prepared in DMSO (5 mg/ml). This stock solution was directly added to culture medium to yield three different final concentrations (4, 8, 16 µg/ml). For time-lapse live cell imaging, HeLa-PH-EGFP cells were plated into a 35-mm glass-bottom dish and cultured for 24 to 48 hours. Cells were serum-starved in 2 mL Leibovitz L15 medium for 1 to 2 h and the medium was replaced with 1 mL of fresh serum-free Leibovitz 3 L15 medium containing a desired concentration of each compound. After 30 min pre-incubation, IGF1 (5 ng/mL) was added and images were taken every 5 to 10 min under a 40× oil objective lens. The relative fluorescent intensity at the membrane versus adjacent cytoplasm was determined. The compounds that led to a greater than 75% inhibition of PH-EGFP membrane translocation at or below 16 µg/ml were identified and designated as the confirmed hits. The representative live images and structure of 55 confirmed hit compounds were shown in Figure S6 and Figure S7. [1] Circular Dichroism (CD) [1] Far-UV CD (260-195 nm) was carried out at 25 °C on a Jasco-810 spectropolarimeter purged with nitrogen gas. Data were acquired in 1-mm quartz cuvette with 1-nm bandwidth, 2-s response time, 10 nm/min scan speed, and four scans. Pure N-terminal 6His-tagged recombinant full length Human Akt1 was purchased from Millipore (www.millipore.com/catalogue/item/14-279). Chemically synthesized and purified SC79 was used. Protein and ligand samples were prepared in 50 mM Tris pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl. Akt1 was incubated with SC79 at 37 °C for 30 min. Data sets were acquired in duplicate. Percent secondary structure was determined using programs K2D (http://www.embl.de/~andrade/k2d.html) and K2D2 (http://www.ogic.ca/projects/k2d2/). |
| Cell Assay |
HsSultan or NB4 cells (2.5 × 105) are plated in a 24-well plate in 500 μL of phenol red-free RPMI medium supplemented with 10% FBS. Each compound (8 µg/mL) is added after 24 hours of incubation, and it is then cultured for an overnight period (16–20 h). Each well receives 50 microliters of MTT solution (5 mg/mL in PBS). After 2 hours of incubation, 500 L of isopropanol with 0.1 M HCl are added directly to each well to dissolve the purple formazan crystals. At a wavelength of 570 nm, the absorbance is measured after removing the cell debris by centrifugation.
SC79-induced cytosolic phosphorylation of Akt analyzed by western blotting. [1] Hela cells were serum starved for 1 hr and treated with IGF (100ng/ml) or SC79 (4 µg/ml) for 30 minutes. Cells were lysed in Lysis buffer containing 250 mM Sucrose, 20 mM HEPES, 10 mM KCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM EGTA supplemented with protease inhibitors. Cells were passed through 25G needle several times and kept on ice for 20 minutes. Total cell lysate was taken at this point. Cell lysates were centrifuged at 100,000g for 30 minutes. Supernatant was collected as the cytosolic fraction . Pellet was washed with lysis buffer and represents the membrane fraction. Total cell lysate, cytosolic and membrane fractions were resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed for phospho-Akt (S473), Total Akt, Tubulin (cytosolic marker) and Orai1 (membrane marker) by western blotting. MTT (3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) assay for cell viability. [1] HsSultan or NB4 cells (2.5 × 105 ) were plated in a 24-well plate in 500 μL of phenol red-free RPMI medium supplemented with 10% FBS. After incubation for 24 hours, each compound (8 µg/ml) was added and cultured for overnight (16–20 h). Fifty microliters of MTT solution (5 mg/mL in PBS) were added to each well. Following 2 hrs incubation, the purple formazan crystals were dissolved by directly adding in 500 μL of isopropanol with 0.1 M HCl to each well. After clearing the cell debris by centrifugation, the absorbance was measured at a wavelength of 570 nm. Neuronal cell cultures and Cytotoxicity [1] Primary cortical or hippocampal neuronal cultures were prepared as previously described. To induce excitotoxicity, the cells were prewashed with Trisbuffered control salt (CSS) solution (120 mM NaCl, 5.4 mM KCl, 1.8 mMCaCl2, 25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, and 15 mM glucose) and treated with CSS containing 50 µM glutamate for 40 min, followed by 4 hr recovery in regular culture medium. SC79 (4 μg/ml) was given 15 min before and during glutamate treatment. Toxicity was assayed 4 h after glutamate exposure by microscopic examination with computerassisted cell counting. Total and dead cells were determined by nuclei staining with Hoechst (0.5 ng/ml) and propidium iodide (1 μg/ml), respectively. After 20 min incubation, the cells were examined under a fluorescence microscope with excitation at 360 nm. Cell death was determined as the ratio of dead-tototal cell number and quantified by counting 1,000 cells. |
| Animal Protocol |
Permanent focal cerebral ischemia mouse model
0.04 mg/g i.p. Permanent focal cerebral ischemia model [1] The permanent focal cerebral ischemia was induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) essentially as described previously(11). Briefly, mice (C57 Black/6) weighing 17–25 g were anesthetized with 4% isoflurane/66% N2O/30% O2 and maintained with 1.5% isoflurane. Permanent focal ischemia was achieved as follows: a 2-mm hole was drilled at a site superior and lateral to the left foramen ovale to expose the left middle cerebral artery. The proximal portion of the left middle cerebral artery (MCA) was permanently occluded over a 1-mm segment distal to the origin of the lenticulostriate branches through the use of a bipolar coagulator. SC79 was injected intraperitoneally (0.04 mg/g mouse body weight) 5 min before permanent MCAO (Figure 4E). In another experiment, extra SC79 was injected (0.04 mg/g mouse body weight, once per hour for 6 hours) (Figure 4F). Akt activation in the brain assessed by immunohistochemistry [1] The mouse brains were perfused from the apex of the heart with PBS and perfusion-fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS. They were then immersion-fixed overnight at 4°C in 4% paraformaldehyde with rocking and subsequently cryoprotected in 10% (2 hours), 15% (2 hours), 20% (2 hours), and 25% (overnight) sucrose in PBS at 4°C. The slices were then embedded in OCT compound and quickly frozen in isopentane. Coronal frozen sections (10-µm) were prepared on a cryostat and stored at -80 °C until use. The frozen sections were thawed, washed three times in PBS, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100/PBS at room temperature for 5 min, and then blocked in 5% skim milk/3% BSA/PBS for 60 min. Total and phosphorylated Akt/PKB were detected using anti-Akt and anti-Phospho-Akt (Ser473) antibodies, respectively. The slides were incubated with primary antibodies (1:200) at 4 °C overnight, and with the secondary antibodies at room temperature for 2 h, and immunoreactivity visualized by the ABC method. Twenty-eight male Fischer 344 rats weighing 220–250 g were used. They were randomly divided into two groups, 14 rats in each group: (1) MCAO/reperfusion, (2) SC79 + MCAO/reperfusion. For the SC79 + MCAO/reperfusion groups, three doses of 0.05 mg/kg of SC79 dissolved in 5% DMSO in normal saline were administered i.p. 10 min before transient middle cerebral artery (MCA) occlusion, upon reperfusion, and one hour after reperfusion. For the MCAO/reperfusion group, at each injection time point, the same volume of vehicle was administered. In each group, 8 rats were used for determination of BBB permeability parameters and 6 rats were used to determine the size of infarcts. In an additional group of rats (SC79H + MCAO/reperfusion, n = 6), ten times the SC79 dose, 0.5 mg/kg × 3 was administered to determine the size of infarct and confirm the effects of higher dose SC79 on neuronal survival. All rats were ventilated through a tracheal tube with 2% isoflurane in an air-oxygen mixture for MCA occlusion. [3] Male, age-matched (6- to 8-week–old) C57BL/6 or BALB/c mice (Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China) weighing 16 to 18 g were used in the animal study. Mice were housed in humidity- and temperature-controlled rooms, with free access to food and water. Mice were pretreated with 10 mg/kg SC79 or dimethyl sulfoxide intraperitoneally at 0.5 hour before the i.p. administration of an agonistic anti-Fas Jo2 antibody at a lethal dose of 0.5 and 0.4 mg/kg for C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice, respectively, within 12 hours. Mouse IgG was used as a control for Jo2. After this lethal challenge, mice were monitored continuously for mortality. For analyses other than mortality, mice were sacrificed at various time points after Jo2 injection. Serum levels of alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase were determined using a standard clinical automatic analyzer (model 7020; Hitachi, Kyoto, Japan). Immediately after the blood samples were obtained retro-orbitally, mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation. The excised liver mass was sectioned, fixed overnight at 4°C in 10% formalin solution, dehydrated, paraffin embedded, cut at 3-mm thickness, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin for histologic examination. Liver tissues were extracted, immediately snap-frozen using liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80°C until analyzed. [4] Male, age-matched (6 to 8 wk old) C57BL/6 mice weighing 16–18 g were used in the study. Mice were housed in humidity- and temperature-controlled rooms, with free access to food and water. Ten mice from each group were pretreated intraperitoneally with 10 mg/kg SC79 or DMSO at 0.5 h before administration of 400 mg/kg ip of d-galactosamine (d-Gal) and 60 µg/kg of LPS for C57BL/6 mice. PBS was used as a control for d-Gal/LPS. Mice were euthanized at 12 h after Gal/LPS injection. Serum levels of alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) were determined using a standard clinical automatic analyzer. Immediately after taking the blood samples retroorbitally, mice were euthanized by cervical dislocation. The excised liver mass was sectioned, fixed overnight at 4°C in 10% formalin solution, dehydrated, paraffin-embedded, cut at 3-mm thickness, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin for histological examination. Liver tissues were extracted, immediately snap-frozen using liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80°C until analyzed. [5] |
| References |
|
| Additional Infomation |
One caveat of using Akt activator as a drug for neurological disorders is that hyperactivation of Akt signaling may induce cancer. Nevertheless, induction of cancer by elevating PtdIns P3/Akt signaling is a progressive process and usually takes several months or even years. For example, in myeloid-specific PTEN knockout mice, we could not find any tumor until 3 months after the birth. When used as a suppressor of neuronal death caused by glutamate-excitotoxicity, Akt activator will only be given for several days, even several hours; thus it is unlikely that this type of treatment will lead to tumorigenesis. Interestingly, it was recently reported that activation of Akt1 decreases mammary epithelial cell migration, and Akt1 prevents an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition that resembles events required for metastasis. Another report showed that in some acute myeloid leukemia (AML), activation of Akt surprisingly reduced leukemic cell growth by inhibiting FOXO, suggesting that Akt activator can even potentially be used to treat certain cancers. Akt is also a key enzyme involved in other processes such as cell migration, immune cell activation, embryonic development, hematopoetic and mesenchymal differentiation, and glucose homeostasis, thus SC79 may potentially be used to modulate cell function in other physiological and pathological situations such as wound healing, host defense, and blood glucose control in diabetes. For example, SC79 may have a potential benefit in regulating glucoregulatory responses and insulin sensitivity in type 1 and 2 diabetes. Phosphorylation and deactivation of GSK3b promotes glycogen synthesis resulting in decreased blood glucose. Akt-mediated GLUT4 translocation mediates glucose transport. GSK3b and FOXO also play a role in expression of genes in gluconeogenesis like G6Pase and PEPCK(4). In innate immunity, activating neutrophil functions by elevating PI3K/Akt pathway using PTEN inhibitor has been previously reported. SC79 may also offer similar effect by directly activating Akt. In addition, SC79 may also be effective in preventing myocardial infarction in heart attack, in which the acquired resistance to apoptosis is mediated at least in part by the sustained activation of Akt. Use of SC79 could exert a wide range of cardio-protective effects in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury, myocardial hypertrophy, hypertension and vascular diseases by suppressing cell death and inducing angiogenesis by regulating eNOS.[1]
Elevating Akt activation is an obvious clinical strategy to prevent progressive neuronal death in neurological diseases. However, this endeavor has been hindered because of the lack of specific Akt activators. Here, from a cell-based high-throughput chemical genetic screening, we identified a small molecule SC79 that inhibits Akt membrane translocation, but paradoxically activates Akt in the cytosol. SC79 specifically binds to the PH domain of Akt. SC79-bound Akt adopts a conformation favorable for phosphorylation by upstream protein kinases. In a hippocampal neuronal culture system and a mouse model for ischemic stroke, the cytosolic activation of Akt by SC79 is sufficient to recapitulate the primary cellular function of Akt signaling, resulting in augmented neuronal survival. Thus, SC79 is a unique specific Akt activator that may be used to enhance Akt activity in various physiological and pathological conditions.[1] Background: BRAT1 (BRCA1-associated ATM activator 1) interacts with both BRCA1, ATM and DNA-PKcs, and has been implicated in DNA damage responses. However, based on our previous results, it has been shown that BRAT1 may be involved in cell growth and apoptosis, besides DNA damage responses, implying that there are undiscovered functions for BRAT1. Methods: Using RNA interference against human BRAT1, we generated stable BRAT1 knockdown cancer cell lines of U2OS, Hela, and MDA-MA-231. We tested cell growth properties and in vitro/in vivo tumorigenic potentials of BRAT1 knockdown cells compared to control cells. To test if loss of BRAT1 induces metabolic abnormalities, we examined the rate of glycolysis, ATP production, and PDH activity in both BRAT1 knockdown and control cells. The role of BRAT1 in growth signaling was determined by the activation of Akt/Erk, and SC79, Akt activator was used for validation. Results: By taking advantage of BRAT1 knockdown cancer cell lines, we found that loss of BRAT1 expression significantly decreases cell proliferation and tumorigenecity both in vitro and in vivo. Cell migration was also remarkably lowered when BRAT1 was depleted. Interestingly, glucose uptake and production of mitochondrial ROS (reactive oxygen species) are highly increased in BRAT1 knockdown HeLa cells. Furthermore, both basal and induced activity of Akt and Erk kinases were suppressed in these cells, implicating abnormality in signaling cascades for cellular growth. Consequently, treatment of BRAT1 knockdown cells with Akt activator can improve their proliferation and reduces mitochondrial ROS concentration.[2] |
| Molecular Formula |
C17H17CLN2O5
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
364.78
|
|
| Exact Mass |
364.082
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 55.98; H, 4.70; Cl, 9.72; N, 7.68; O, 21.93
|
|
| CAS # |
305834-79-1
|
|
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
2810830
|
|
| Appearance |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| Density |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| Boiling Point |
524.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| Flash Point |
271.2±30.1 °C
|
|
| Vapour Pressure |
0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| Index of Refraction |
1.564
|
|
| LogP |
3.23
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
1
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
7
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
7
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
25
|
|
| Complexity |
611
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
ClC1C([H])=C([H])C2=C(C=1[H])C([H])(C(C(=O)OC([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])=C(N([H])[H])O2)C([H])(C#N)C(=O)OC([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
DXVKFBGVVRSOLI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H17ClN2O5/c1-3-23-16(21)11(8-19)13-10-7-9(18)5-6-12(10)25-15(20)14(13)17(22)24-4-2/h5-7,11,13H,3-4,20H2,1-2H3
|
|
| Chemical Name |
ethyl 2-amino-6-chloro-4-(1-cyano-2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate
|
|
| Synonyms |
SC79; SC-79; 305834-79-1; SC79; ethyl 2-amino-6-chloro-4-(1-cyano-2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate; SC 79; SC-79; 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-acetic acid, 2-amino-6-chloro-alpha-cyano-3-(ethoxycarbonyl)-, ethyl ester; 2-amino-6-chloro-alpha-cyano-3-(ethoxycarbonyl)-4h-1-benzopyran-4-acetic acid ethyl ester; MFCD02681303;
SC 79
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: This product is not stable in solution, please use freshly prepared working solution for optimal results. |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO: 72 mg/mL (~197.4 mM)
Water: <1 mg/mL Ethanol: 72 mg/mL (~197.4 mM) |
|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: 5 mg/mL (13.71 mM) in 5% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 50% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with sonication.
Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.85 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.85 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 4: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.85 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 5: 2% DMSO+corn oil: 5mg/mL |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7414 mL | 13.7069 mL | 27.4138 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5483 mL | 2.7414 mL | 5.4828 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2741 mL | 1.3707 mL | 2.7414 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
Loss of BRAT1 leads to inhibition of Akt activity and Akt activation by SC79 partially restores BRAT1 knockdown cells. BMC Cancer. 2014 Jul 29;14:548. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-548. |
 |
 |