
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
SB408124 (SB-408124; SB 408124) is a potent, novel, selective, non-peptide antagonist for OX1 receptor with Ki of 57 nM and 27 nM in both whole cell and membrane, respectively, it exhibits 50-fold selectivity over OX2 receptor. In primary astrocyte cultures from the rat cerebral cortex, pretreatment with SB408124 significantly reduced the orexin A a stimulating effect on basal-induced cAMP production and forskolin.
| Targets |
OX1 Receptor ( Ki = 57 nM ); OX Receptor ( Ki = 27 nM )
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
|
||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Enzyme Assay |
SB-408124 is a non-peptide antagonist that shows 50-fold selectivity over OX2 receptor and has a Ki of 57 nM and 27 nM in whole cell and membrane, respectively, for the OX1 receptor.
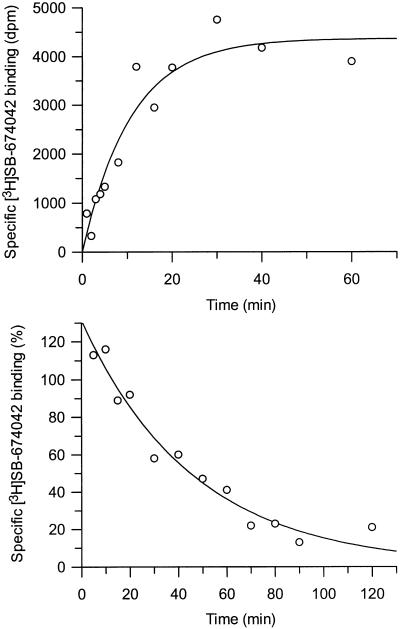
[3H]SB-674042 whole cell binding assays[1] After overnight culture in 96-well Packard Cultur plates, the medium was discarded and cells were incubated in buffer containing 150 mM NaCl, 20 mM HEPES and 0.5% bovine serum albumin (pH 7.4) for 60 min at 25°C. Saturation studies were carried out by incubating cells with a range of concentrations of [3H]SB-674042 (0.2–24 nM); the total assay volume was 250 μl. Protein content was assayed by lysing cells with 0.1 M NaOH and using the Bradford method (Bradford, 1976) with bovine serum albumin (BSA) as a standard. Association kinetic studies were performed by measuring the specific binding of [3H]SB-674042 (3 nM) at 1–60 min after addition of [3H]SB-674042. For dissociation studies, cells were first incubated with [3H]SB-674042 (3 nM) for 60 min. Specific binding was then measured at 2–120 min after the addition of 3 μM SB-408124. Competition studies were performed by incubating cells with [3H]SB-674042 (3 nM) and a range of concentrations of the test compound. All assays were terminated by washing the cells three times with 250 μl ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline. A volume of 100 μl of Microscint 40 was added to each well and the plate was left at room temperature for 2 h. Cell-associated radioactivity was then measured using a Packard Topcount, with a count time of 2 min well−1. [3H]SB-674042 membrane-based SPA binding assays[1] CHO-K1_OX1 cell membranes (75 μg ml−1) were precoupled by shaking with wheatgerm-agglutinin polyvinyltoluene (WGA-PVT) scintillation proximity assay (SPA) beads (5 mg ml−1) in buffer containing 25 mM HEPES, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM EDTA and 0.025% bacitracin (pH 7.4) at 4°C for 1 h. The bead-membrane suspension was centrifuged at 300 × g and resuspended in the same volume of room temperature assay buffer. A volume of 100 μl of bead-membrane suspension was incubated with [3H]SB-674042 (5 nM) in a total assay volume of 200 μl in a 96-well Packard Optiplate to give a final protein concentration of 7.5 μg well−1. Nonspecific binding was measured as that remaining in the presence of 3 μM SB-408124. Assay plates were shaken for 10 min and then incubated at room temperature for 4 h before being counted on a Packard TopCount scintillation counter (count time 2 min well−1). Saturation studies were carried out by incubating bead-membranes (equivalent to 7.5 μg protein well−1 and 2.5 mg beads ml−1) with a range of concentrations of [3H]SB-674042 (0.1–20 nM). Protein content was assayed using the Bradford method (Bradford, 1976) using bovine serum albumin as a standard. Association kinetic studies were performed by measuring specific binding of [3H]SB-674042 (5 nM) at 1–30 min after addition of bead-membranes (equivalent to 7.5 μg protein well−1 and 2.5 mg beads ml−1). For dissociation studies, bead-membranes were first incubated with [3H]SB-674042 (5 nM) for 30 min. Specific binding was then measured at 2–120 min after the addition of 3 μM SB-408124. Competition studies were performed by incubating bead-membranes (equivalent to 7.5 μg protein well−1 and 2.5 mg beads ml−1) with [3H]SB-674042 (5 nM) and a range of concentrations of the test compound. |
||
| Cell Assay |
SB-408124 has a pKi of 7.57 when it comes to binding the hypocretin type 1 receptor (HcrtR1). According to studies on calcium mobilization, SB-408124 functions as a functional antagonist of the OX1 receptor and has an affinity that is roughly 50 times more selective than the OX2 receptor. According to a recent study, the stimulatory action of Orexin A on basal and forskolin-acivated cAMP production was significantly reduced when primary cultures of rat astrocytes were pretreated with SB-401824 prior to Orexin A administration.
|
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References | |||
| Additional Infomation |
1-(6,8-difluoro-2-methyl-4-quinolinyl)-3-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]urea is a member of quinolines and an organohalogen compound.
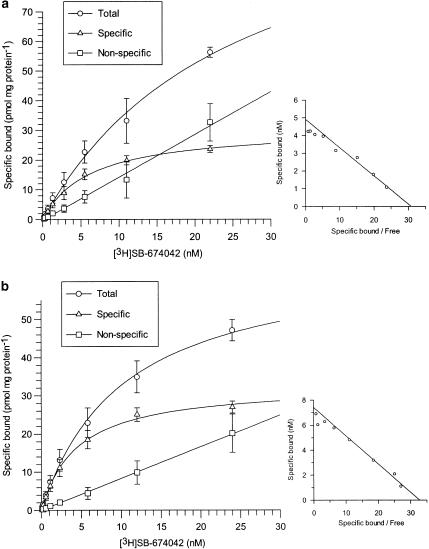
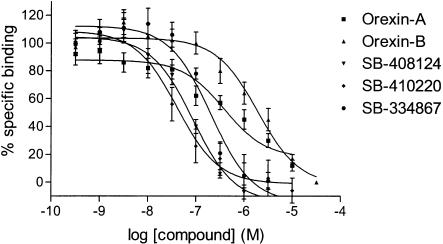
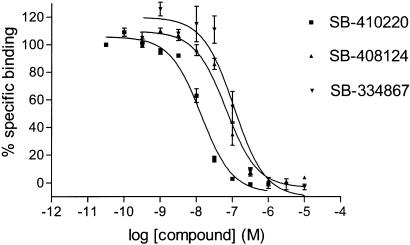
1. This study characterises the binding of a novel nonpeptide antagonist radioligand, [(3)H]SB-674042 (1-(5-(2-fluoro-phenyl)-2-methyl-thiazol-4-yl)-1-((S)-2-(5-phenyl-(1,3,4)oxadiazol-2-ylmethyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-methanone), to the human orexin-1 (OX(1)) receptor stably expressed in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells in both a whole cell assay and in a cell membrane-based scintillation proximity assay (SPA) format. 2. Specific binding of [(3)H]SB-674042 was saturable in both whole cell and membrane formats. Analyses suggested a single high-affinity site, with K(d) values of 3.76+/-0.45 and 5.03+/-0.31 nm, and corresponding B(max) values of 30.8+/-1.8 and 34.4+/-2.0 pmol mg protein(-1), in whole cell and membrane formats, respectively. Kinetic studies yielded similar K(d) values. 3. Competition studies in whole cells revealed that the native orexin peptides display a low affinity for the OX(1) receptor, with orexin-A displaying a approximately five-fold higher affinity than orexin-B (K(i) values of 318+/-158 and 1516+/-597 nm, respectively). 4. SB-334867, SB-408124 (1-(6,8-difluoro-2-methyl-quinolin-4-yl)-3-(4-dimethylamino-phenyl)-urea) and SB-410220 (1-(5,8-difluoro-quinolin-4-yl)-3-(4-dimethylamino-phenyl)-urea) all displayed high affinity for the OX(1) receptor in both whole cell (K(i) values 99+/-18, 57+/-8.3 and 19+/-4.5 nm, respectively) and membrane (K(i) values 38+/-3.6, 27+/-4.1 and 4.5+/-0.2 nm, respectively) formats. 5. Calcium mobilisation studies showed that SB-334867, SB-408124 and SB-410220 are all functional antagonists of the OX(1) receptor, with potencies in line with their affinities, as measured in the radioligand binding assays, and with approximately 50-fold selectivity over the orexin-2 receptor. 6. These studies indicate that [(3)H]SB-674042 is a specific, high-affinity radioligand for the OX(1) receptor. The availability of this radioligand will be a valuable tool with which to investigate the physiological functions of OX(1) receptors.[1] The effects of orexins, which are also named hypocretins, on cAMP formation were examined in primary cultures of rat astrocytes. Orexin A, an agonist of OX₁ and OX₂ receptors, stimulated cAMP production with an EC₅₀ value of 0.68 μM and potentiated the forskolin-induced increase in the nucleotide synthesis. [Ala¹¹-D-Leu¹⁵]orexin B, an agonist of OX₂ receptors, was inactive. The effects of orexin A were antagonized by SB 408124, a selective blocker of OX₁ receptors, but were not affected by TCS OX2 29, a selective antagonist of OX₃ receptors. We hypothesized that the activation of OX₁ receptors stimulated cAMP synthesis in primary rat astrocyte cultures.[2] |
| Molecular Formula |
C19H18F2N4O
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
356.37
|
|
| Exact Mass |
356.144
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 64.04; H, 5.09; F, 10.66; N, 15.72; O, 4.49
|
|
| CAS # |
288150-92-5
|
|
| Related CAS # |
SB-408124 Hydrochloride; 1431697-90-3
|
|
| PubChem CID |
4331799
|
|
| Appearance |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| Density |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| Boiling Point |
430.3±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| Flash Point |
214.0±28.7 °C
|
|
| Vapour Pressure |
0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| Index of Refraction |
1.697
|
|
| LogP |
4.53
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
2
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
5
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
3
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
26
|
|
| Complexity |
484
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
FC1=C([H])C(=C([H])C2C1=NC(C([H])([H])[H])=C([H])C=2N([H])C(N([H])C1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1[H])N(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])=O)F
|
|
| InChi Key |
JTARFZSNUAGHRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C19H18F2N4O/c1-11-8-17(15-9-12(20)10-16(21)18(15)22-11)24-19(26)23-13-4-6-14(7-5-13)25(2)3/h4-10H,1-3H3,(H2,22,23,24,26)
|
|
| Chemical Name |
1-(6,8-difluoro-2-methylquinolin-4-yl)-3-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]urea
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.02 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 2: 30% propylene glycol, 5% Tween 80, 65% D5W: 30mg/mL (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8061 mL | 14.0304 mL | 28.0607 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5612 mL | 2.8061 mL | 5.6121 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2806 mL | 1.4030 mL | 2.8061 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
 |
|---|
 |
  |