
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
Purity: ≥98%
SB271046 (SB 271046; SB-271046; SB-271046A; SB271046A) is a novel, potent, selective and orally bioactive 5-HT6 receptor antagonist with important biological activity. It has 200 times more selectivity than other 5-HT receptor subtypes and inhibits 5-HT6 with a pKi of 8.9. Human 5-HT6 receptors that were recombinantly expressed in HeLa cells in vitro were replaced by SB-271046 with [125I]-SB-258585 and [3H]-LSD. Moreover, [125I]-SB-258585 was transferred by SB-271046 from the rat and pig striatum membranes to the human caudate putamen. In HeLa cells that are stable expression hosts of human 5-HT6 receptors, adenylyl cyclase activity is stimulated by 5-HT alone or in response to increasing concentrations of SB-271046 (10, 30, 100, and 300 nM).
| Targets |
5-HT6 Receptor ( pKi = 8.92-9.09 )
|
|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
In vitro activity :SB 271046 competitively inhibited 5-HT-induced stimulation of adenylyl cyclase activity in functional studies on human 5-HT6 receptors, with a pA2 of 8.71[1].
|
| ln Vivo |
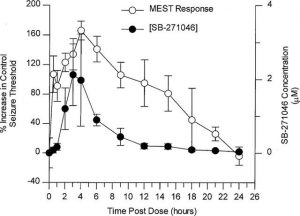
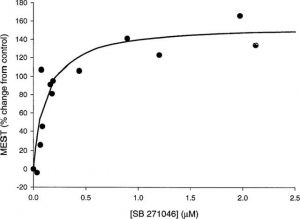
SB-271046 results in a minimum effective dose of approximately 0.1 mg/kg p.o. and maximum effect at 4 hours post-dose in the rat maximal electroshock seizure threshold (MEST) test. This rises the seizure threshold over a broad dose range. The blood and brain concentrations of SB 271046 (EC50 of 0.16 μM) and Cmax (0.01-0.04 μM) showed a strong correlation with the achieved level of anticonvulsant activity[1].
|
| Enzyme Assay |
SB271046 Hcl is an effective, pKi of 8.9, selective, and oral 5-HT6 receptor antagonist. IC50 Value: 8.9(pKi). A sulfonamidal benzothiophene derivative, SB 271046 hydrochloride has been demonstrated to function as a selective 5-HT6 antagonist, with pKi values of 9.02-8.92, 6.55, 6.35, 6.27, 6.05, 5.95, 5.76, 5.73, 5.62, 5.55, 5.41, 5.39, 5.27, and < 4.99 for 5-HT6, 5-HT1D, 5-HT1A, D3, 5-HT1B, 5-HT1F, α1B, 5-HT2C, 5-HT2A, D2, 5-HT2B, 5-HT7, 5-HT4 and 5-HT1E, respectively. It is also > 200-fold selective over 55 other receptors, enzymes, and ion channels.
Radioligand binding [1] Radioligand binding was carried out as described (Hirst et al., 2000). In brief, radioligand binding was performed on membranes from HeLa cells stably transfected with the human 5-HT6 receptor (see above) and striatal tissue from adult rats (Sprague-Dawley, 200–250 g), adult pigs (from a local abattoir) and human caudate putamen tissues (from non-identifiable patients aged 64–76 years, whose cause of death was non-neurological). Membranes were incubated with 1 nM [125I]-SB-258585 (Hirst et al., 2000) or 2 nM [3H]-LSD for 45 min at 37°C. Non-specific binding was defined by the inclusion of 10 μM methiothepin and the assay was terminated by rapid filtration through Whatman GF/B filters. For receptor selectivity studies on other 5-HT receptors, details of the radioligands used and assay conditions are given in Hirst et al. (2000). SB-271046 was also tested in a further 55 binding assays by CEREP. |
| Animal Protocol |
Male Sprague Dawley rats; Dissolved in 1% methyl cellulose in water; 30 mg/kg; Oral gavage
Maximal electroshock seizure threshold (MEST) test [1] Male Sprague Dawley rats (100–150 g), supplied by Charles River, U.K. were housed in groups of 10 at a room temperature of 20–22°C. Animals were maintained on a 12 h light/dark cycle with lights on between 0600 and 1800 h Food nd water were available ad libitum. Drug treatments were evaluated between 1400 and 1800 h alongside time-matched vehicle-treated controls. The threshold current for electroshock-induced tonic hindlimb extensor seizure was determined using a Hugo Sachs Electronik stimulator, which delivered an adjustable constant current (1–300 mA) of 0.3 s duration, 50 Hz, sinewave form, via corneal electrodes. The stimulus intensity was varied, from a typical baseline of 25 mA, by an ‘up and down' method of shock titration (see Upton et al., 1997, for details). Data generated from treatment groups of n=11–14 were used to calculate the seizure threshold (current producing tonic hindlimb extensor seizure in 50% of animals)±s.e. values according to the method of Kimball et al. (1957). Elevation of seizure threshold is indicative of an anticonvulsant effect whereas a reduction in seizure threshold is indicative of proconvulsant activity. The effects of the selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonists, SB-271046 (0.1–30 mg kg−1 p.o., 4 h pre-test), SB-258510 (10 mg kg−1 p.o., 2–6 h pre-test) (Bromidge et al., 1999) and Ro 04-6790 (0.3–30 mg kg−1 i.p., 1 h pre-test) (Sleight et al., 1998), on seizure threshold were determined. The doses of Ro 04-6790 selected for this study cover the range previously reported to evoke a number of behavioural effects in rats (Sleight et al., 1998; Bentley et al., 1999). SB-271046 and SB-258510 were suspended in 1% methyl cellulose in water and Ro 04-6790 was dispersed in saline. A 1 ml kg−1 dose volume was used for all treatments and doses are expressed as free base. In order to evaluate the relationship between the level of anticonvulsant activity achieved and blood concentration, the duration of action of a high submaximal dose (10 mg kg−1 p.o.) of SB-271046 in the rat MEST test was evaluated in detail over a 24 h period. Following the conclusion of this study, whole brain and blood samples were taken from randomly selected animals (n=5) at 13 different timepoints. Samples were assayed for SB-271046 using a method based on protein precipitation with acetonitrile, followed by LC/MS/MS analysis employing positive-ion electrospray ionization, with a lowest limit of quantification (LLQ) of 0.01 μM. |
| References | |
| Additional Infomation |
SB-271046, potently displaced [(3)H]-LSD and [(125)I]-SB-258585 from human 5-HT(6) receptors recombinantly expressed in HeLa cells in vitro (pK(i) 8.92 and 9.09 respectively). SB-271046 also displaced [(125)I]-SB-258585 from human caudate putamen and rat and pig striatum membranes (pK(i) 8.81, 9.02 and 8.55 respectively). SB-271046 was over 200 fold selective for the 5-HT(6) receptor vs. 55 other receptors, binding sites and ion channels. In functional studies on human 5-HT(6) receptors SB-271046 competitively antagonized 5-HT-induced stimulation of adenylyl cyclase activity with a pA(2) of 8.71. SB-271046 produced an increase in seizure threshold over a wide-dose range in the rat maximal electroshock seizure threshold (MEST) test, with a minimum effective dose of < or =0.1 mg kg(-1) p.o. and maximum effect at 4 h post-dose. The level of anticonvulsant activity achieved correlated well with the blood concentrations of SB-271046 (EC(50) of 0.16 microM) and brain concentrations of 0.01-0.04 microM at C(max). These data, together with the observed anticonvulsant activity of other selective 5-HT(6) receptor antagonists, SB-258510 (10 mg kg(-1), 2-6 h pre-test) and Ro 04-6790 (1-30 mg kg(-1), 1 h pre-test), in the rat MEST test, suggest that the anticonvulsant properties of SB-271046 are likely to be mediated by 5-HT(6) receptors. Overall, these studies demonstrate that SB-271046 is a potent and selective 5-HT(6) receptor antagonist and is orally active in the rat MEST test. SB-271046 represents a valuable tool for evaluating the in vivo central function of 5-HT(6) receptors. [1]
The present study shows that SB-271046 produces potent and long-lasting anticonvulsant activity in the rat MEST test, a model of previously reported utility for studying the role of serotonergic pathways in seizure regulation (e.g. Upton et al., 1998). Since SB-271046 is a very selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist (Bromidge et al., 1999; Routledge et al., 1999), the anticonvulsant properties of SB-271046 are likely to be mediated by blockade of 5-HT6 receptors. This is further supported by the demonstrated close correlation between the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles of the compound and the presently observed anticonvulsant activity of other selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonists, SB-258510 (Bromidge et al., 1999; pKi at human 5-HT6 receptor 9.2) and the chemically distinct agent Ro 04-6790 (Sleight et al., 1998). Overall, these data suggest that the MEST test may provide a robust model of in vivo 5-HT6 receptor function, and also illustrate that SB-271046 is a potent and orally active 5-HT6 receptor antagonist. However, the magnitude of these anti-seizure effects was modest in comparison to that of known anti-epileptic drugs For example, using identical test conditions, agents such as carbamazepine can elevate seizure threshold by >1200% (Upton et al., 1997) as compared to the maximum increase of only 132 and 166% produced by SB-258510 and SB-271046, respectively. This low level of anticonvulsant efficacy associated with 5-HT6 receptor blockade probably contributes to the apparent lack of dose-dependency for SB-271046, SB-258510 and Ro 04-6790 in the MEST test, since the anticonvulsant activity of SB-271046 is clearly related to the level of exposure in blood. Therefore, the relevance of this observation to the possible clinical utility of SB-271046 in the treatment of epilepsy is, at this stage, unclear. Taken together, these data demonstrate that SB-271046 is a potent, selective and orally active 5-HT6 receptor antagonist. This compound provides a useful tool for further elucidating the physiological function of 5-HT6 receptors in vivo. [1] |
| Molecular Formula |
C20H22CLN3O3S2
|
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
451.99
|
| Exact Mass |
487.056
|
| CAS # |
209481-20-9
|
| Related CAS # |
SB 271046 Hydrochloride; 209481-24-3
|
| PubChem CID |
5312149
|
| Appearance |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| Density |
1.400
|
| Boiling Point |
664.3ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| Melting Point |
240-241℃ (DEC.)
|
| Flash Point |
355.5ºC
|
| LogP |
6.431
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
2
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
7
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
5
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
29
|
| Complexity |
656
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
0
|
| SMILES |
CC1=C(SC2=C1C=C(C=C2)Cl)S(=O)(=O)NC3=CC(=C(C=C3)OC)N4CCNCC4
|
| InChi Key |
LOCQRDBFWSXQQI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H22ClN3O3S2/c1-13-16-11-14(21)3-6-19(16)28-20(13)29(25,26)23-15-4-5-18(27-2)17(12-15)24-9-7-22-8-10-24/h3-6,11-12,22-23H,7-10H2,1-2H3
|
| Chemical Name |
5-chloro-N-(4-methoxy-3-piperazin-1-ylphenyl)-3-methyl-1-benzothiophene-2-sulfonamide
|
| Synonyms |
SB-271046; SB 271046; SB271046; 209481-20-9; Sb 271046; SB-271046; SB271046; 5-chloro-N-(4-methoxy-3-(piperazin-1-yl)phenyl)-3-methylbenzo[b]thiophene-2-sulfonamide; 5-chloro-N-(4-methoxy-3-piperazin-1-ylphenyl)-3-methyl-1-benzothiophene-2-sulfonamide; L3SK5KX24S; Benzo[b]thiophene-2-sulfonamide, 5-chloro-N-[4-methoxy-3-(1-piperazinyl)phenyl]-3-methyl-; SB-271046 HCl; SB-271046 hydrochloride
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO: ~40 mg/mL (~81.9 mM)
Water: <1 mg/mL Ethanol: <1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
1% methylcellulose: ~30 mg/mL (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.)
|
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2124 mL | 11.0622 mL | 22.1244 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4425 mL | 2.2124 mL | 4.4249 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2212 mL | 1.1062 mL | 2.2124 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
 |
 |