
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
Purity: ≥98%
Pancuronium dibromide (OrgNA97; NA-97; Org NA 97; Pavulon), a neuromuscular relaxant used in euthanasia, is a bis-quaternary steroid and a competitive nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist with an IC50 of 5.5 nM. As a neuromuscular blocking agent, Pancuronium bromide is more potent than curare but has less effect on the circulatory system and on histamine release. Pancuronium dibromide interrupts neuromuscular transmission by competing with acetylcholine for receptor sites on the motor end-plate.
| ln Vitro |
Pancuronium's effect on transmembrane sodium conductance is examined in chick embryonic dorsal root ganglion neurons. Pancuronium, when externally perfused at concentrations between 50 μM and 1 mM, quickly and reversibly inhibits current flow. With a half-effective dose of 170 μM, inhibition is concentration-dependent but not voltage-dependent. By interacting with the sodium channels in both the resting and open states, pancuronium may lower the sodium current[2].
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| ln Vivo |
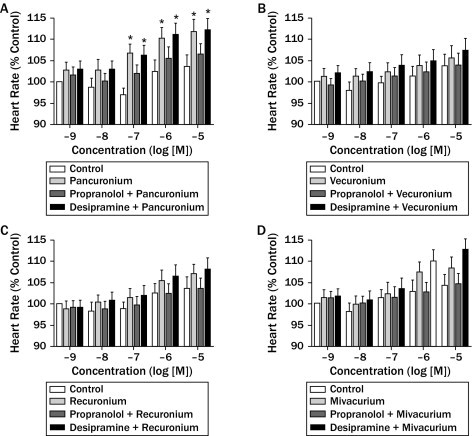
In male guinea pigs weighing 250–300 g, pancuronium (0.5 mg/kg) administered intravenously reverses the bradycardia caused by vagal nerve stimulation and injected acetylcholine (ACh). Vagally-induced bronchoconstriction is amplified by pancuronium (0.04 mg/kg) at levels that result in 100% neuromuscular blockade[1]. Rat anococcygeus and vas deferens exhibit pancuronium-mediated adrenergic nerve stimulation potentiation[3].
|
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
241 to 280 mL/kg Plasma cl=1.1–1.9 mL/minute/kg BOTH LIVER & KIDNEYS ARE INVOLVED IN DEGRADATION & EXCRETION OF ... PANCURONIUM ... AFTER IV INJECTION, EFFECTS...BECOME MAXIMAL IN LESS THAN 3 MIN IN ADULTS & 90 SEC IN CHILDREN. ... PLASMA HALF-LIFE IS PROBABLY SLIGHTLY LESS THAN 2 HR. PANCURONIUM IS MOSTLY EXCRETED UNCHANGED INTO URINE. PLACENTAL TRANSFER OF...PANCURONIUM BROMIDE...OCCURS RAPIDLY AFTER ADMIN TO MOTHERS, BUT FETAL:MATERNAL DRUG CONCN RATIO ARE VERY LOW. PLASMA LEVELS OF PANCURONIUM OBEYED TWO-COMPARTMENT KINETICS IN SEVEN PATIENTS ON IV INJECTION & THE BETA-PHASE HALF-TIME VARIED BETWEEN 90 AND 162 MIN. THE MEAN VOLUME OF THE CENTRAL COMPARTMENT WAS 100 ML/KG, WHILE THE OVERALL DISTRIBUTION VOLUME WAS 261 MG/KG. IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE, THE PLASMA CLEARANCE...WAS SIGNIFICANTLY REDUCED, WHILE VOLUMES OF BOTH THE OVERALL & CENTRAL COMPARTMENTS WERE SIGNIFICANTLY INCREASED. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for PANCURONIUM BROMIDE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Hepatic. IN CATS, 8 HR AFTER IV INJECTION OF PANCURONIUM BROMIDE, UNCHANGED PANCURONIUM BROMIDE IN URINE, BILE, & LIVER ACCOUNTED FOR 58% OF DOSE, 3-HYDROXY-DERIV FOR 14.5%, 17-HYDROXY-DERIV FOR 7% & 3,17-DIHYDROXY-DERIV FOR 4.5%. Biological Half-Life 1.5 to 2.7 hours. PLASMA HALF-LIFE IS PROBABLY SLIGHTLY LESS THAN 2 HR. |
||
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of pancuronium during breastfeeding. Because it is highly polar and poorly absorbed orally, it is not likely to reach the breastmilk in high concentration or to reach the bloodstream of the infant. When a combination of anesthetic agents is used for a procedure, follow the recommendations for the most problematic medication used during the procedure. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding 77 to 91% Interactions FROM CLINICAL VIEWPOINT, MOST IMPORTANT PHARMACOLOGICAL INTERACTIONS OF THESE DRUGS ARE WITH CERTAIN GENERAL ANESTHETICS, CERTAIN ANTIBIOTICS, AND ANTI-CHOLINESTERASE COMPOUNDS. /NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKING AGENTS/ ...DIETHYL ETHERS, AS WELL AS PRIOR SUCCINYLCHOLINE, INTENSIFY & PROLONG ACTION /OF PANCURONIUM/. ETHER EXERTS STABILIZING EFFECT ON POSTJUNCTIONAL MEMBRANE & THEREFORE, ACTS SYNERGISTICALLY WITH COMPETITIVE BLOCKING AGENTS. ... HALOTHANE, CYCLOPROPANE, FLUROXENE, METHOXYFLURANE, & ENFLURANE LIKEWISE ACT SYNERGISTICALLY WITH COMPETITIVE BLOCKING AGENTS, BUT TO LESSER EXTENT. /NEUROMUSCULAR COMPETITIVE BLOCKING AGENTS/ AMINOGLYCOSIDE ANTIBIOTICS PRODUCE NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKADE BY INHIBITING ACETYLCHOLINE RELEASE FROM THE PREGANGLIONIC TERMINAL (THROUGH COMPETITION WITH CA(2+)) AND ... BY STABILIZING THE POSTJUNCTIONAL MEMBRANE. THE BLOCKADE IS ANTAGONIZED BY CALCIUM SALTS, BUT ONLY INCONSISTENTLY BY ANTICHOLINESTERASE AGENTS. THE TETRACYCLINE ANTIBIOTICS ALSO CAN PRODUCE NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCK, POSSIBLY BY CHELATION OF CALCIUM IONS. ADDITIONAL ANTIBIOTICS THAT HAVE NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKING ACTION ... INCLUDE POLYMYXIN B, COLISTIN, CLINDAMYCIN, & LINCOMYCIN. /NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKING AGENTS/ For more Interactions (Complete) data for PANCURONIUM BROMIDE (27 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Rat oral 202 mg/kg LD50 Rat ip 479 ug/kg LD50 Rat sc 436 ug/kg LD50 Rat iv 153 ug/kg For more Non-Human Toxicity Values (Complete) data for PANCURONIUM BROMIDE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
||
| References |
|
||
| Additional Infomation |
Pancuronium is a steroid ester in which a 5alpha-androstane skeleton is C-3alpha- and C-17beta-disubstituted with acetoxy groups and 2beta- and 16beta-disubstituted with 1-methylpiperidinium-1-yl groups. It is a non-depolarizing curare-mimetic muscle relaxant. It has a role as a muscle relaxant, a cholinergic antagonist and a nicotinic antagonist. It is a steroid ester and an acetate ester.
A bis-quaternary steroid that is a competitive nicotinic antagonist. As a neuromuscular blocking agent it is more potent than curare but has less effect on the circulatory system and on histamine release. Pancuronium is a Nondepolarizing Neuromuscular Blocker. The physiologic effect of pancuronium is by means of Neuromuscular Nondepolarizing Blockade. Pancuronium is a synthetic, long-acting bis-quaternary steroid and non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent, with muscle relaxant activity. Pancuronium competitively binds to and blocks the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor at the neuromuscular junction, thereby preventing acetylcholine (ACh) binding and resulting in skeletal muscle relaxation and paralysis. A bis-quaternary steroid that is a competitive nicotinic antagonist. As a neuromuscular blocking agent it is more potent than CURARE but has less effect on the circulatory system and on histamine release. See also: Pancuronium Bromide (has salt form); Pancuronium bromide monohydrate (is active moiety of). Drug Indication Used as a muscle relaxant during anesthesia and surgical procedures. Mechanism of Action Nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents inhibit neuromuscular transmission by competing with acetylcholine for the cholinergic receptors of the motor end plate, thereby reducing the response of the end plate to acetylcholine. This type of neuromuscular block is usually antagonized by anticholinesterase agents. LOW CONCN OF PANCURONIUM BROMIDE (5X10-8 G/ML OR LESS), HAD NO PRESYNAPTIC EFFECT ON MURINE PHRENIC NERVE-DIAPHRAGM PREPN. AT HIGH CONCN (5X10-7 G/ML), PANCURONIUM BROMIDE DEPRESSED QUANTAL RELEASE TO 26% OF CONTROL IN CUT-FIBER PREPN & 40% OF CONTROL IN HIGH-MAGNESIUM PREPN. POSTSYNAPTIC EFFECTS REVEALED DEPRESSION TO 16 & 22% OF CONTROL, RESPECTIVELY, AT A CONCN OF 5X10-7 G/ML. PANCURONIUM BROMIDE HAD NO EFFECT ON DIRECTLY ELICITED ACTION POTENTIALS & ELECTRIC MEMBRANE CONSTANTS. THUS, PRESYNAPTIC AS WELL AS POSTSYNAPTIC EFFECTS OF PANCURONIUM BROMIDE IN PARALYTIC DOSES ARE ESSENTIAL IN CONTRIBUTING TO THE TOTAL EFFICACY OF NEUROMUSCULAR DEPRESSION. THE PHARMACODYNAMICS OF D-TUBOCURARINE (D-TC), PANCURONIUM BROMIDE, METOCURINE, & GALLAMINE WERE STUDIED IN RAT PHRENIC NERVE-HEMIDIAPHRAGM PREPN WITH VASCULAR PERFUSION AT 25, 31, & 37 °C. D-TC, METOCURINE, & GALLAMINE EACH DEMONSTRATED A NEAR 2-FOLD INCREASE IN ED50 AT 25 °C COMPARED WITH 37 °C. NO SUCH RELATIONSHIP WAS APPARENT WITH PANCURONIUM BROMIDE. SLOPES OF THE DOSE-RESPONSE CURVES WERE NOT INFLUENCED BY TEMP; HOWEVER, THE SLOPES FOR METOCURINE & D-TC WERE LOWER THAN THOSE FOR PANCURONIUM BROMIDE & GALLAMINE. THUS, IN THE RAT, PANCURONIUM BROMIDE RETAINS POTENCY AT HYPOTHERMIA, WHEREAS THE OTHER RELAXANTS DECREASE POTENCY. IN ADDITION, METOCURINE & D-TC EXHIBIT LESS STEEP DOSE-RESPONSE CURVES UNDER THESE EXPTL CONDITIONS. Therapeutic Uses Neuromuscular Nondepolarizing Agents; Nicotinic Antagonists THE MAIN CLINICAL USE OF THE NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKING AGENTS IS AS AN ADJUVANT IN SURGICAL ANESTHESIA TO OBTAIN RELAXATION OF SKELETAL MUSCLE, PARTICULARLY OF THE ABDOMINAL WALL ... MUSCLE RELAXATION IS ALSO OF VALUE IN VARIOUS ORTHOPEDIC PROCEDURES, SUCH AS THE CORRECTION OF DISLOCATIONS & THE ALIGNMENT OF FRACTURES. /NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKING AGENTS/ ...MAY BE USED MORE SAFELY IN PT WITH CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE OR BRONCHIAL ASTHMA THAN ANY OTHER NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKING DRUG. ...IT HAS ACTUALLY BEEN USED IN MGMNT OF STATUS ASTHMATICUS TO RELAX MUSCLES, THEREBY FACILITATING ARTIFICIAL RESPIRATION & DECR OXYGEN DEMAND. ... DURATION OF ACTION OF USUAL DOSE IS GENERALLY 30-60 MIN... /NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKING AGENTS/ HAVE BEEN USED TO FACILITATE LARYNGOSCOPY, BRONCHOSCOPY, & ESOPHAGOSCOPY, IN COMBINATION WITH A GENERAL ANESTHETIC AGENT. /NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKING AGENTS/ For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for PANCURONIUM BROMIDE (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings THE NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKING AGENTS ARE POTENTIALLY HAZARDOUS DRUGS. CONSEQUENTLY, THEY SHOULD BE ADMINISTERED TO PATIENTS ONLY BY ANESTHESIOLOGISTS & OTHER CLINICIANS WHO HAVE HAD EXTENSIVE TRAINING IN THEIR USE & IN A SETTING WHERE FACILITIES FOR RESPIRATORY & CARDIOVASCULAR RESUSCITATION ARE IMMEDIATELY AT HAND. /NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKING AGENTS/ ...IT IS ADVISABLE TO USE DRUG CAUTIOUSLY IN PRESENCE OF RENAL OR LIVER DISEASES. EFFECT OF SPECIFIC DOSE OF ... PANCURONIUM MAY /POSSIBLY/ BE REDUCED IN PT WITH HIGH PLASMA GLOBULIN LEVELS (EG THOSE WITH LIVER DISEASE). GREAT CARE SHOULD BE TAKEN WHEN ADMIN MUSCLE RELAXANTS TO DEHYDRATED OR SEVERELY ILL PATIENTS. /NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKING AGENTS/ For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for PANCURONIUM BROMIDE (17 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| Molecular Formula |
C35H60N2O4.2BR
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
732.67
|
|
| Exact Mass |
730.292
|
|
| CAS # |
15500-66-0
|
|
| Related CAS # |
16974-53-1 (cation);15500-66-0 (bromide);22189-36-2 (bromide hydrate);
|
|
| PubChem CID |
441289
|
|
| Appearance |
Off-white to pink solid powder
|
|
| Melting Point |
214 - 217ºC
|
|
| LogP |
0.036
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
0
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
4
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
6
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
41
|
|
| Complexity |
1000
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
10
|
|
| SMILES |
CC(=O)O[C@H]1C[C@@H]2CC[C@@H]3[C@@H]([C@]2(C[C@@H]1[N+]4(CCCCC4)C)C)CC[C@]5([C@H]3C[C@@H]([C@@H]5OC(=O)C)[N+]6(CCCCC6)C)C
|
|
| InChi Key |
NPIJXCQZLFKBMV-YTGGZNJNSA-L
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C35H60N2O4.2BrH/c1-24(38)40-32-21-26-13-14-27-28(35(26,4)23-31(32)37(6)19-11-8-12-20-37)15-16-34(3)29(27)22-30(33(34)41-25(2)39)36(5)17-9-7-10-18-36;;/h26-33H,7-23H2,1-6H3;2*1H/q+2;;/p-2/t26-,27+,28-,29-,30-,31-,32-,33-,34-,35-;;/m0../s1
|
|
| Chemical Name |
1,1-((2S,3S,5S,8R,9S,10S,13S,14S,16S,17R)-3,17-diacetoxy-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-2,16-diyl)bis(1-methylpiperidin-1-ium) bromide
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.41 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.41 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.41 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 4: 100 mg/mL (136.49 mM) in PBS (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with ultrasonication. |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.3649 mL | 6.8244 mL | 13.6487 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2730 mL | 1.3649 mL | 2.7297 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1365 mL | 0.6824 mL | 1.3649 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
 |
|---|
|