
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
Mirabegron (formerly YM-178; YM178; Myrbetriq; Betanis; Betmiga) is a potent and selective β3-adrenoceptor agonist with similar effects to antimuscarinic medications. It stimulates the β3-adrenoceptor with an EC50 of 22.4 nM. The medication mirabegron is authorized for the management of overactive bladder. When the β3 adrenergic receptor in the bladder's detrusor muscle is activated by mirabegron, the muscle relaxes and the bladder's capacity increases.
| Targets |
β3-adrenoceptor ( EC50 = 22.4 nM )
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
|
||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Enzyme Assay |
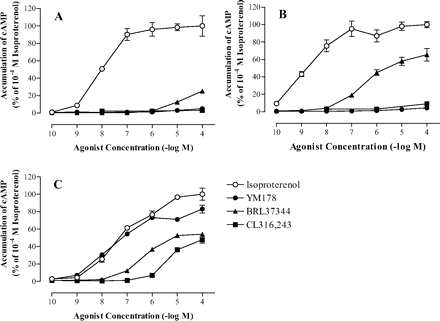
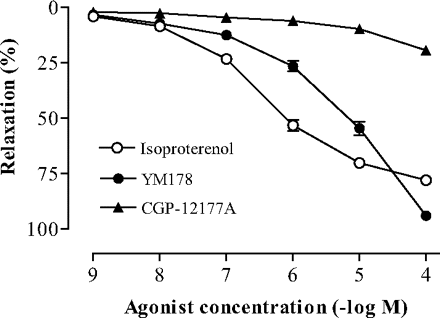
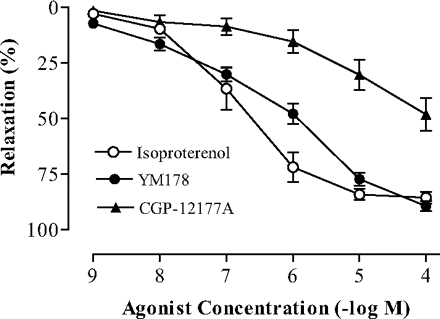
We evaluated the pharmacological characteristics of (R)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-4′-{2-[(2-hydroxy-2-phenylethyl)amino]-ethyl} acetanilide (YM178). YM178 increased cyclic AMP accumulation in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells expressing human β3-adrenoceptor (AR). The half-maximal effective concentration (EC50) value was 22.4 nM. EC50 values of YM178 for human β1- and β2-ARs were 10,000 nM or more, respectively. The ratio of intrinsic activities of YM178 versus maximal response induced by isoproterenol (nonselective β-AR agonist) was 0.8 for human β3-ARs, 0.1 for human β1-ARs, and 0.1 for human β2-ARs. [1]
|
||
| Cell Assay |
In every well of a 24-well culture plate, 105 CHO cells are deposited and allowed to grow. A pH 7.4 Hanks balanced salt solution containing 0.1 mM 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine is added to each well of the medium three days later. 250 μL of 0.2 M HCl is added to end the incubation of the cells after they have been exposed to each compound (isoproterenol, Mirabegron, BRL37344, and CL316,243) for 10 minutes at 37°C. The compounds are added at final concentrations of 10-10 to 10- M. Through radioimmunoassay with a 125I-cAMP assay system and a gamma counter, the concentration of cAMP in the reaction mixture is determined. The reaction is stopped by adding 400 μL of buffer solution after 50 microliters of reaction mixture and 50 μL of succinyl agent are incubated for 10 minutes at room temperature. For 24 hours at 4°C, 50 microliters of succinylated sample are incubated with 50 μL of 125I-cAMP and 50 μL of anti-cAMP antibody. After the incubation period, add 250 μL of charcoal suspension, and centrifuge at 2800g for 10 minutes at 4°C. After being transferred into a tube, 250 microliters of supernatant are counted for one minute using a gamma counter. The maximal response of each compound is used to calculate the intrinsic activity (I.A.) relative to isoproterenol for each β-adrenoceptor agonist.
|
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The absolute bioavailability of orally administered mirabegron ranges from 29% at a dose of 25 mg to 35% at a dose of 50 mg. The Tmax for the extended-release tablet and suspension formulations are approximately 3.5 hours, while the Tmax for the granule formulation is 4-5 hours. Both Cmax and AUC increase more than dose proportionally - an increase in dose from 50mg to 100mg results in a 2.9- and 2.6-fold increase in Cmax and AUC, respectively, whereas an increase from 50mg to 200mg results in a 8.4- and 6.5-fold increase in Cmax and AUC, respectively. Steady-state concentrations of mirabegron are achieved after approximately 7 days of once-daily administration. Of a 160mg radiolabeled dose administered to healthy volunteers, approximately 55% of the radioactivity was recovered in the urine and 34% in the feces. Approximately 25% of unchanged mirabegron was recovered in the urine while 0% was recovered in the feces. Renal elimination is achieved primarily via active tubular secretion with some contribution by glomerular filtration. Following intravenous administration, mirabegron has an apparent steady-state volume of distribution (Vd) of 1670 L indicating extensive distribution. Total plasma clearance following intravenous administration is approximately 57 L/h, with renal clearance accounting for roughly 25% at approximately 13 L/h. Metabolism / Metabolites Mirabegron is extensively metabolized via a number of mechanisms, although unchanged parent drug is still the major circulating component following oral administration. Presumed metabolic pathways and their resultant metabolites include amide hydrolysis (M5, M16, M17), glucuronidation (mirabegron O-glucuronide, N-glucuronide, N-carbamoylglucuronide, M12), and secondary amine oxidation or dealkylation (M8, M9, M15), amongst others. The enzymes responsible for the oxidative metabolism of mirabegron are thought to be CYP3A4 and CYP2D6, while the UDP-glucuronosyltransferases responsible for conjugation reactions have been identified as UGT2B7, UGT1A3, and UGT1A8. Other enzymes that may be involved in the metabolism of mirabegron include butylcholinesterase and possibly alcohol dehydrogenase. Biological Half-Life The mean terminal elimination half-life of mirabegron in adults being treated for overactive bladder is approximately 50 hours. In pediatric patients receiving the granule formulation for the treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity, the mean terminal elimination half-life is approximately 26-31 hours. |
||
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Hepatotoxicity
In preregistration clinical trials, serum aminotransferase elevations were uncommon and mild in patients treated with mirabegron and rates of serum enzyme elevations were similar to those with placebo treatment. Among several thousands of patients treated, there were no episodes of clinically apparent liver injury. Since its approval and more widescale use, there have not been any published reports of hepatotoxicity attributed to mirabegron. However, the product label for mirabegron mentions occasional elevations in ALT and AST associated with treatment as well as a case of Stevens Johnson syndrome with aminotransferase elevations. Thus, mirabegron may cause hepatic injury as a part of a generalized hypersensitivity reactions. Likelihood score: E* (unproven but suspected rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of mirabegron during breastfeeding. Because of moderately high protein binding and only relatively low bioavailability, exposure of the breastfed infant is likely to be low. If mirabegron is required by the mother, it is not a reason to discontinue breastfeeding, but until more data become available, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Mirabegron is approximately 71% protein-bound in plasma, primarily to albumin and alpha-1-acid glycoprotein. |
||
| References | |||
| Additional Infomation |
Mirabegron is a monocarboxylic acid amide obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of 2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-ylacetic acid with the anilino group of (1R)-2-{[2-(4-aminophenyl)ethyl]amino}-1-phenylethanol. Used for the treatment of overactive bladder syndrome. It has a role as a beta-adrenergic agonist. It is a member of 1,3-thiazoles, an aromatic amide, a member of ethanolamines and a monocarboxylic acid amide.
Mirabegron is a sympathomimetic beta-3 adrenergic receptor agonist used to relax the smooth muscle of the bladder in the treatment of urinary frequency and incontinence. It is unique amongst overactive bladder treatment options in that, unlike other treatments such as [solifenacin] and [darifenacin], it lacks significant antimuscarinic activity, which is responsible both for the therapeutic effects of these medications and their broad range of adverse effects. Mirabegron has a comparatively favorable adverse effect profile as compared to other available treatment options, and its complementary mechanism to the antimuscarinics that came before it allows for its use alongside solifenacin in refractory cases. Mirabegron first received FDA approval in 2012, under the brand name Myrbetriq, for the treatment of adults with overactive bladder. An extended-release granule formulation was subsequently granted approval in March 2021 for the treatment of pediatric patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity. Mirabegron is also used in other jurisdictions across the globe, including Canada, the EU, and Japan. Mirabegron is a beta3-Adrenergic Agonist. The mechanism of action of mirabegron is as an Adrenergic beta3-Agonist, and Cytochrome P450 2D6 Inhibitor, and Cytochrome P450 3A Inhibitor, and P-Glycoprotein Inhibitor. Mirabegron is a beta-3 adrenergic agonist that is used for treatment of overactive bladder syndrome. Mirabegron has not been implicated in causing liver enzyme elevations or clinically apparent acute liver injury. Mirabegron is an orally bioavailable agonist of the human beta-3 adrenergic receptor (ADRB3), with muscle relaxing, neuroprotective and potential antineoplastic activities. Upon oral administration, mirabegron binds to and activates ADRB3, which leads to smooth muscle relaxation. Mirabegron also restores sympathetic stimulation in mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) niches, inhibits JAK2-mutated hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) expansion and blocks the progression of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs). Lack of sympathetic stimulation of the MSC and HSC niche is associated with the development of MPNs. Drug Indication Mirabegron is indicated for the treatment of overactive bladder (OAB) - with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency, and urinary frequency - either alone or in combination with [solifenacin]. It is also indicated for the treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity (NDO) in pediatric patients 3 years of age and older and weighing 35kg or more. Symptomatic treatment of urgency. Increased micturition frequency and / or urgency incontinence as may occur in adult patients with overactive-bladder syndrome. Treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity Treatment of idiopathic overactive bladder Mechanism of Action Mirabegron is a potent and selective agonist of beta-3 adrenergic receptors. The activation of beta-3 receptors relaxes detrusor smooth muscle during the storage phase of the urinary bladder fill-void cycle, which increases the bladder's storage capacity thereby alleviating feelings of urgency and frequency. Pharmacodynamics Mirabegron exerts its pharmacologic effects by forcing bladder smooth muscle to relax, thereby expanding its capacity and relieving urgency. Mirabegron does not appear to adversely affect the mean maximum flow rate or mean detrusor pressure at maximum flow rate in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms and bladder outlet obstruction (BOO), but should be used with in patients with BOO due to reports of significant urinary retention. Furthermore, mirabegron increases both blood pressure and heart rate in a dose-dependent manner and should therefore be used with caution in patients with severely uncontrolled hypertension or others for whom these increases may prove dangerous. |
| Molecular Formula |
C21H24N4O2S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
396.51
|
|
| Exact Mass |
396.161
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 63.61; H, 6.10; N, 14.13; O, 8.07; S, 8.09
|
|
| CAS # |
223673-61-8
|
|
| Related CAS # |
(Rac)-Mirabegron-d5; 1215807-38-7
|
|
| PubChem CID |
9865528
|
|
| Appearance |
White to light yellow solid powder
|
|
| Density |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| Boiling Point |
690.0±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| Melting Point |
138-140°C
|
|
| Flash Point |
371.1±31.5 °C
|
|
| Vapour Pressure |
0.0±2.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| Index of Refraction |
1.681
|
|
| LogP |
1.29
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
4
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
6
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
9
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
28
|
|
| Complexity |
467
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
S1C(N([H])[H])=NC(=C1[H])C([H])([H])C(N([H])C1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N([H])C([H])([H])[C@@]([H])(C1C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C=1[H])O[H])=O
|
|
| InChi Key |
PBAPPPCECJKMCM-IBGZPJMESA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C21H24N4O2S/c22-21-25-18(14-28-21)12-20(27)24-17-8-6-15(7-9-17)10-11-23-13-19(26)16-4-2-1-3-5-16/h1-9,14,19,23,26H,10-13H2,(H2,22,25)(H,24,27)/t19-/m0/s1
|
|
| Chemical Name |
2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-N-[4-[2-[[(2R)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylethyl]amino]ethyl]phenyl]acetamide
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.25 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.25 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.25 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 4: Mirabegron (10 mg/ml) dissolved in DMSO (50%, vol%) and polyethylene glycol (50%, vol%) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5220 mL | 12.6100 mL | 25.2200 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5044 mL | 2.5220 mL | 5.0440 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2522 mL | 1.2610 mL | 2.5220 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
Study to Test the Long Term Safety and Efficacy of the Beta-3 Agonist Mirabegron (YM178) in Patients With Symptoms of Overactive Bladder
CTID: NCT00688688
Phase: Phase 3 Status: Completed
Date: 2024-11-20
 |
|---|
 |
 |