
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
Purity: ≥98%
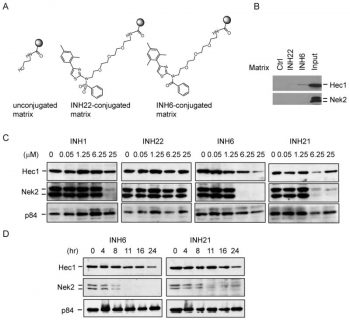
INH6 (INH-6; INH 6) is a novel, potent and cell-permeable inhibitor of High expression in cancer 1 (Hec1) with potential anticancer activity. It specifically inhibits the Hec1-Nek2 protein-protein interactions disrupts, thus causing chromosome mis-alignment and cell death. INH6 shows potent anti-proliferative activity in vitro against various cancer cell lines such as MDA-MB468, MDA-MB231 human breast cancer cells, HeLa human cervical cancer line and K562 human erythromyeloblastoid leukemia cells with IC50 values of 2.1, 1.7, 2.4 and 2.5 µM, respectively.
| ln Vitro |
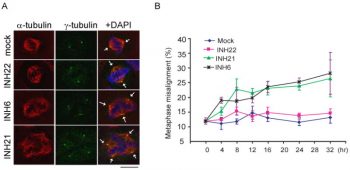
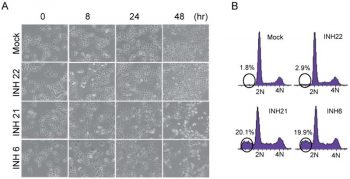
Many human cancers overexpress the oncogene Hec1. The mitotic pathway's Hec1/Nek2 function is inactivated by the small molecule INH (Inhibitor of Nek2/Hec1), which targets Hec1 and its regulator, Nek2. This process is mediated by protein degradation, which ultimately results in chromosome missegregation and cell death. Increased mitotic population and multipolar spindle configurations are seen in cells treated with INH6. After HeLa cells expressing the chromosome marker protein H2B-GFP are treated with INH6, a higher rate of chromosome misalignment is observed. INH6-treated cells exhibit progressive morphological changes indicative of dying cells, such as membrane bubbling, which are further supported by FACS analysis and cell cycle profiling. Seventy-two hours after treatment, 20% of INH6-treated cells undergo apoptosis[1].
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References |
| Molecular Formula |
C19H18N2OS
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
322.42
|
|
| Exact Mass |
322.113
|
|
| CAS # |
1001753-24-7
|
|
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
7918451
|
|
| Appearance |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| Density |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| Index of Refraction |
1.647
|
|
| LogP |
5.7
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
1
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
3
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
3
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
23
|
|
| Complexity |
398
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
0
|
|
| InChi Key |
WCZLNJTXHZPHLM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C19H18N2OS/c1-12-9-13(2)17(14(3)10-12)16-11-23-19(20-16)21-18(22)15-7-5-4-6-8-15/h4-11H,1-3H3,(H,20,21,22)
|
|
| Chemical Name |
N-[4-(2,4,6-Trimethylphenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]benzamide
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.75 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1015 mL | 15.5077 mL | 31.0154 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6203 mL | 3.1015 mL | 6.2031 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3102 mL | 1.5508 mL | 3.1015 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
 |
|---|
 |
 |