
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
HA14-1 is a novel, potent and non-peptidic inhibitor of a B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) surface pocket with IC50 of ~9 μM. By imitating the BH3 domain necessary for the formation of homo- and hetero-dimers, HA14-1 binds to Bcl-2 and inhibits Bcl-2 by blocking the binding of these proteins. HA14-1 has received a lot of attention in apoptosis research, which makes it more promising as a cancer treatment.
| Targets |
Bcl-2 (IC50=9 μM ); Bcl-xL
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
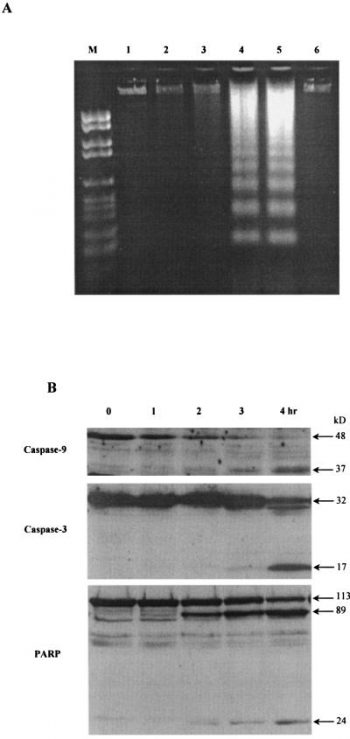
HA14-1 is a nonpeptidic ligand of a Bcl-2 surface pocket. Apaf-1 and caspases are activated by HA14-1, possibly by binding to the Bcl-2 protein and preventing it from performing its intended function. As a series of synthetic analogs derived from HA14-1 containing various modifications are found to have greatly different Bcl-2 binding activities, it appears that the interaction of HA14-1 with the Bcl-2 surface pocket is specific for the chemical structure of HA14-1. HL-60 cells are exposed to various concentrations of HA14-1 for 4 hours in order to investigate the impact of HA14-1 on cell viability. HL-60 cells are killed by HA14-1 in a dose-dependent manner. More than 90% of the cells lose viability at a concentration of 50 M of HA14-1[1]. HA14-1 is a Bcl-2/Bcl-xL antagonist[2].
|
||
| ln Vivo |
Swiss nude mice injected with human glioblastoma multiforme cells are also given i.p. low doses of Etoposide (2.5 mg/kg in 200 L of 0.9% NaCl 5 days a week starting on day 2 after cell injection) along with HA14-1 or mock treatment to examine whether HA14-1 treatment might increase the efficacy of another antitumoral treatment. Etoposide treatment is insufficient to stop the growth of glioblastoma cells on its own, but when combined with HA14-1, it significantly slows tumor growth, as shown by the ability of the combined therapy to lengthen the tumor volume's time to double[3].
|
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References |
.
|
||
| Additional Infomation |
2-amino-6-bromo-4-(1-cyano-2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester is a 1-benzopyran.
|
| Molecular Formula |
C17H17BRN2O5
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
409.23
|
|
| Exact Mass |
408.032
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 49.89; H, 4.19; Br, 19.53; N, 6.85; O, 19.55
|
|
| CAS # |
65673-63-4
|
|
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
3549
|
|
| Appearance |
White to light yellow solid powder
|
|
| Density |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| Boiling Point |
535.1±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| Melting Point |
105ºC
|
|
| Flash Point |
277.4±30.1 °C
|
|
| Vapour Pressure |
0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| Index of Refraction |
1.574
|
|
| LogP |
3.7
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
1
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
7
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
7
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
25
|
|
| Complexity |
611
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
BrC1C([H])=C([H])C2=C(C=1[H])C([H])(C(C(=O)OC([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])=C(N([H])[H])O2)C([H])(C#N)C(=O)OC([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
SXJDCULZDFWMJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H17BrN2O5/c1-3-23-16(21)11(8-19)13-10-7-9(18)5-6-12(10)25-15(20)14(13)17(22)24-4-2/h5-7,11,13H,3-4,20H2,1-2H3
|
|
| Chemical Name |
ethyl 2-amino-6-bromo-4-(1-cyano-2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.11 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.11 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: 1% DMSO+30% polyethylene glycol+1% Tween 80: 30mg/mL |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4436 mL | 12.2181 mL | 24.4361 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4887 mL | 2.4436 mL | 4.8872 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2444 mL | 1.2218 mL | 2.4436 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
 |
|---|
|