
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
GW5074 (GW-5074; GW 5074) is a novel, potent and selective c-Raf inhibitor with potential neuroprotective activity. With an IC50 of 9 nM, it inhibits c-Raf but has no effect on JNK1/2/3, MKK6/7, CDK1/2, MEK1, c-Src, VEGFR2, p38 MAP, or c-Fms. In an animal model of Huntington's disease, GW-5074 is able to stop neurodegeneration and enhance behavioral outcomes. For the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases in people, GW 5074 has therapeutic potential.
| Targets |
C-Raf (IC50 = 9 nM)
|
|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
GW5074 is a potent and specific inhibitor of c-Raf with an IC50 value of 9 nM; it has no effect in vitro on MKK6, MKK7, p38 MAP kinase, or cdks. However, treatment with GW5074 in neuronal cultures allows for the accumulation of activating modifications on both c-Raf and B-Raf. In cerebellar granule neurons, GW5074 does not require MEK or ERK to prevent LK-induced apoptosis. Although apoptosis is inhibited by GW5074 through an Akt-independent mechanism, Akt activity is delayed during this process. Nuclear factor-kappa B, c-jun, and Ras are all impacted by GW5074. In granule cells and other neuronal types, GW5074 prevents neurotoxins from causing cell death. [1]
|
| ln Vivo |
GW5074 is preventative in a Huntington's disease experimental in vivo model. In mice, 3-NP-induced extensive bilateral striatal lesions were completely stopped by GW5074 (5 mg/Kg).[1] In mice, GW5074 reduces the airway hyperresponsiveness brought on by sidestream smoke.[3]
|
| Enzyme Assay |
The Kinase Profiling service of Upstate Biotechnology typically uses purified kinase and synthetic substrates under standard conditions to perform in vitro kinase assays. In a nutshell, 5–10 mU of purified kinase are utilized for each assay. For GSK3β, cdk1, cdk2, cdk3, and cdk5, the kinase is incubated with 1 μM GW5074 for 40 min at room temperature in a buffer containing 8 mM MOPS, pH 7.2, 0.2 mM EDTA, 10 mM magnesium acetate, and [c- 33P-ATP]. With an aliquot spotted on P30 filters, washed in 50 mM phosphoric acid, and scintillation counted, 33P incorporation is measured to determine the amount of kinase activity. For [c- 33P-ATP], 50 mM Tris pH 7.5, 0.1 mM EGTA, 10 mM magnesium acetate, and [c- Raf, JNK1, JNK2, JNK3, MEK1, MKK6, and MKK7, the buffer's component parts are. These are the peptide substrates employed: MBP concentrations for c-Raf are 0.66 mg/mL, cdks are 0.1 mg/mL, JNKs are 3 μM ATF2, MEK1 is 1 μM MAPK2, MKK6 is 1 μM SAPK2a, and MKK7 is 2 μM JNK1α.
|
| Cell Assay |
HCA is diluted from 100-fold concentrated solutions with a pH of 7.5. When cortical neurons are exposed to HCA, GW5074 is added in order to assess its effects on the cytotoxicity caused by HCA. 24 hours later, viability is evaluated.
|
| Animal Protocol |
On the sixth day after receiving injections of saline, 3-NP, or a combination of 3-NP and GW5074 over the previous five days, the locomotor activity of mice is measured using the Tru-Scan® activity monitoring system (7 mice per group). The animal is put in a Perspex arena that measures 25.9 x 25.9 cm and has infrared beams that are spaced 0.6 inches apart in the X-Y plane. A second infrared beam system at the Z plane, positioned 2.54 cm above the X-Y plane, is also installed in the arena. In this system, interruptions in the 1717-grid system caused by the infrared beams in both the X-Y and Z planes are used to accurately measure animal movement. The animal is allowed to stay in the arena for 15 minutes, during which time data is collected using a Pentium PC running Tm Scan 99 software and the Tru Scan Line interface box. We choose the following behavioral criteria: (i) Total movement distance: the total of all vectored A-Y coordinate changes in the floor plane; (ii) mean velocity: the mean velocity of all X-Y coordinate change defined movements; and (iii) total vertical plane entries: the total number of times any part of the animal entered the vertical plane (Z plane). Each movement in the floor plane is a series of coordinate changes with no rest for at least one sample interval.
|
| References |
| Molecular Formula |
C15H8BR2INO2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
520.94
|
|
| Exact Mass |
518.796
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 34.58; H, 1.55; Br, 30.68; I, 24.36; N, 2.69; O, 6.14
|
|
| CAS # |
220904-83-6
|
|
| Related CAS # |
(Z)-GW 5074;1233748-60-1
|
|
| PubChem CID |
5924208
|
|
| Appearance |
Light yellow to yellow solid powder
|
|
| Density |
2.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| Boiling Point |
561.4±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| Flash Point |
293.3±30.1 °C
|
|
| Vapour Pressure |
0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| Index of Refraction |
1.790
|
|
| LogP |
6.36
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
2
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
2
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
1
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
21
|
|
| Complexity |
447
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
IC1C([H])=C([H])C2=C(C=1[H])/C(=C(\[H])/C1C([H])=C(C(=C(C=1[H])Br)O[H])Br)/C(N2[H])=O
|
|
| InChi Key |
LMXYVLFTZRPNRV-KMKOMSMNSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C15H8Br2INO2/c16-11-4-7(5-12(17)14(11)20)3-10-9-6-8(18)1-2-13(9)19-15(10)21/h1-6,20H,(H,19,21)/b10-3-
|
|
| Chemical Name |
(3Z)-3-[(3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxyphenyl)methylidene]-5-iodo-1H-indol-2-one
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.80 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 30% propylene glycol, 5% Tween 80, 65% D5W: 30mg/mL (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9196 mL | 9.5980 mL | 19.1961 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3839 mL | 1.9196 mL | 3.8392 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1920 mL | 0.9598 mL | 1.9196 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT03406364 | Completed | Drug: MG005 | Solid Tumor | Metagone Biotech Inc. | June 6, 2018 | Phase 1 |
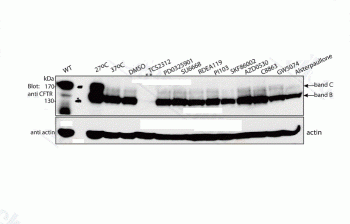
Effect of kinase inhibitors on cell surface expression of DF508-CFTR analyzed by flow cytometry. Summary of increase in cell surface expression of DF508-CFTR (% change in fluorescence intensity) of the hits analyzed by flow cytometry (two independent experiments, 10,000 live cells per treatment per experiment). |
 |