
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
Esmolol HCl (Brevibloc; ASL-8052; ASL 8052), the hydrochloride salt of esmolol, is a potent and cardioselective beta-blocker used to control rapid heartbeats or abnormal heart rhythms. Esmolol is an enantiomeric pair with one asymmetric center; the (+)-enantiomer is inactive and the (-)-enantiomer is active. This is similar to other P-blockers that have an oxypropranolamine nucleus. Esmolol exhibits a swift onset and offset of action, with its primary site of action being on the conduction systems of the sinus node and atrioventricular (AV) node.
| Targets |
Adrenergic receptor
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
|
||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
It is not known whether esmolol and/or ASL 8123 cross the placenta in humans, but the drug has been shown to cross the placenta in animals. In animals, fetal artery esmolol concentrations were about 10% of maternal concentrations at the completion of infusion. It also is not known whether esmolol and/or ASL 8123 are distributed into milk. Following IV administration, esmolol is rapidly and widely distributed. The apparent volumes of distribution of esmolol and its de-esterifed metabolite (ASL 8123) in healthy adults are approximately 3.4 and 0.41 l/kg, respectively, following iv administration. In healthy adults, the volumes of distribution of esmolol in the central compartment and at steady state are approximately 0.87 and 1.2 l/kg, respectively, following IV administration. The apparent volume of distribution appears to be decreased in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery and increased in patients with renal impairment undergoing peritoneal dialysis and in patients with liver cirrhosis. Following IV administration in rats, esmolol is ditributed into liver and kidneys, but only minimally into CSF, spleen, or testes. In vitro, esmolol is approximately 55% bound to plasma proteins, mainly albumin and alpha-1-acid glycoprotein. Protein binding of esmolol to alpha-1-acid glycoprotein does not appear to be concentration dependent at esmolol concentrations of 3-110 ug/ml. In vitro, ASL 8123 is approximately 10% bound to plasma proteins. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for ESMOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Esmolol is rapidly and extensively metabolized via esterases (probably arylesterase), principally in the cytosol of erythrocytes. Metabolism of the drug also may occur in highly perfused tissues that contain esterases (eg, liver, kidneys). Hydrolysis of the methyl ester moiety results in formation of the de-esterified (free acid) metabolite, 4-(2-hydroxy-3-((1-methylethyl)amino) propoxy)benzenepropanoic acid (ASL 8123), and methanol. Esmolol does not appear to be susceptible to hydrolysis via serum cholinesterase (pseudocholinesterase), acetylcholinesterase, or carbonic anhydrase. It is estimated that about 83% of an esmolol dose is metabolized to ASL 8123. ASL 8123 has a low affinity for beta-adrenergic receptors, exhibiting only minimal (about 1,000- to 1,500-fold less potent than esmolol) beta-blocking activity in animals and no appreciable blockade in humans. Unlike esmolol, ASL 8123 is eliminated principally by the kidneys, and the elimination half-life of the metabolite may be increased up to tenfold in patients with renal impairment; however, such accumulation is not thought to be clinically important since ASL 8123 has only minimal beta-blocking activity. The amount of methanol formed during hydrolysis of the drug does not appear to be clinically important. Following IV infusion of esmolol hydrochloride doses of 300 ug/kg per minute for up to l6 hours of 150 ug/kg per minute for 24 hours, blood methanol concentrations ranged from 2.8-5.9 or 2.9-13.2 ug/ml, respectively, being less than 2% of those usually associated with methanol toxicity. Biological Half-Life Following IV infusion in adults, the half life of esmolol averages about 2 minutes in the initial distribution phase and about 9 minutes (range: 5-23 minutes) in the terminal elimination phase, although considerable interindividual variation in blood elimination half life exists. Free acid metabolite: approx 3.7 hr (increased up to tenfold in renal failure) |
||
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Interactions
When esmolol and a catecholamine-depleting drug (eg, reserpine) are administered concomitantly, the effects of the drugs may be additive. Concomitant administration of esmolol and morphine in healthy adults resulted in about a 50% increase in steady-state blood esmolol concentrations, although the pharmacokinetics of morphine were not affected. Esmolol may prolong the effects of succinylcholine, although the onset of neuromuscular blockade is not affected. Succinylcholine-induced neuromuscular blockade has been prolonged by about 60% during concomitant esmolol administration in some patients. ... In addition, the duration of neuromuscular blockade was not prolonged in other patients during concomitant therapy. Blood esmolol concentration may be increased slightly during concomitant warfarin therapy ... . For more Interactions (Complete) data for ESMOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Mice iv 93 mg/kg LD50 Rat iv 71 mg/kg LD50 Rabbit iv 40 mg/kg LD50 Dogs iv 32 mg/kg LD50 Mice iv 452 mg/kg /De-estrified metabolite (ASL 8123) of esmolol/ |
||
| References | |||
| Additional Infomation |
Esmolol Hydrochloride is the hydrochloride salt form of esmolol, a short and rapid-acting beta adrenergic antagonist belonging to the class II anti-arrhythmic drugs and devoid of intrinsic sympathomimetic activity. Esmolol hydrochloride competitively blocks beta-1 adrenergic receptors in cardiac muscle and reduces the contractility and cardiac rate of heart muscle, thereby decreasing cardiac output and myocardial oxygen demands. This agent also decreases sympathetic output centrally and blocks renin secretion. At higher doses, esmolol hydrochloride also blocks beta-2 receptors located in bronchial and vascular smooth muscle, thereby leading to smooth muscle relaxation.
See also: Esmolol (has active moiety). Mechanism of Action Esmolol selectively inhibits response to adrenergic stimuli by competitively blocking cardiac B1-adrenergic receptors, while having little effect on the B2-adrenergic receptors of bronchial and vascular smooth muscle. At high doses (e.g., greater than 300 ug/kg per minute), this selectivity of esmolol for B1-adrenergic receptors usually diminishes, and the drug will competitively inhibit B1-and B2-adrenergic receptors. By inhibiting myocardial beta1-adrenergic receptors, esmolol produces negative chronotropic and inotropic activity. Through its myocardial B1-adrenergic blocking action, esmolol decreases resting and exercise-induced heart rate, reflex orthostatic tachycardia, myocardial contractility, rate of left ventricular pressure rise (dp/dt), right ventricular contractility, and cardiac index. The decrease in myocardial contractility, arterial pressure, and heart rate produced by esmolol can lead to a reduction in myocardial oxygen consumption, which may account for the effectiveness of the drug in myocardial ischemia. Therapeutic Uses Adrenergic Beta-Antagonists Esmolol is used IV principally to provide rapid, temporary control of ventricular rate in patients with supraventricular tachyarrhythmias (SVT) (eg, atrial flutter and/or fibrillation, sinus tachycardia). Esmolol may be preferred to longer-acting B-adrenergic blocking agents for the short-term control of ventricular rate in patients with SVT because of the drug's rapid onset and short duration of effects, ... . Esmolol is indicated for rapid and short-term control of ventricular rate in patients with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter in perioperative, postoperative, or other emergency situations. It is also indicated in noncompensatory sinus tachycardia judged by the physician to need intervention. (Esmolol is used for control of heart rate in patients with myocardial ischemia. /NOT included in US product labeling/) It is not recommended for use in chronic situations where transfer to another agent is anticipated. /Included in US product labeling/ For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for ESMOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings Because of the risk of esmolol induced hypotension, blood pressure should be monitored closely during therapy with this drug, especially in patients with low pretreatment blood pressure (eg, systolic blood pressure less than 105 mm Hg). Hypotension can occur at any dose level with esmolol but usually is dose related, and doses exceeding 200 ug/kg per minute recommended by the manufacturer for the management of supraventricular tachyarrhythmias. Reversal of hypotension usually occurs within 30 minutes of discontinuing the drug or reducing the rate of IV infusion. ... Esmolol is contraindicated in patients with second- or third-degree atrioventricular blocks, sinus bradycardia, cardiogenic shock, or overt cardiac failure. Esmolol may mask signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia (eg, tachycardia, palpitation, blood pressure changes, tremor, feelings of anxiety, but not sweating or dizziness) and may potentiate insulin-induced hypoglycemia; therefore, the drug should be used with caution in patients with diabetes mellitus or hypoglycemia. Because of de-esterified metabolite (ASL 8123) of esmolol is eliminated mainly by the kidneys, ... the drug should be used with caution in patients with renal impairment, especially severe impairment. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for ESMOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| Molecular Formula |
C16H26CLNO4
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
331.83
|
|
| Exact Mass |
331.155
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 57.91; H, 7.90; Cl, 10.68; N, 4.22; O, 19.29
|
|
| CAS # |
81161-17-3
|
|
| Related CAS # |
Esmolol-d7 hydrochloride; 1346598-13-7
|
|
| PubChem CID |
104769
|
|
| Appearance |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| Density |
1.026
|
|
| Boiling Point |
430.2ºC at 760 mmHg
|
|
| Melting Point |
48-50ºC
|
|
| Flash Point |
214ºC
|
|
| LogP |
2.722
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
3
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
5
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
10
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
22
|
|
| Complexity |
288
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
Cl.O=C(CCC1C=CC(OCC(CNC(C)C)O)=CC=1)OC
|
|
| InChi Key |
GEKNCWBANDDJJL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C16H25NO4.ClH/c1-12(2)17-10-14(18)11-21-15-7-4-13(5-8-15)6-9-16(19)20-3;/h4-5,7-8,12,14,17-18H,6,9-11H2,1-3H3;1H
|
|
| Chemical Name |
methyl 3-[4-[2-hydroxy-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propoxy]phenyl]propanoate;hydrochloride
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.75 mg/mL (8.29 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 27.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.75 mg/mL (8.29 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 27.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.75 mg/mL (8.29 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 4: 100 mg/mL (301.36 mM) in PBS (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with ultrasonication. |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0136 mL | 15.0680 mL | 30.1359 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6027 mL | 3.0136 mL | 6.0272 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3014 mL | 1.5068 mL | 3.0136 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
Effect of Controlled Hypotension on Cerebral Oxygen Saturation
CTID: NCT02967029
Phase: Phase 4 Status: Completed
Date: 2021-09-01
--
A prospective, randomized, double blinded, crossover, two-treatment, two-sequence, short term pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and tolerability, single centre study to compare AOP200704 vs. Esmolol in healthy subjects.
CTID: null
Phase: Phase 2 Status: Completed
Date: 2011-02-04
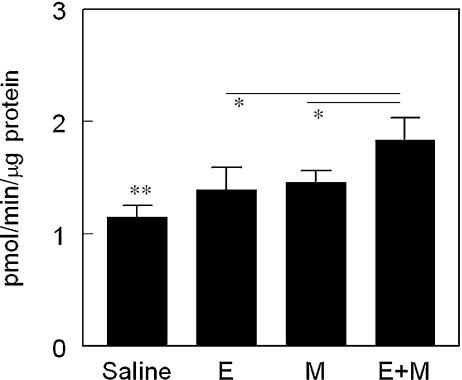
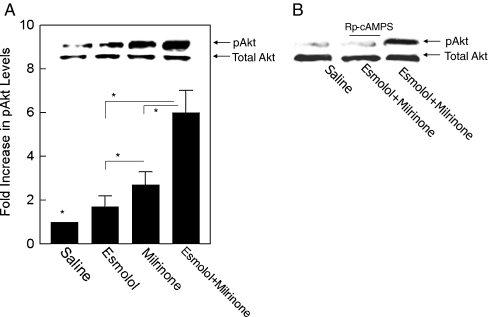
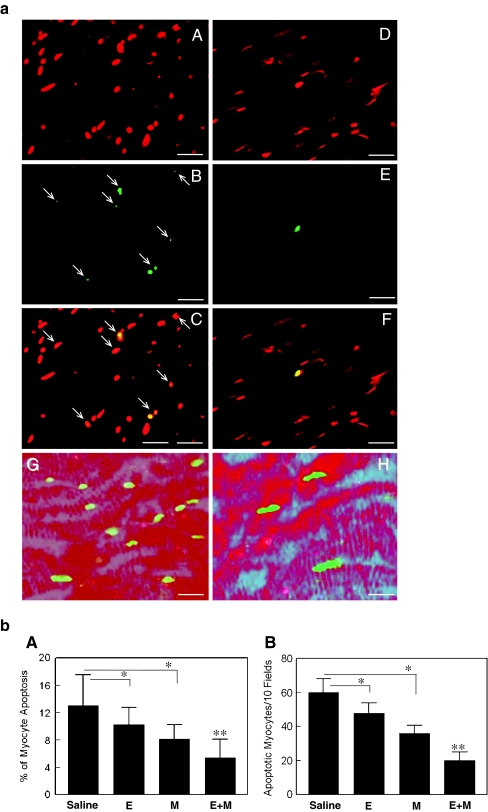
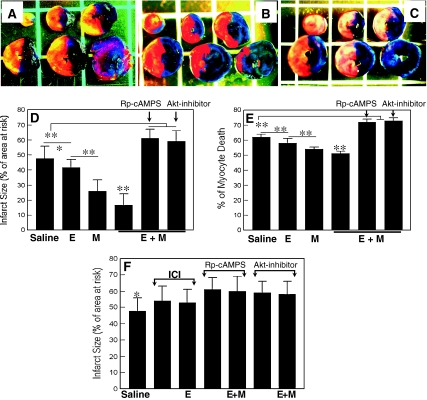 Panels A, B and C show representative cases of IS in the animals treated with saline (a), esmolol + milrinone (E + M) (b) and E + M in the presence of Rp-cAMPS (c). Infarcted tissue is indicated with yellow color.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2011 Jun; 25(3): 223–232. Panels A, B and C show representative cases of IS in the animals treated with saline (a), esmolol + milrinone (E + M) (b) and E + M in the presence of Rp-cAMPS (c). Infarcted tissue is indicated with yellow color.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2011 Jun; 25(3): 223–232. |
|---|
  |
 |