
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
Desloratadine (formerly SCH34117, NSC 675447; SCH-34117, NSC-675447; Clarinex; Neoclarityn; Descarboethoxyloratadine; Aerius) is the active metabolite of loratadine which is an anti-histamine drug of the tricyclic class used to treat allergies. Desloratadine is a potent antagonist of the human histamine H1 receptor with an IC50 of 51 nM.
| Targets |
Histamine H1 receptor ( IC50 = 51 nM )
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
|
||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Desloratadine administered orally for ten days to healthy volunteers as a 5 mg tablet once daily resulted in a mean Tmax of approximately 3 hours, a mean steady-state Cmax of 4 ng/ml, and a mean steady-state AUC of 56.9 ng\*hr/ml. A similar profile was observed using 10 ml of an oral solution containing 5 mg of desloratadine. Food was found not to affect desloratadine absorption. Approximately 87% of a 14C-desloratadine dose was equally recovered in urine and feces as metabolic products. Metabolism / Metabolites Desloratadine is metabolized to the active metabolite 3-hydroxydesloratadine, which is subsequently glucuronidated. Desloratadine is a known human metabolite of Rupatadine and loratadine. Route of Elimination: Desloratadine (a major metabolite of loratadine) is extensively metabolized to 3-hydroxydesloratadine, an active metabolite, which is subsequently glucuronidated. Approximately 87% of a 14C-desloratadine dose was equally recovered in urine and feces. Half Life: 50 hours Biological Half-Life Desloratadine has a mean plasma elimination half-life of approximately 27 hours. |
||
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Toxicity Summary
Like other H1-blockers, Desloratadine competes with free histamine for binding at H1-receptors in the GI tract, uterus, large blood vessels, and bronchial smooth muscle. This blocks the action of endogenous histamine, which subsequently leads to temporary relief of the negative symptoms (eg. nasal congestion, watery eyes) brought on by histamine. Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Because of its expected low milk levels and lack of sedation and anticholinergic effects, maternal use of desloratadine is unlikely to affect a breastfed infant or milk production. Desloratadine might have a negative effect on lactation in combination with a sympathomimetic agent such as pseudoephedrine. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Antihistamines in relatively high doses given by injection can decrease basal serum prolactin in nonlactating women and in early postpartum women. However, suckling-induced prolactin secretion is not affected by antihistamine pretreatment of postpartum mothers. Whether lower oral doses of antihistamines have the same effect on serum prolactin or whether the effects on prolactin have any consequences on breastfeeding success have not been studied. The prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed Protein Binding Desloratadine is bound approximately 82 to 87% to plasma proteins, while its active metabolite, 3-hydroxydesloratadine, is bound approximately 85 to 89%. |
||
| References | |||
| Additional Infomation |
Desloratadine is loratadine in which the ethoxycarbonyl group attached to the piperidine ring is replaced by hydrogen. The major metabolite of loratidine, desloratadine is an antihistamine which is used for the symptomatic relief of allergic conditions including rhinitis and chronic urticaria. It does not readily enter the central nervous system, so does not cause drowsiness. It has a role as a H1-receptor antagonist, an anti-allergic agent, a cholinergic antagonist and a drug metabolite.
Desloratadine is a second generation, tricyclic antihistamine that which has a selective and peripheral H1-antagonist action. It is the active descarboethoxy metabolite of loratidine (a second generation histamine). Desloratidine has a long-lasting effect and does not cause drowsiness because it does not readily enter the central nervous system. Desloratadine is a Histamine-1 Receptor Antagonist. The mechanism of action of desloratadine is as a Histamine H1 Receptor Antagonist. Desloratadine has been reported in Bos taurus with data available. Desloratadine is a long-acting piperidine derivate with selective H1 antihistaminergic and non-sedating properties. Desloratadine diminishes the typical histaminergic effects on H1-receptors in bronchial smooth muscle, capillaries and gastrointestinal smooth muscle, including vasodilation, bronchoconstriction, increased vascular permeability, pain, itching and spasmodic contractions of gastrointestinal smooth muscle. Desloratadine is used to provide symptomatic relieve of allergic symptoms. Desloratadine is a second generation, tricyclic antihistamine that which has a selective and peripheral H1-antagonist action. It is the active descarboethoxy metabolite of loratidine (a second generation histamine). Desloratidine has a long-lasting effect and does not cause drowsiness because it does not readily enter the central nervous system. See also: Desloratadine; pseudoephedrine sulfate (component of). Drug Indication For the relief of symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis, perennial (non-seasonal) allergic rhinitis. Desloratidine is also used for the sympomatic treatment of pruritus and urticaria (hives) associated with chronic idiopathic urticaria. FDA Label Neoclarityn is indicated for the relief of symptoms associated with: allergic rhinitisurticaria Aerius is indicated for the relief of symptoms associated with: allergic rhinitis; urticaria. Azomyr is indicated for the relief of symptoms associated with: allergic rhinitis (see section 5. 1)urticaria (see section 5. 1) Treatment of allergic rhinitis and urticaria. Desloratadine ratiopharm is indicated in adults for the relief of symptoms associated with: allergic rhinitischronic idiopathic urticaria as initially diagnosed by a physician Desloratadine Teva is indicated for the relief of symptoms associated with: allergic rhinitis; urticaria. Dasselta is indicated for the relief of symptoms associated with: allergic rhinitis; urticaria. Aerius is indicated for the relief of symptoms associated with: - allergic rhinitis (see section 5. 1)- urticaria (see section 5. 1) Opulis is indicated for the relief of symptoms associated with: - allergic rhinitis (see section 5. 1)- urticaria (see section 5. 1) Mechanism of Action Like other H1-blockers, Desloratadine competes with free histamine for binding at H1-receptors in the GI tract, uterus, large blood vessels, and bronchial smooth muscle. This blocks the action of endogenous histamine, which subsequently leads to temporary relief of the negative symptoms (eg. nasal congestion, watery eyes) brought on by histamine. Pharmacodynamics Desloratadine is a long-acting second-generation H1-receptor antagonist which has a selective and peripheral H1-antagonist action. Histamine is a chemical that causes many of the signs that are part of allergic reactions, such as the swelling of tissues. Histamine is released from histamine-storing cells (mast cells) and attaches to other cells that have receptors for histamine. The attachment of the histamine to the receptors causes the cell to be "activated," releasing other chemicals which produce the effects that we associate with allergies. Desloratadine blocks one type of receptor for histamine (the H1 receptor) and thus prevents activation of cells by histamine. Unlike most other antihistamines, Desloratadine does not enter the brain from the blood and, therefore, does not cause drowsiness. |
| Molecular Formula |
C19H19CLN2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
310.82
|
|
| Exact Mass |
310.123
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 73.42; H, 6.16; Cl, 11.41; N, 9.01
|
|
| CAS # |
100643-71-8
|
|
| Related CAS # |
Desloratadine-d4; 381727-29-3; Desloratadine-d9; 1795024-82-6; Desloratadine-3,3,5,5-d4; 2713301-38-1; Desloratadine-d5; 1020719-34-9
|
|
| PubChem CID |
124087
|
|
| Appearance |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| Density |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| Boiling Point |
467.9±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| Melting Point |
150-151°C
|
|
| Flash Point |
236.8±28.7 °C
|
|
| Vapour Pressure |
0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| Index of Refraction |
1.626
|
|
| LogP |
6.77
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
1
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
2
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
0
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
22
|
|
| Complexity |
425
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
ClC1C([H])=C([H])C2=C(C=1[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C1C([H])=C([H])C([H])=NC=1/C/2=C1\C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N([H])C([H])([H])C\1([H])[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
JAUOIFJMECXRGI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C19H19ClN2/c20-16-5-6-17-15(12-16)4-3-14-2-1-9-22-19(14)18(17)13-7-10-21-11-8-13/h1-2,5-6,9,12,21H,3-4,7-8,10-11H2
|
|
| Chemical Name |
13-chloro-2-piperidin-4-ylidene-4-azatricyclo[9.4.0.03,8]pentadeca-1(11),3(8),4,6,12,14-hexaene
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.04 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.04 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.04 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 4: 30% Propylene glycol , 5% Tween 80 , 65% D5W: 30 mg/mL |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2173 mL | 16.0865 mL | 32.1730 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6435 mL | 3.2173 mL | 6.4346 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3217 mL | 1.6086 mL | 3.2173 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
Efficacy and Safety of Desloratadine vs. Fexofenadine 180 mg. vs. Placebo for Treating Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis (SAR)(Study P04053)(COMPLETED)
CTID: NCT00783211
Phase: Phase 4 Status: Completed
Date: 2024-08-15
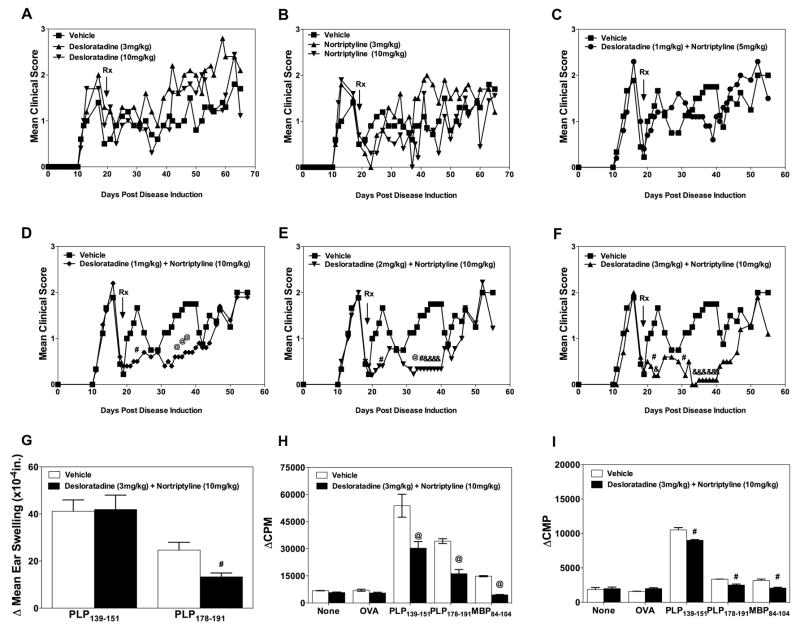
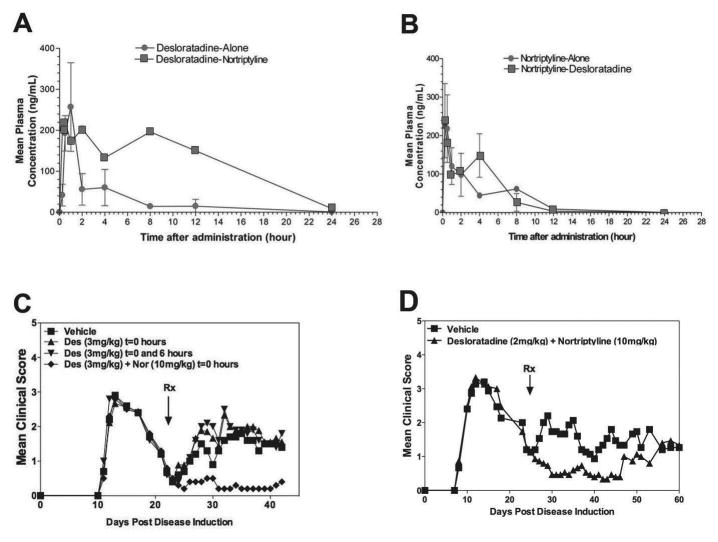
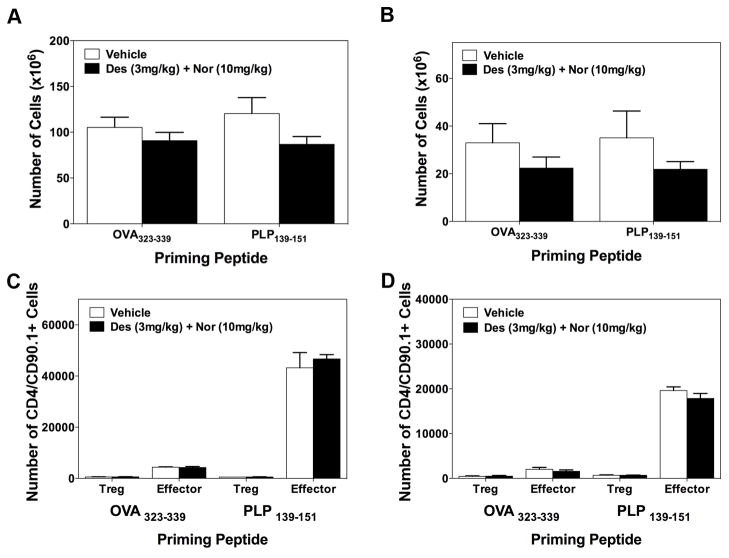
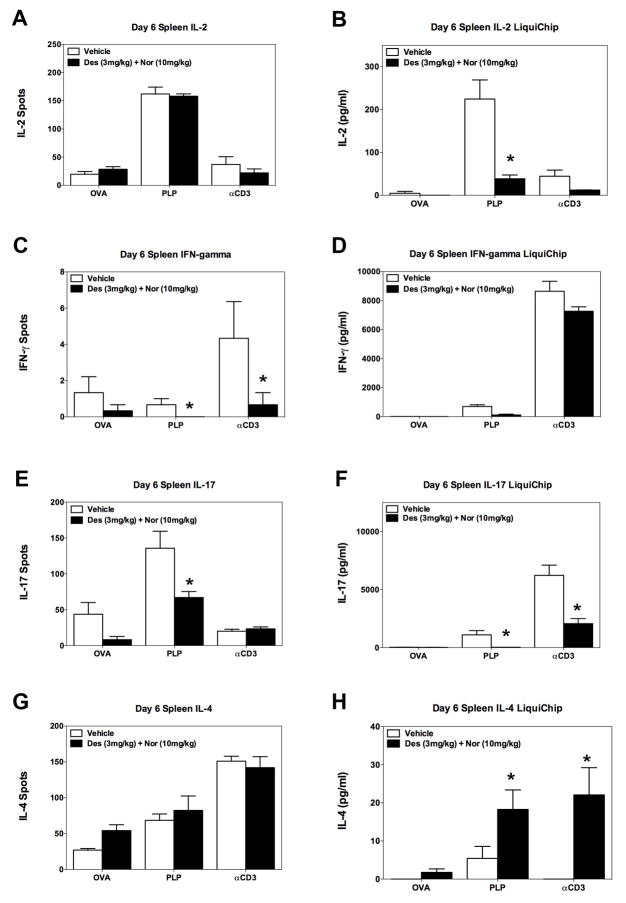
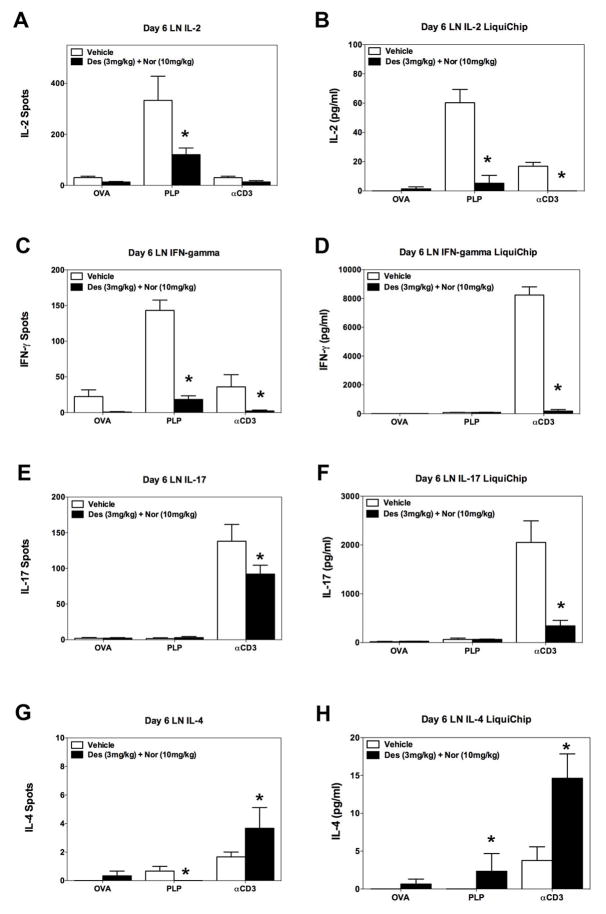
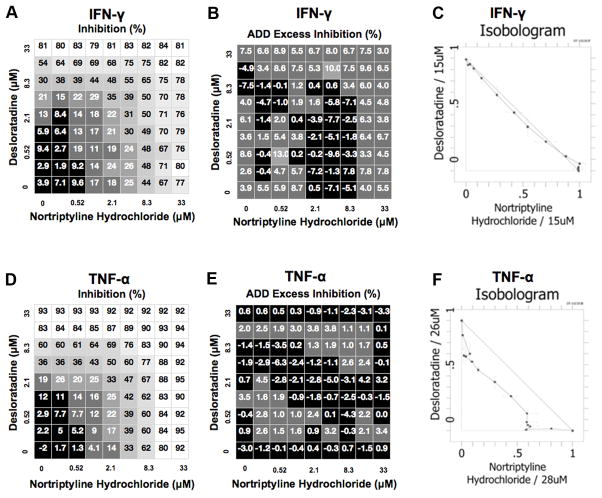 Identification of CRx-153, i.e., the combination of desloratadine and nortriptyline activity.Cell Immunol. 2011; 270(2): 237–250. Identification of CRx-153, i.e., the combination of desloratadine and nortriptyline activity.Cell Immunol. 2011; 270(2): 237–250. |
|---|
 |
 |
 |
|---|
 |
 |