
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
Purity: ≥98%
AGK2 is a novel, potent, and selective inhibitor of SIRT2 (sirtuin 2, histone deacetylase) with potential anti-inflammatory activity. As a cell-permeable epigenetic modifier, AGK2 inhibits SIRT2 with an IC50 value of 3.5 μM and showed little effects on SIRT1 and 3 at concentrations of over 40 μM. AGK 2 increased the level of acetylated tubulin heterodimers in bovine brain. In primary rat astrocytes, AGK-2 (35 μM) significantly inhibited astrocyte viability and proliferation and also inhibited astrocyte activation induced by beta amyloid 1-42 (Aβ 1-42).
| Targets |
SIRT2 (IC50 of 3.5 μM); SIRT1/3 (IC50s = 30 and 91 μM)
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
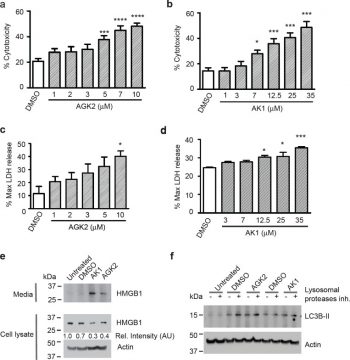
Cell growth is strongly inhibited by AGK2 in a dose-dependent manner. Additionally, in a dose-dependent way, AGK2 strongly suppresses cell growth without causing cytotoxicity at low concentrations. After being treated with AGK2 (5 μM) for 12 days, the cells' ability to form colonies in soft agar decreases significantly, reaching 46% of the control cells. A dose-dependent reduction in CDK4 or CDK6 and cyclin D1 levels is observed following AGK2 treatment, according to Western blot analysis. Furthermore, p53 protein expression is inhibited by AGK2[2]. PAR signals are significantly increased when 10 μM AGK2 is applied to microglial BV2 cells. When microglial BV2 cells are treated with 10 μM AGK2, there is a notable reduction in intracellular ATP and a notable elevation in both late-stage apoptosis and necrosis of the cells [3].
It was demonstrated that the Sirt1 and Sirt2 inhibitors EX527 and AGK2 suppressed cell growth and caused G1 phase arrest by inhibiting the expression of Cdk6 and/or Cdk4. An agar colony formation assay revealed that EX527 and AGK2 decreased colony formation in soft agar. Furthermore, EX527 and AGK2 pretreatment inhibited the expression of HSF1 and HSP27 and induced HSF1 ubiquitination. Sirt1 overexpression increased HSF1 expression and/or stabilization and induced cell migration in a scratch assay. Overall, these results indicate that EX527 and AGK2 suppress cell growth and migration by inhibiting HSF1 protein stability. [2] Sirtuin 2 (SIRT2), a sirtuin family protein, is a tubulin deacetylase. Recent studies have indicated that SIRT2 plays a key role in programmed necrosis, and the SIRT2 inhibitor AGK2 can decrease the cell death both in a cellular model of Parkinson's disease and in an animal model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. However, there has been little information regarding the role of SIRT2 in microglial survival and functions, which play critical roles in multiple neurological disorders. Our current study found that AGK2 at 10 μM - a widely used AGK2 concentration - can induce both late-stage apoptosis and necrosis, as well as a decrease in the intracellular ATP levels of microglial BV2 cells. Our study also showed that both the AGK2-induced cell death and the AGK2-induced ATP decline are mediated by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) activation. Collectively, our study has provided the first evidence suggesting a significant role of SIRT2 in the basal survival of microglia, as well as a mechanism accounting for the effects of SIRT2 on intracellular ATP levels. [3] Cytotoxic effect of the Sirt1/2 inhibitors EX527 and AGK2 on cell proliferation [2] To examine the effect of Sirt1/2 inhibitors, EX527 and AGK2, on the growth of HeLa cells, we performed MTT assays. The cells were exposed to increasing concentrations of nicotinamide (NAM), EX527 and AGK2 for 24 h, and the cell viability was monitored (Fig. 1). EX527 and AGK2 significantly inhibited cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. EX527 at concentrations of 50 and 100 μM resulted in cell growth inhibition of 68 and 54%, respectively, at 24 h (Fig. 1B). Similarly, AGK2 also significantly inhibited cell growth in a dose-dependent manner without inducing cytotoxicity at low doses (≥1 μM; Fig. 1C). However, these cells exhibited no significant decrease in cell proliferation after NAM treatment for 24 h (survival rate >93%; Fig. 1A). EX527 and AGK2 induce G1 cell cycle arrest in HeLa cells [2] It was hypothesized that EX527 or AGK2 induce alterations in cell cycle regulation. Using flow cytometry, we analyzed the effect of EX527 or AGK2 on cell cycle progression. As shown in Fig. 2A–C, EX527 and AGK2 induced cell cycle arrest at the G1 phase. Western blot analysis showed that the levels of CDK4 or CDK6 and cyclin D1 were decreased after EX527 or AGK2 treatment in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, EX527 and AGK2 inhibited the expression of p53 protein (Fig. 2D). These results suggest that the effects of EX527 and AGK2 on G1 cell cycle progression were associated with the inhibition of cell growth. To determine whether EX527 and AGK2 induce death in HeLa cells, we quantified apoptosis by flow cytometry using the Annexin V-FITC/PI double staining assay. As shown in Fig. 2E–H, after 24 h of incubation, there was no significant decrease in living cells upon EX527 treatment; 93% of the control cells were alive, while only 3.3% of the EX527-treated cells underwent cell death. Similarly, apoptotic cells were not markedly observed after AGK2 treatment (Fig. 2G). Consistent with this observation, caspase-3 and PARP were not cleaved in cells treated with EX527 or AGK2 compared with the control (Fig. 2H). In addition, key autophagy proteins, LC3B and beclin-1, were not activated after treatment with EX527 or AGK2 (Fig. 2I). EX527 and AGK2 inhibit the HSF1/HSP27 pathway [2] A previous study suggested that Sirt1 deacetylates HSF1 and activates heat shock proteins (HSPs) under a heat stress condition (21). We investigated the possibility that Sirt1 and Sirt2 inhibition by EX527 and AGK2 may be responsible for HSF1 inactivation. Therefore, we subjected EX527- or AGK2-treated cells to heat shock (1 h at 42°C) and analyzed the expression of endogenous Sirt1, Sirt2 and HSF1, as well as HSPs such as Hsp27 and Hsp70. EX527 or AGK2 treatment decreased the expression of HSF1 and HSP27 in non-stress or heat stress condition (Fig. 3A and B), which indicated that Sirt1 and Sirt2 are required for the regulation of the HSF1 pathway. Furthermore, EX527 and AGK2 also decreased HSF1 phosphorylation after heat shock. However, NAM decreased HSF1 expression/phosphorylation and HSP27 expression under heat shock conditions (Fig. 3C). To determine whether EX527 and AGK2 influence HSF1 transcription in HeLa cells, RT-PCR was performed using specific oligonucleotides against the HSF1 gene. As shown in Fig. 3D, the HSF1 mRNA level was not altered by EX527 or AGK2. To verify the significance of the regulation of HSF1 by Sirt1, cells were transfected with or without Sirt1, exposed to a 42°C heat shock for 1 h, allowed to recover at 37°C for 24 h, and analyzed for HSF1 expression. As expected, the heat shock induced HSP27 expression, which increased with recovery time. Importantly, at the same time-points, we observed that the cells overexpressing Sirt1 showed increased HSF1 expression compared with the heat shock-treated cells (Fig. 3E). Sirt1/Sirt2 inhibition is linked to increased HSF1 ubiquitination [2] To determine whether HSF1 deacetylation by Sirt1 is involved in HSF1 ubiquitination/stabilization, we examined the acetylation and ubiquitination status of HSF1 after EX527 and AGK2 treatment. HeLa cells were treated with or without EX527 and AGK2 and exposed to a 42°C heat shock for 1 h. Then, the samples were immunoprecipitated with an anti-HSF1 antibody and analyzed for HSF1 acetylation. Acetylated HSF1 was detected in the untreated cells but was decreased in the cells exposed to heat shock stress conditions. However, acetylated HSF1 levels were induced in the EX527- or AGK2-treated cells before heat shock (Fig. 4A). In addition, EX527 and AGK2 induced HSF1 ubiquitination (Fig. 4B). EX527 and AGK2 inhibit cell migration [2] To investigate whether Sirt1/HSF1 modulate cell motility, we treated HeLa cells with EX527 and AGK2 for 36 h and performed a wound-healing experiment. EX527- or AGK2-treated cells showed reduced migration ability when compared with the control or heat shock-treated cells (Fig. 5A). |
||
| ln Vivo |
In comparison to vehicle control, AGK2 significantly lowers mortality and cytokine levels in blood (TNF-α: 298.3±24.6 vs 26.8±2.8 pg/mL, p=0.0034; IL-6: 633.4±82.8 vs 232.6±133.0 pg/mL, p=0.0344) and peritoneal fluid (IL-6: 704.8±67.7 vs 391.4±98.5 pg/mL, p=0.033). Additionally, AGK2 inhibits the generation of IL-6 and TNF-α in cultured splenocytes (IL-6: 73.1±4.2 vs 49.6±3.0 pg/mL; p=0.0051; TNF-α: 68.1 ±6.4 vs 23.9±2.8 pg/mL, p=0.0009)[4].
AGK2 significantly reduced mortality and decreased levels of cytokines in blood (TNF-α: 298.3±24.6 vs 26.8±2.8 pg/ml, p=0.0034; IL-6: 633.4±82.8 vs 232.6±133.0 pg/ml, p=0.0344) and peritoneal fluid (IL-6: 704.8±67.7 vs 391.4±98.5 pg/ml, p=0.033) compared to vehicle control. Also, AGK2 suppressed the TNF-α and IL-6 production in the cultured splenocytes (TNF-α: 68.1±6.4 vs 23.9±2.8 pg/ml, p=0.0009; IL-6: 73.1±4.2 vs 49.6±3.0 pg/ml; p=0.0051). The TEG data showed that the mice subjected to CLP displayed prolonged fibrin formation and fibrin cross-linkage time, slower clot formation, decreased platelet function, and clot rigidity. AGK2 treatment was associated with dramatic improvements in fibrin cross-linkage and clot formation times, without a significant impact on the clot initiation parameters or platelet function. Additionally, AGK2 significantly attenuated the bone marrow atrophy (58.3±6.5 vs 30.0±8.2%, p=0.0262).[4] AGK2 Significantly Improves Survival in a Mouse Model of CLP-Induced Septic Shock [4] C57BL/6J mice were intraperitoneally given either AGK2 (82 mg/kg) in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or DMSO alone, and 2 h later subjected to CLP. All mice from the vehicle DMSO alone group died in less than 3 days whereas the majority (55.6%) of mice treated with AGK2 survived for the duration of the 240 hours following CLP (55.6% vs 0% survival, p<0.0001; Fig. 1). AGK2 Decreases Levels of Cytokine in Blood and Peritoneal Cavity [4] Blood samples and peritoneal fluid were obtained after CLP. Levels of TNF-α and IL-6 were determined by ELISA. Normally no TNF-α and IL-6 were detected in blood and peritoneal fluid. CLP induced sepsis significantly increased the levels of the cytokines in circulation and within the peritoneal fluid. Mice treated with AGK2 has significantly decreased the levels of cytokines in circulation (TNF-α: 298.3±24.6 vs 26.8±2.8 pg/ml, p=0.0034; IL-6: 633.4±82.8 vs 232.6±133.0 pg/ml, p=0.0344; Figs. 2, 3) and within peritoneal fluid compared to DMSO vehicle (IL-6: 704.8±67.7 vs 391.4±98.5 pg/ml, p=0.033; Fig. 3). AGK2 Decreases Levels of Cytokine in Cultured Splenocyte Supernatant [4] Using ELISA, levels of TNF-α and IL-6 were measured in the supernatant of the cultured mouse primary splenocytes treated with LPS in the presence or absence of AGK2 for 6 hours. Sham group of normal primary splenocytes (without any treatment) served as a control, and revealed expectedly low concentrations of TNF-α and IL-6. LPS stimulated an increase of TNF-α and IL-6 in the supernatant of the cells. AGK2 treatment significantly decreased the LPS-induced TNF-α and IL-6 production (TNF-α: 23.9±2.8 vs 68.1±6.4 pg/ml, p=0.0009; IL-6: 49.6±3.0 vs 73.1±4.2 pg/ml; p=0.0051; Fig. 4). Effect of AGK2 Treatment on Thrombelastograph Parameters in the Septic Shock Model [4] Whole blood samples were collected 48 h after CLP, and subjected to the TEG® 5000. Thrombelastograph® Hemostasis Analyzer System for analysis. As shown in Fig. (5), the DMSO treated mice displayed prolonged K, slower Angle, and decreased MA compared to sham animals (Fig. 5A). However, selective inhibition of SIRT2 with AGK2 significantly improved K (17.0±3.5 vs 6.2±1.0 min, p=0.0392) and Angle (10.3±2.5 vs 32.3±3.8 degree, p=0.0012; Fig. 5B), without a significant effect on the clot initiation parameters (SP: 8.1±1.1 vs 7.0±0.9 min; R: 11.5±2.2 vs 8.8±1.0 min) and MA (28.7±6.0 vs 47.5±4.3 mm, p=0.0514; Fig. 5C). AGK2 Reduces Atrophy of Bone Marrow in the Septic Shock Model [4] Bone samples of femur and tibia were collected 48 h after CLP, processed and stained with H&E. Normal cell composition and histology of bone marrow were noted in the sham group. The ratio of bone marrow cells to veins was increased 48 h after CLP in the DMSO vehicle group, with bone marrow cell depletion and venous dilation (0±0 vs 58.3±6.5%). AGK2 treatment significantly attenuated the bone marrow depletion (Fig. 6A, magnification 40x) and atrophy (Fig. 6B) (58.3±6.5 vs 30.0±8.2%, p=0.0262). |
||
| Enzyme Assay |
FACS-based Annexin V/7-AAD staining assay [3]
The FACS assay was performed to measure the degrees of both apoptosis and necrosis using ApoScreen Annexin V kit according to the manufacturer's protocol. Briefly, BV2 cells were digested by 0.1% trypsin and resuspended in cold binding buffer (10 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 140 mM NaCl, 2.5 mM CaCl2, 0.1% BSA) at concentrations between 1 × 106 and 1 × 107 cells/ml. 10 μl of labeled Annexin V was added into 100 μl of the cell suspension. After 15-min incubation on ice, 380 μl binding buffer and 10 μl 7-AAD solution were added into the cell suspension. The number of stained cells was assessed by a BD flow cytometer (FACSAriaII). Extracellular and intracellular lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) assays [3] Extracellular LDH assay was conducted to determine cell death, as described previously. In brief, 100 μl of extracellular media was mixed with 150 μl potassium phosphate buffer (500 mM, pH 7.5) containing 1.5 mM NADH and 7.5 mM sodium pyruvate. Subsequently changes of the A340nm of the samples were monitored over 90 s. Intracellular LDH assays were also conducted to determine cell survival, as described previously. Briefly, cells were lysed for 20 min in lysing buffer containing 0.04% Triton X-100, 2 mM HEPES, 0.2 mM dithiothreitol, 0.01% bovine serum albumin, and 0.1% phenol red (pH 7.5). Fifty microliter cell lysates were mixed with 150 μl potassium phosphate buffer (500 mM, pH 7.5) containing 1.5 mM NADH and 7.5 mM sodium pyruvate. Subsequently changes of the A340nm of the samples were monitored over 90 s. Percentage of cell survival was calculated by normalizing the LDH activity of the lysates of a sample to the LDH activity of the lysates of controls. Immunostaining of poly (ADP-ribose) (PAR) [3] Cell cultures were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 min, followed by one wash in PBS, and then the cell were treated with 0.1% Triton-X100 (dilute in PBS) for 20 min at RT. The cells were incubated in 10% goat serum for 1 h at RT and then incubated with a mouse anti-PAR antibody (1:200 dilution) in PBS containing 1% goat serum overnight at 4 °C. After three washes with PBS, the cells were incubated with Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-mouse secondary antibody diluted at 1:300 containing 1% goat serum for 1 h at RT. After counter-staining of the cells with DAPI, the fluorescence images of the cell cultures were photographed under a Leica confocal fluorescence microscope. ATP assay [3] ATP levels were determined by using Roche ATP Bioluminescence Assay Kit (HS II). In brief, cells were lysed with the Cell Lysis Reagent, and 50 μl of the lysates was mixed with 150 μl of the Luciferase Reagent. Subsequently the luminescence of the samples was detected using a plate reader. BCA assay was used to determine the protein concentrations of the samples. The ATP concentrations of the sample were calculated using an ATP standard, and normalized against the protein of the samples. |
||
| Cell Assay |
Cell proliferation assay [2]
Cell proliferation was assessed using a 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazolyl-2)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. The cells were seeded in a 96-well plate at a density of 1×104 cells/well. The next day, the cells were washed twice with PBS, and 500 μg/ml MTT was added to the wells. The MTT solution was removed after 4 h of incubation at 37°C. A mixture of 0.01 M glycine and DMSO as added to each well. The absorbance was measured at 540 nm with a Benchmark microplate reader. Immunoprecipitation [2] Total cell extracts were incubated with anti-HSF1 in NP-40 lysis buffer (0.5% NP-40, 0.5% Triton X-100, 150 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris HCl pH 7.4, 1 mM EDTA, 50 mM NaF, 1 mM B-glycerophosphate, 1 mM sodium orthovanadate, 0.5 μg/ml leupeptin, 1 μg/ml pepstatin, 0.2 mM PMSF). The extract mixtures were incubated at 4°C overnight with rotation before the addition of 20 μl of protein A/G beads for 3 h at 4°C. The beads were washed three times with the same buffer and suspended in 2X SDS sample buffer. The samples were resolved in SDS-polyacrylamide gels for western blot analysis with specific antibodies as indicated. Western blot analysis [2] Cell lysates (50 μg) were placed in lysis buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 1% NP-40, 0.5% Na-deoxycholate, 0.1% SDS, and a protease inhibitor cocktail containing 1 μg/ml aprotinin and leupeptin) and separated by 12% SDS-PAGE. The resolved proteins were transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, UK) according to standard procedures. The membrane was blocked in 5% non-fat dry milk for 3 h and incubated with the primary antibodies for 3 h at room temperature (RT). After incubation with a specific peroxidase-coupled secondary antibody for 1 h, the blotted bands were detected using an enhanced chemiluminescence detection kit. Wound-scratch assays [2] Cells were allowed to grow in a culture dish overnight, and a scratch ~3-mm wide was created in the monolayer using a pipette tip. After washing twice with PBS, the cells were treated with or without the Sirt1/Sirt2 inhibitors, and images were captured after 12 or 36 h. Cells were imaged in 5 random microscopic fields per well using an Olympus IX2-SLP inverted microscope at a ×100 magnification. Annexin V-FITC/PI double staining [2] The cells were harvested and fixed with 70% ethanol for 1 h at 4°C for cell cycle analysis. After washing with cold PBS, the cells were incubated with DNase-free RNase and propidium iodide (PI) at 37°C for 30 min. The specific binding of Annexin V-FITC/PI was performed by incubating the cells for 15 min at RT in a binding buffer (10 mM HEPES, 140 mM NaCl, 2.5 mM CaCl2, pH 7.4) containing saturated concentrations of Annexin V-FITC and PI. After incubation, the cells were pelleted and analyzed in a FACScan analyzer. Flow cytometry and cell cycle analysis [2] The cell cycle distribution was analyzed by flow cytometry. Briefly, 1×106 cells were harvested and washed in PBS, and then fixed in 70% alcohol for 30 min at 4°C. After washing three times in cold PBS, the cells were resuspended in 1 ml of PBS solution containing 50 μl of 1 mg/ml PI and 1 unit of DNase-free RNase for 30 min at 37°C. The samples were then analyzed for their DNA content by FACS. Soft agar colony formation assay [2] Briefly, the cells (8×103 cells/well) were exposed to different concentrations of EX527 or AGK2 in 1 ml of 0.3% basal medium Eagle's agar containing 10% FBS. The cultures were maintained at 37°C in a 5% CO2 incubator for 10–15 days, and the cell colonies were scored using an Olympus IX2-SLP inverted microscope. |
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References |
|
||
| Additional Infomation |
2-cyano-3-[5-(2,5-dichlorophenyl)-2-furanyl]-N-(5-quinolinyl)-2-propenamide is a member of quinolines.
A series of 114 SIRT inhibitor candidates was assembled using 'click chemistry', by reacting two alkynes bearing 2-anilinobenzamide pharmacophore with 57 azide building blocks in the presence of Cu(I) catalyst. Screening identified two SIRT2-selective inhibitors, which were more SIRT2-selective than AGK2, a known SIRT2 inhibitor. These findings will be useful for further development of SIRT2-selective inhibitors.[1] As described above, our findings suggest that the expression/activation of HSF1/HSP27 depend at least in part on the Sirt1/Sirt2 pathway. This finding prompted us to investigate whether the Sirt1/2-regulated HSF1/HSP27 pathway may affect motility such as migration. We demonstrated that the inhibition of Sirt1/2 by EX527 or AGK2 decreased cell motility in a scratch assay. Our data indicate that Sirt1 and HSF1/HSP27 play an important role in cell migration, as specifically demonstrated by the findings that overexpression of Sirt1 and HSF1 increased cell migration, whereas downregulation of HSP27 by siRNA decreased Sirt1- and HSF1-induced cell migration. The direct causal association between the HSF1/HSP27 pathway and Sirt1/2 was apparent by the finding that modulation of Sirt1/2 activity by EX527 and AGK2 strongly affected HSF1 expression/activation and modulated cell migration. The molecular basis for the activity of HSF1/HSP27 in affecting cell motility and in modulating the response to Sirt1 and Sirt2 still needs to be clarified. It should also be considered that, although Sirt1 is involved in HSF1 deacetylation, additional deacetylation sites by Sirt2 on HSF1 activation are present, which could be differentially regulated by Sirt1 and Sirt2 and may modulate other cellular functions in these cells. In conclusion, the inhibition of Sirt1/2 by EX527 or AGK2 inhibited cell growth and colony formation. Our study is the first to demonstrate that blocking Sirt1 and Sirt2 can induce HSF1 ubiquitination and degradation in vitro, suggesting that Sirt1/2 is involved in the activation of heat shock response signaling pathways. Furthermore, we observed a consistent reduction in cell migration after EX527 and AGK2 treatment. Our results suggest that Sirt1 and Sirt2 regulate cell migration via HSF1/Hsp27-mediated signaling. [2] Our study has shown that AGK2 can induce a decrease in the intracellular ATP levels of the microglia, which is consistent with our previous finding that both pharmacological and genetic inhibition of SIRT2 can lead to a decrease in the intracellular ATP levels of PC12 cells. Collectively, these findings have suggested a key role of SIRT2 in cellular energy metabolism. Our current study has suggested that PARP mediates the AGK2-induced decrease in ATP levels, thus suggesting a mechanism accounting for the significant effects of SIRT2 on cellular energy metabolism. Future studies are warranted to further investigate the roles of SIRT2 in microglial survival under both resting and activated conditions of the cells. It is also warranted to determine if the detrimental effects of AGK2 on basal microglial survival produce beneficial or detrimental effects on tissue injury in such diseases as PD and brain ischemia.[3] Background: Seven isoforms of histone deacetylase Class III have been reported - Sirtuin (SIRT) 1-7. We recently demonstrated that EX-527, an inhibitor of SIRT1, reduces mortality in a mouse model of lethal-cecal-ligationand- puncture (CLP)-induced septic shock. Our present study was aimed at determining whether selective inhibition of SIRT2, with AGK2, would decrease animal death and attenuate the inflammatory response in a septic model. Methods: Experiment I: C57BL/6J mice were intraperitoneally given either AGK2 (82 mg/kg) in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or DMSO alone, and 2 h later subjected to CLP. Survival was monitored for 240 hours. Experiment II: mice treated the same way as Experiment I, were grouped into (i) DMSO vehicle, and (ii) AGK2, with sham mice (operating but without any treatment) serving as controls. Peritoneal fluid and peripheral blood were examined at 24 and 48 hours for cytokine production. Samples of blood at 48 h were also allocated to assess coagulability using Thrombelastography (TEG). Morphological changes of bone marrow were evaluated from long bones (femurs and tibias) with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. Bone marrow atrophy was quantified by a blinded pathologist. Experiment III: cytokines in supernatant of the cultured normal primary splenocytes were measured after the cells were stimulated by lipopolysaccharide and treated with or without AGK2 (10 µM) for 6 hours. Results: AGK2 significantly reduced mortality and decreased levels of cytokines in blood (TNF-α: 298.3±24.6 vs 26.8±2.8 pg/ml, p=0.0034; IL-6: 633.4±82.8 vs 232.6±133.0 pg/ml, p=0.0344) and peritoneal fluid (IL-6: 704.8±67.7 vs 391.4±98.5 pg/ml, p=0.033) compared to vehicle control. Also, AGK2 suppressed the TNF-α and IL-6 production in the cultured splenocytes (TNF-α: 68.1±6.4 vs 23.9±2.8 pg/ml, p=0.0009; IL-6: 73.1±4.2 vs 49.6±3.0 pg/ml; p=0.0051). The TEG data showed that the mice subjected to CLP displayed prolonged fibrin formation and fibrin cross-linkage time, slower clot formation, decreased platelet function, and clot rigidity. AGK2 treatment was associated with dramatic improvements in fibrin cross-linkage and clot formation times, without a significant impact on the clot initiation parameters or platelet function. Additionally, AGK2 significantly attenuated the bone marrow atrophy (58.3±6.5 vs 30.0±8.2%, p=0.0262). Conclusion: Selective inhibition of SIRT2 significantly improves survival, and attenuates sepsis-associated "cytokine storm", coagulopathy, and bone marrow atrophy in a mouse model of lethal septic shock.[4] |
| Molecular Formula |
C23H13CL2N3O2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
434.27
|
|
| Exact Mass |
433.038
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 63.61; H, 3.02; Cl, 16.33; N, 9.68; O, 7.37
|
|
| CAS # |
304896-28-4
|
|
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
2130404
|
|
| Appearance |
Light yellow to green yellow solid powder
|
|
| Density |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| Boiling Point |
675.1±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| Flash Point |
362.1±31.5 °C
|
|
| Vapour Pressure |
0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| Index of Refraction |
1.718
|
|
| LogP |
5.39
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
1
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
4
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
4
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
30
|
|
| Complexity |
706
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
C1=CC2=C(C=CC=N2)C(=C1)NC(=O)/C(=C/C3=CC=C(O3)C4=C(C=CC(=C4)Cl)Cl)/C#N
|
|
| InChi Key |
SVENPFFEMUOOGK-SDNWHVSQSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H13Cl2N3O2/c24-15-6-8-19(25)18(12-15)22-9-7-16(30-22)11-14(13-26)23(29)28-21-5-1-4-20-17(21)3-2-10-27-20/h1-12H,(H,28,29)/b14-11+
|
|
| Chemical Name |
2-Cyano-3-[5-(2,5-dichlorophenyl)-2-furanyl]-N-5-quinolinyl-2-propenamide
|
|
| Synonyms |
AGK-2; AGK-2; AGK2; 304896-28-4; UNII-DDF0L8606A; DDF0L8606A; 2-Propenamide, 2-cyano-3-(5-(2,5-dichlorophenyl)-2-furanyl)-N-5-quinolinyl-; MFCD01909444; AGK-2.
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 0.5 mg/mL (1.15 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 5.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 0.5 mg/mL (1.15 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 5.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 0.5 mg/mL (1.15 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 4: 8% DMSO+30% PEG 300+ddH2O:~1.5 mg/mL |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3027 mL | 11.5136 mL | 23.0271 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4605 mL | 2.3027 mL | 4.6054 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2303 mL | 1.1514 mL | 2.3027 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
 |
|---|