
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
Afatinib dimaleate (the maleate salt form of Afatinib, also know as BIBW-2992; BIBW2992) is a potent, covalent/irreversible, and orally bioavailable dual EGFR/HER2 receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitor with potential antineoplastic activity. Afatinib is an FDA-approved anticancer medication used to treat lung cancer that is not small cell (NSCLC). In the USA, Gilotrif is the brand name under which it is sold. It is 100 times more active against the Gefitinib-resistant L858R-T790M EGFR mutant. It irreversibly binds to and inhibits EGFR/HER2, including EGFR(wt), EGFR(L858R), EGFR(L858R/T790M), and HER2. In cell-free assays, its IC50 values are 0.5 nM, 0.4 nM, 10 nM, and 14 nM, respectively.
| Targets |
EGFRL858R (IC50 = 0.4 nM); EGFR (IC50 = 0.5 nM); EGFRL858R/T790M (IC50 = 10 nM); HER2 (IC50 = 14 nM); HER3
- EGFR (wild-type):Afatinib (BIBW2992) inhibits wild-type EGFR with an IC₅₀ of 0.5 nM. [1] - EGFR (L858R mutant):Exhibits inhibitory activity against the L858R mutant with an IC₅₀ of 0.4 nM. [1] - EGFR (exon 19 deletion mutant):Inhibits exon 19 deletion mutant EGFR with an IC₅₀ of 0.3 nM. [1] - HER2 (ErbB2):Inhibits HER2 kinase activity with an IC₅₀ of 14 nM. [1] |
|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
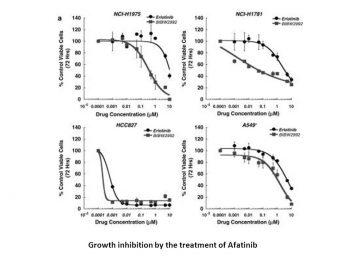
BIBW2992 is more efficient at preventing lung cancer cell lines carrying wild-type (H1666) or L858R/T790M (NCI-H1975) EGFR from surviving than erlotinib, gefitinib, or lapatinib. Comparably effective against NSCLC lines expressing EGFR E746_A750del (HCC827) or HER2 776insV (NCI-H1781), BIBW2992 exhibits no activity against A549 cells, which express EGFR and HER2 in their wild-type forms.[1] Afatinib increases the apoptosis that topotecan and mitoxantrone induce in SP cells as well as the cytotoxicity of these substances to SP cells.[2]
- Antiproliferative activity:Afatinib inhibits proliferation of EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines (HCC827, PC-9) with IC₅₀ values of 10–20 nM, and HER2+ breast cancer cells (SK-BR-3) with an IC₅₀ of 30 nM in MTT assays. [1][2] - Signal pathway inhibition:In HCC827 cells, afatinib (50 nM, 4 hours) reduces phosphorylation of EGFR (Tyr1068), AKT (Ser473), and ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204) by 90%, 85%, and 80%, respectively, as measured by Western blot. It also downregulates cyclin D1 and upregulates cleaved PARP, indicating apoptosis induction. [1][2] - Synergy with radiation:In head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) cells (SCC-25), afatinib (10 nM) enhances radiation-induced cell killing, increasing the radiation sensitivity factor by 1.5-fold. [3] |
| ln Vivo |
BIBW2992 (20 mg/kg, p.o.) causes a significant tumor regression with a cumulative treated/control tumor volume ratio (T/C ratio) of 2% in the MDA-MB-453 xenograft model. It also results in the downregulation of EGFR and AKT phosphorylation.[1] Applying BIBW 2992 (30 mg/kg, p.o.) to xenograft models A7, A431, FaDu, UT-SCC-14, and UT-SCC-15 significantly extends the time for tumor growth.[3] Afatinib (30 mg/kg, p.o.) causes a notable inhibition of tumor growth and a notable extension of overall survival in HER2-amplified xenograft models. *[4] Afatinib (25 mg/kg, p.o.) causes a dramatic tumor volume regression within 4 days and nearly complete tumor resolution after 21 days of treatment in HER2-positive gastric cancer NCI-N87 xenograft.[5]
- Tumor growth inhibition in NSCLC xenografts:Oral afatinib (20 mg/kg, daily) reduces tumor volume by 70–80% in HCC827 and PC-9 xenografts in nude mice after 21 days, with decreased Ki-67 and p-EGFR expression in tumor tissues. [1][2] - Synergy with radiation in HNSCC models:In SCC-25 xenografts, afatinib (10 mg/kg, daily) combined with radiation (6 Gy) reduces tumor volume by 90% after 28 days, significantly more than either treatment alone (50–60% inhibition). [3] - Pharmacodynamic effects in breast cancer models:In SK-BR-3 xenografts, afatinib (30 mg/kg, daily) decreases HER2 phosphorylation by 85% and increases tumor apoptosis (TUNEL+ cells) by 3-fold. [4] |
| Enzyme Assay |
EGFR kinase: 10 μL of inhibitor in 50% Me2SO, 20 μL of substrate solution (200 mM HEPES pH 7.4, 50 mM Mg-acetate, 2.5 mg/mL poly (EY), 5 μg/mL bio-pEY), and 20 µL enzyme preparation were included in each 100 µL enzyme reaction. The addition of 50 µL of a 100 µM ATP solution prepared in 10 mM MgCl2 initiates the enzymatic reaction. After 30 minutes of assaying at room temperature, 50 µL of stop solution (250 mM EDTA in 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4) is added to end the assay. 100 µL are added to a microtiterplate coated with streptavidin, and after 60 minutes of room temperature incubation, the plate is cleaned with 200 µL of wash solution (50 mM Tris, 0.05% Tween20). The wells are filled with a 100 µL aliquot of PY20H Anti-Ptyr:HRP, a 250 ng/mL HRPO-labeled anti-PY antibody. Following a 60-minute incubation period, the plate is three times cleaned using a 200 µL wash solution. Following that, 100µL of TMB Peroxidase Solution (A:B=1:1) is used to develop the samples. After ten minutes, the reaction is stopped. After the plate is placed in an ELISA reader, the extinction at OD450nm is calculated. The enzyme HER2-IC: The assay of enzyme activity is conducted in 50% Me2SO with or without serial inhibitor dilutions. Similar components as described for the EGFR kinase assay are included in each 100 µL reaction, along with the addition of 1000 µM Na3VO4. The addition of 50µL of a 500 µM ATP solution prepared in 10 mM magnesium acetate initiates the enzymatic reaction. The enzyme is diluted to the point where the amount of enzyme and the amount of time it takes for phosphate to be incorporated into bio-pEY are linear. The mixture of 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4, 130 mM NaCl, 0.05% Triton X-100, 1 mM DTT, and 10% glycerol is used to dilute the enzyme preparation. After 30 minutes of assaying at room temperature, 50 µL of stop solution is added to end the procedure. Src kinase assays: 10 µL of inhibitor in 50% Me2SO, 20 µL of enzyme preparation, and 20 µL of substrate solution enhanced with 1000 µM Na3VO4 were included in each 100 µL reaction. The addition of 50 µL of a 1000 µM ATP solution prepared in 10 mM Mg-acetate initiates the enzymatic reaction. Assay for BIRK kinase: 50 µL of a 2 mM ATP solution prepared in 8 mM MnCl2 and 20 mM Mg-acetate is added to 250 mM Tris pH 7.4, 10 mM DTT, 2.5 mg/mL poly(EY), and 5 mg/mL bio-pEY as the substrate solution to initiate the enzymatic reaction. HGFR kinase and VEGF2 assays: The assay is completed by adding 10 µL of 5% H3PO4 after it has been running at room temperature for 20 minutes. The precipitate is then collected using a 96 well filter mate universal harvester and trapped onto GF/B filters. The filter plate is thoroughly cleaned, dried for one hour at 50°C, sealed, and the radioactivity is measured using scintillation counting with either a TopCountTM or a Microbeta b counterTM.
- EGFR kinase activity assay: 1. Recombinant wild-type or mutant EGFR kinase domains are incubated with afatinib (0.01–100 nM) and [γ-³²P]ATP in kinase buffer. 2. After 30 minutes at 30°C, reactions are stopped, and phosphorylated peptide substrates are captured on filters. 3. Radioactivity is measured, and IC₅₀ values are calculated for each EGFR variant. [1] - HER2 kinase assay: 1. Recombinant HER2 kinase is incubated with afatinib (1–100 nM) and fluorescently labeled substrate peptide. 2. Kinase activity is measured via fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) to detect substrate phosphorylation. 3. The IC₅₀ for HER2 inhibition is determined as 14 nM. [1] |
| Cell Assay |
Proliferation and signaling assay:
1. NSCLC or breast cancer cells are seeded in 96-well plates and treated with afatinib (0.1–1,000 nM) for 72 hours.
2. Cell viability is measured by MTT assay to determine IC₅₀ values.
3. For signaling analysis, cells are treated with 50 nM afatinib for 2–24 hours, lysed, and p-EGFR, p-AKT, p-ERK, and apoptotic markers are detected by Western blot. [1][2][4]
- Radiation synergy assay: 1. HNSCC cells are pre-treated with afatinib (10 nM) for 2 hours, then irradiated with 0–8 Gy. 2. Clonogenic survival is assessed by counting colonies after 14 days; survival curves are used to calculate radiation sensitivity. [3] The MTT assay is used to determine cytotoxicity. The drug concentration that causes 50% of cells to die is known as the IC 50 value. The Bliss method is used to calculate the IC50 as well as the fitted sigmoidal dose response curve. |
| Animal Protocol |
SCID mice harbouring ARK2 xenografts
25 mg/kg p.o. Four bitransgenic mice on continuous doxycycline diets for more than 6 weeks were subjected to MRI (Figure 4) to document the lung tumor burden. Afatinib (BIBW2992) formulated in 0.5% methocellulose-0.4% polysorbate-80 (Tween 80) was administered orally by gavage at 20 mg/kg once daily dosing schedule. Rapamycin was dissolved in 100% ethanol, freshly diluted in 5% PEG400 and 5% Tween 80 before treatment and administered by intraperitoneal injection at 2 mg/kg daily dosage. Mice were monitored by MRI every 1 or 2 weeks to determine reduction in tumor volume and killed for further histological and biochemical studies after drug treatment. For immunohistochemistry staining, three tumor-bearing mice in each group were treated three times with either Afatinib (BIBW2992) (20 mg/kg) alone or Afatinib (BIBW2992) (20 mg/kg) and rapamycin 2 mg/kg at 24 h intervals and killed 1 h after the last drug delivery. All the mice were kept on the doxycycline diet throughout the experiments. Littermates were used as controls.[1] - NSCLC xenograft model: 1. Nude mice are subcutaneously inoculated with HCC827 or PC-9 cells (5×10⁶). 2. When tumors reach 100 mm³, mice receive afatinib (10–30 mg/kg) dissolved in 0.5% methylcellulose (oral, daily) for 21 days. 3. Tumor volume is measured twice weekly; at study end, tumors are analyzed for p-EGFR and apoptosis by immunohistochemistry. [1][2] - HNSCC radiation combination model: 1. Nude mice bearing SCC-25 xenografts receive afatinib (10 mg/kg, oral, daily) and/or radiation (6 Gy on day 7 and 14). 2. Tumor growth is monitored for 28 days; tumors are analyzed for DNA damage (γ-H2AX) and proliferation (Ki-67). [3] |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
- Oral absorption:In mice, afatinib (20 mg/kg, oral) achieves Cmax of 1.2 μg/mL at 2 hours, with oral bioavailability of ~40%. [2]
- Half-life:Terminal elimination half-life in mice is 6–8 hours; in humans, it is 37 hours at steady state. [2][5] - Distribution:In tumor-bearing mice, afatinib accumulates in tumors, with a tumor-to-plasma ratio of 3–5:1. [2] - Metabolism:Primarily metabolized by CYP3A4; <5% is excreted unchanged in urine. [5] |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
- Preclinical toxicity:In rats, afatinib (50 mg/kg, daily for 28 days) causes mild diarrhea and skin rash but no significant肝肾 damage (ALT/AST and BUN within normal ranges). [2][4]
- Clinical toxicity:Common adverse events include diarrhea (60%), rash (45%), and stomatitis (30%); Grade 3+ events are rare (<10%). Plasma protein binding is >95%. [5] |
| References | |
| Additional Infomation |
Afatinib dimaleate is a maleate salt obtained by combining afatinib with two molar equivalents of maleic acid. Used for the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. It has a role as a tyrosine kinase inhibitor and an antineoplastic agent. It contains an afatinib.
Afatinib Dimaleate is the dimaleate salt form of afatinib, an orally bioavailable anilino-quinazoline derivative and inhibitor of the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) epidermal growth factor receptor (ErbB; EGFR) family, with antineoplastic activity. Upon administration, afatinib selectively and irreversibly binds to and inhibits the epidermal growth factor receptors 1 (ErbB1; EGFR), 2 (ErbB2; HER2), and 4 (ErbB4; HER4), and certain EGFR mutants, including those caused by EGFR exon 19 deletion mutations or exon 21 (L858R) mutations. This may result in the inhibition of tumor growth and angiogenesis in tumor cells overexpressing these RTKs. Additionally, afatinib inhibits the EGFR T790M gatekeeper mutation which is resistant to treatment with first-generation EGFR inhibitors. EGFR, HER2 and HER4 are RTKs that belong to the EGFR superfamily; they play major roles in both tumor cell proliferation and tumor vascularization and are overexpressed in many cancer cell types. A quinazoline and butenamide derivative that acts as a tyrosine kinase inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptors (ERBB RECEPTORS) and is used in the treatment of metastatic NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER. See also: Afatinib (has active moiety). Drug Indication Giotrif as monotherapy is indicated for the treatment ofEpidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) TKI-naïve adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with activating EGFR mutation(s); locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC of squamous histology progressing on or after platinum-based chemotherapy. - Mechanism of action:Afatinib irreversibly binds to the ATP-binding site of EGFR, HER2, and HER4, inhibiting their kinase activity and blocking downstream PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. [1][2] - Indications:Approved for EGFR-mutant NSCLC and HER2+ breast cancer; investigated in combination with radiation for HNSCC. [2][3][4] - Pharmacodynamic marker:Reduction in plasma CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen) correlates with tumor response in NSCLC patients. [5] |
| Molecular Formula |
C32H33CLFN5O11
|
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
717.18
|
| Exact Mass |
717.184
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 53.52; H, 4.63; Cl, 4.94; F, 2.65; N, 9.75; O, 24.51
|
| CAS # |
850140-73-7
|
| Related CAS # |
Afatinib;850140-72-6;Afatinib-d6 dimaleate;Afatinib oxalate;1398312-64-5
|
| PubChem CID |
15606394
|
| Appearance |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| LogP |
4.536
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
6
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
16
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
12
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
50
|
| Complexity |
821
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
1
|
| SMILES |
C(/C(=O)O)=C/C(=O)O.N(C1C=CC(F)=C(Cl)C=1)C1=NC=NC2=CC(=C(C=C12)NC(=O)/C=C/CN(C)C)O[C@@H]1COCC1
|
| InChi Key |
USNRYVNRPYXCSP-JUGPPOIOSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C24H25ClFN5O3.2C4H4O4/c1-31(2)8-3-4-23(32)30-21-11-17-20(12-22(21)34-16-7-9-33-13-16)27-14-28-24(17)29-15-5-6-19(26)18(25)10-15;2*5-3(6)1-2-4(7)8/h3-6,10-12,14,16H,7-9,13H2,1-2H3,(H,30,32)(H,27,28,29);2*1-2H,(H,5,6)(H,7,8)/b4-3+;2*2-1-/t16-;;/m0../s1
|
| Chemical Name |
(Z)-but-2-enedioic acid;(E)-N-[4-(3-chloro-4-fluoroanilino)-7-[(3S)-oxolan-3-yl]oxyquinazolin-6-yl]-4-(dimethylamino)but-2-enamide
|
| Synonyms |
Afatinib dimaleate; BIBW 2992; Afatinib (diMaleate); BIBW-2992; BIBW2992; UNII-V1T5K7RZ0B; Afatinib dimaleate [USAN]; trade name: Gilotrif, Tomtovok and Tovok
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: 100 mg/mL (139.26 mM) in PBS (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with sonication.
Solubility in Formulation 2: 5% DMSO+30% PEG 300+ddH2O: 28 mg/mL (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.3944 mL | 6.9718 mL | 13.9435 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2789 mL | 1.3944 mL | 2.7887 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1394 mL | 0.6972 mL | 1.3944 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT04439136 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Afatinib Dimaleate | Advanced Lymphoma Refractory Lymphoma |
National Cancer Institute (NCI) |
August 12, 2015 | Phase 2 |
| NCT02438722 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Afatinib Dimaleate Biological: Cetuximab |
Recurrent Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Stage IV Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer |
SWOG Cancer Research Network | May 7, 2015 | Phase 2 Phase 3 |
| NCT02465060 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Afatinib Drug: Afatinib Dimaleate |
Bladder Carcinoma Glioma |
National Cancer Institute (NCI) |
August 17, 2015 | Phase 2 |
| NCT03083678 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Afatinib | Chordoma | Leiden University Medical Center | June 21, 2018 | Phase 2 |
| NCT03827070 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Afatinib Drug: Talcum powder |
Non Small Cell Lung Cancer | Center Trials & Treatment Europe | March 5, 2019 | Phase 1 |
|
 |
Afatinib covalently binds to cysteine number 797 of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) via a Michael addition (IC50 = 0.5 nM).Schubert-Zsilavecz, M, Wurglics, M,Neue Arzneimittel Frühjahr 2013.(in German) |