
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g | |||
| Other Sizes |
Purity: ≥98%
Tivantinib (formerly also known as ARQ-197; ARQ197), an experimental drug developed by by Arqule, Inc, is the first non-ATP-competitive, orally bioavailable and selective small molecule c-Met inhibitor with potential antineoplastic activity. It prevents c-Met in a cell-free assay with a Ki of 0.355 μM and exhibits negligible or no activity against Ron, EGFR, InsR, PDGFRα, and FGFR1/4. As it works, tirantinib binds to the c -Metaprotein and interfering with c -Met signal transduction pathways, which in tumor cells overexpressing c may cause cell death -Met protein or constitutively activated C expression Met the protein.
| Targets |
c-Met (Ki = 355 nM)
|
|
|---|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
|
|
| ln Vivo |
|
|
| Enzyme Assay |
For thirty minutes at room temperature, recombinant c-Met protein (100 ng) is preincubated with increasing concentrations of ARQ-197. After preincubation, the reaction mixture is mixed with different concentrations of ATP containing 5 μCi of [γ-32P]ATP and 100 μM of poly-Glu-Tyr substrate. After five minutes of room temperature incubation, the reaction is halted by adding five microliters of SDS-polyacrylamide gel, which reduces the sample buffer. After that, the samples are put onto a 7.5% acrylamide gel, and SDS-PAGE is carried out. The final method used to visualize the phosphorylated poly-Glu-Tyr substrates is autoradiography. Densitometry is used to measure c-Met activity.
|
|
| Cell Assay |
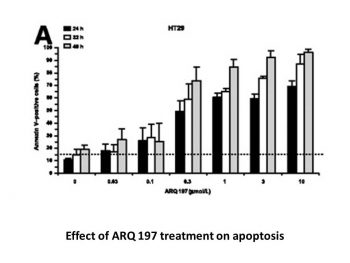
In black 96-well plates, 5 × 103 cells are seeded per well and left overnight in a medium containing 10% FBS for HT29, MKN-45, and MDA-MB-231 cells. Next day, cells are exposed to progressively higher concentrations of ARQ-197 (0.03-10 μM) at 37 °C for 24, 32, and 48 hours. Following treatment with ARQ-197, the drug-containing medium is removed, and the cells are incubated in a labeling solution (10 mM HEPES, 140 mM NaCl, and 6 mM CaCl2) containing 1 μg/mL propidium iodide (red channel), 500-times diluted Annexin V-FITC (green channel), and 2 μg/mL Hoescht 33342 (blue channel). This process continues for at least 10 minutes. Acquisition and analysis of high-content images are done. Four pictures are supposed to be taken per well by the program. For the 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, FITC, and rhodamine channels, the exposure times are set at 16.7 ms/10% gain, 500 ms/35% gain, and 300 ms/30% gain, respectively. After processing the images, the quantity of positive cells in each channel and condition is calculated. Furthermore, the identical protocols are carried out when HT29 cells are treated for 32 hours with varying doses of ARQ-197 in the presence or absence of 25, 50, and 100 μM ZvAD-FMK (irreversible general caspase inhibitor). Each experiment is carried out three times. The impact of ARQ-197 when glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and c-Met are knocked down using siRNA is examined in order to ascertain whether the apoptotic effect is caused by c-Met inhibition. SiRNAs that are nontargeted, gapgh-targeted, or met-targeted are transfected into HT29, MKN-45, and MDA-MB-231 cells. Following three days, particular antibodies are used to measure the expression levels of β-actin, GAPDH, and c-Met. After transfecting HT29, MKN-45, and MDA-MB-231 cells with a met-targeted siRNA for two days, the cells are cultured either in the absence or with increasing concentrations of ZvAD-FMK for an additional day to ascertain whether the effect is caspase dependent. Also transfected in parallel as controls are a nontargeted siRNA and a gapgh-targeted siRNA (siRNA GAPDH). Annexin V-FITC and propidium iodide are then used to stain the cells, allowing for the calculation of the percentage of apoptotic cells.
|
|
| Animal Protocol |
|
|
| References | ||
| Additional Infomation |
LSM-1131 is a member of indoles.
Tivantinib has been investigated in Solid Tumors. Tivantinib is an orally bioavailable small molecule inhibitor of c-Met with potential antineoplastic activity. c-Met inhibitor ARQ 197 binds to the c-Met protein and disrupts c-Met signal transduction pathways, which may induce cell death in tumor cells overexpressing c-Met protein or expressing constitutively activated c-Met protein. c-Met protein, the product of the proto-oncogene c-Met, is a receptor tyrosine kinase also known as hepatocyte growth factor receptor (HGFR); this protein is overexpressed or mutated in many tumor cell types and plays key roles in tumor cell proliferation, survival, invasion, and metastasis, and tumor angiogenesis. Drug Indication Treatment of hepatoblastoma Mechanism of Action Tivantinib mediates its effects by inhibiting the activity of c-Met, a receptor tyrosine kinase that plays multiple key roles in human cancer, including cancer cell growth, survival, angiogenesis, invasion and metastasis. C-Met is abnormally activated in most cancers and is believed to control multiple signal transduction pathways involved in tumor growth and metastasis. |
| Molecular Formula |
C23H19N3O2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
369.42
|
|
| Exact Mass |
369.147
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 74.78; H, 5.18; N, 11.37; O, 8.66
|
|
| CAS # |
905854-02-6
|
|
| Related CAS # |
(3S,4S)-Tivantinib;905854-03-7;(Rac)-Tivantinib;1239986-50-5;(rel)-Tivantinib;905853-99-8
|
|
| PubChem CID |
11494412
|
|
| Appearance |
white solid powder
|
|
| Density |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| Boiling Point |
716.0±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| Flash Point |
386.8±32.9 °C
|
|
| Vapour Pressure |
0.0±2.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| Index of Refraction |
1.797
|
|
| LogP |
3.26
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
2
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
2
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
2
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
28
|
|
| Complexity |
666
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
2
|
|
| SMILES |
O=C1NC(=O)[C@@H](C2=CNC3C=CC=CC2=3)[C@@H]1C1=CN2CCCC3C2=C1C=CC=3
|
|
| InChi Key |
UCEQXRCJXIVODC-PMACEKPBSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H19N3O2/c27-22-19(16-11-24-18-9-2-1-7-14(16)18)20(23(28)25-22)17-12-26-10-4-6-13-5-3-8-15(17)21(13)26/h1-3,5,7-9,11-12,19-20,24H,4,6,10H2,(H,25,27,28)/t19-,20-/m0/s1
|
|
| Chemical Name |
(3R,4R)-3-(1-azatricyclo[6.3.1.04,12]dodeca-2,4,6,8(12)-tetraen-3-yl)-4-(1H-indol-3-yl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.77 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 +5% Tween-80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 + to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7069 mL | 13.5347 mL | 27.0695 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5414 mL | 2.7069 mL | 5.4139 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2707 mL | 1.3535 mL | 2.7069 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
ARQ 197 in Combination With Chemotherapy in Patients With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
CTID: NCT01075048
Phase: Phase 1/Phase 2 Status: Completed
Date: 2021-04-08
|
 |
 |