
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
PHA-665752 (PHA665752) is a novel, potent, selective and ATP-competitive small molecule inhibitor of c-Met Kinase with potential antitumor activity. In cell-free experiments, it inhibits c-Met with an IC50 of 9 nM and demonstrates >50-fold selectivity in inhibiting c-Met relative to other kinases like RTKs or STKs. It has the ability to target human cancers with overactivated c-Met. By inhibiting the hepatocyte growth factor-induced cell proliferation and radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells, it demonstrates strong anti-proliferative activity in vitro.
| Targets |
c-Met (IC50 = 9 nM); RON (IC50 = 68 nM); Flk1 (IC50 = 200 nM)
|
|
|---|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
|
|
| ln Vivo |
|
|
| Enzyme Assay |
The c-Met assay uses the GST-fusion protein containing the c-Met kinase domain. Based on the phosphorylation of kinase peptide substrates or poly-glu-tyr in the presence of ATP and divalent cations (MgCl2 or MnCl2 10–20 mM), PHA-665752's IC50 value for the inhibition of c-Met is determined. For c-Met, the linear range—that is, the duration during which the rate stays equal to the initial rate—is established, and the kinetic measurement and IC50 calculation are carried out inside of this range.
|
|
| Cell Assay |
Cells are grown in 0.1% FBS medium for 48 hours in order to perform proliferation assays. Afterward, the cells are treated with varying concentrations of PHA-665752 in HGF (50 ng/mL) in a medium containing 2% FBS. Following 18 hours, cells are fixed, stained with an anti-BrdUrd peroxidase-conjugated antibody, and then incubated with BrdUrd for an hour. The plates are then read at 630 nm. Cells are grown in 2% FBS medium with and without HGF (50 ng/mL) and different concentrations of PHA-665752 for 72 hours in order to perform apoptosis assays. After 72 hours, a mixture containing acridine orange and ethidium bromide is added, and fluorescent microscopy is used to count the number of apoptotic cells (bright orange cells or cell fragments).
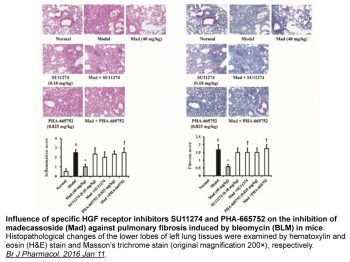
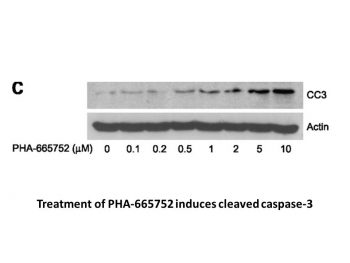
The effect of PHA665752 treatment was determined on cell growth, motility and migration, apoptosis, and cell-cycle arrest of TPR-MET-transformed cells. Moreover, the effect of PHA665752 on the phosphorylation on MET, as well as its downstream effectors, p-AKT and p-S6K, was also determined. Finally, growth of TPR-MET-transformed cells was tested in the presence of PHA665752 and rapamycin. H441 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells (with activated c-Met) were also tested against both PHA665752 and rapamycin [2]. |
|
| Animal Protocol |
Female athymic mice (nu/nu) bearing S114 or GTL-16 tumor xenografts
~30 mg/kg/day Injection via bolus i.v. Treatment of Nude Mice for Studying the Effect of c-Met Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors on Tumorigenicity and Immunohistochemistry of Tumors[3] NCI-H441, A549, and NCI-H69 cells were cultured and harvested with trypsin/EDTA. The viability of these cells was determined by trypan blue and only cell populations with 90% or greater viability were used for this investigation. The tumorigenicity of these lung cancer cells was determined by intradermally injecting 5 × 106 viable cells in balanced salt solution into the flank or leg region of nude mice to produce s.c. tumors. Once daily intratumoral injections of PHA665752, were given 8 days after the lung cancer cells were injected when tumors were visible. One group of animals was given PHA665752 (16.5 μg in 100 μL of 2% DMSO) and group 2 was injected with diluent (2% DMSO) alone. The mice were euthanized at the indicated times and tumors were measured with calipers, fixed in 4% formalin, embedded in paraffin, and stained with H&E.[3] Immunohistochemical staining of tumors was done using monoclonal antibodies against CD31, VEGF, TSP-1, and phosphospecific antibodies to c-Met pY1230/1234/1235 and pY1003. The immunostaining procedures used have been previously described by Ma et al. Appropriate negative controls for the immunostaining were prepared by omitting the primary antibody step and substituting it with nonimmune rabbit serum. To estimate the number of blood vessels in tumors before and after treatment, 10 microscopic fields were counted at 20× magnification and the number of blood vessels were evaluated. All of the slides were reviewed and scored by two investigators independently.[3] |
|
| References | ||
| Additional Infomation |
PHA-665752 is a member of the class of indolones that is 1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one which is substituted by a (2,6-dichlorobenzyl)sulfonyl group at position 5 and by a (1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylidene group at position 2, the pyrrole ring of which is substituted by methyl groups at positions 3 and 5, and by a [2-(pyrrolidin-1-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl]carbonyl group at position 4 (the Z,R isomer). It has a role as a c-Met tyrosine kinase inhibitor and an antineoplastic agent. It is a member of indolones, a pyrrolecarboxamide, a N-acylpyrrolidine, a sulfone, a dichlorobenzene, an enamide, a secondary carboxamide and a tertiary carboxamide.
|
| Molecular Formula |
C32H34CL2N4O4S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
641.61
|
|
| Exact Mass |
640.167
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 59.90; H, 5.34; Cl, 11.05; N, 8.73; O, 9.97; S, 5.00
|
|
| CAS # |
477575-56-7
|
|
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
10461815
|
|
| Appearance |
Yellow to orange solid powder
|
|
| Density |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| Boiling Point |
890.2±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| Flash Point |
492.2±34.3 °C
|
|
| Vapour Pressure |
0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| Index of Refraction |
1.656
|
|
| LogP |
4
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
2
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
5
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
7
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
43
|
|
| Complexity |
1180
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
ClC1C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C(C=1C([H])([H])S(C1C([H])=C([H])C2=C(C=1[H])/C(/C(N2[H])=O)=C(\[H])/C1=C(C([H])([H])[H])C(=C(C([H])([H])[H])N1[H])C(N1C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[C@]1([H])C([H])([H])N1C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])[H])=O)(=O)=O)Cl
|
|
| InChi Key |
OYONTEXKYJZFHA-SSHUPFPWSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C32H34Cl2N4O4S/c1-19-29(35-20(2)30(19)32(40)38-14-6-7-21(38)17-37-12-3-4-13-37)16-24-23-15-22(10-11-28(23)36-31(24)39)43(41,42)18-25-26(33)8-5-9-27(25)34/h5,8-11,15-16,21,35H,3-4,6-7,12-14,17-18H2,1-2H3,(H,36,39)/b24-16-/t21-/m1/s1
|
|
| Chemical Name |
(3Z)-5-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)methylsulfonyl]-3-[[3,5-dimethyl-4-[(2R)-2-(pyrrolidin-1-ylmethyl)pyrrolidine-1-carbonyl]-1H-pyrrol-2-yl]methylidene]-1H-indol-2-one
|
|
| Synonyms |
PHA-665752; PHA665752; PHA-665752 hydrate; TCMDC-125885; UNII-0VXU5T5R3J; (R,Z)-5-((2,6-dichlorobenzyl)sulfonyl)-3-((3,5-dimethyl-4-(2-(pyrrolidin-1-ylmethyl)pyrrolidine-1-carbonyl)-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)indolin-2-one; PHA 665752
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.90 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 2.5 mg/mL (3.90 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.90 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 4: 2% DMSO+castor oil: 5 mg/mL |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.5586 mL | 7.7929 mL | 15.5858 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3117 mL | 1.5586 mL | 3.1172 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1559 mL | 0.7793 mL | 1.5586 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
|
 |
 |