
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
Purity: ≥98%
Vadimezan (DMXAA, NSC-640488, AS1404, ASA-404) is a potent vascular disrupting agents (VDA) and competitive inhibitor of DT-diaphorase with potential antitumor activity. It inhibits VDA and DT-diaphorase with Ki of 20 μM and IC50 of 62.5 μM in cell-free assays, respectively.
| Targets |
STING (stimulator of interferon genes); type I IFNs
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
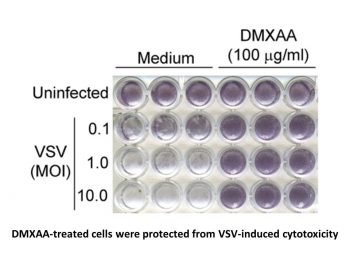
Vadimezan (DMXAA) is a strong inducer of type I interferons and other cytokines, a vascular disruptor, and a mouse agonist of stimulator of interferon genes (STING). There is no negative impact on the viability of 344SQ-ELuc cells by vadimezan (DMXAA). Research has revealed that Vadimezan-mediated activation of the NF-κB pathway is indicated by enhanced p65 phosphorylation in M2 macrophages [1]. The findings demonstrated that Vadimezan (DMXAA)-treated cells were shielded from VSV-induced cytotoxicity at all MOIs in contrast to medium-pretreated macrophages. Two influenza virus strains were successfully suppressed by vadimezan (DMXAA), indicating the drug's potential to treat drug-resistant strains of human influenza [2].
1. M2 Macrophage Repolarization Activity: - In vitro-cultured murine bone marrow-derived M2 macrophages (induced by IL-4 and IL-13) were treated with Vadimezan (DMXAA) at concentrations of 1, 5, and 10 μg/mL for 24 hours. Quantitative PCR (qPCR) results showed that DMXAA dose-dependently reduced the expression of M2 marker genes (Arg1, Ym1, Fizz1): at 10 μg/mL, Arg1 mRNA levels decreased by 65 ± 7%, Ym1 by 58 ± 6%, and Fizz1 by 62 ± 8% compared to the untreated M2 group. Meanwhile, it increased the expression of M1 marker genes (iNOS, TNF-α): iNOS mRNA increased by 3.2 ± 0.4-fold, and TNF-α by 2.8 ± 0.3-fold. This repolarization effect was comparable to that of the endogenous STING agonist 2'3'-cGAMP (10 μg/mL) [1] 2. IFN-β Induction and Antiviral Activity: - In murine RAW 264.7 macrophages, treatment with Vadimezan (DMXAA) (0.1, 0.5, 1 μg/mL) for 16 hours induced dose-dependent secretion of interferon-β (IFN-β). At 1 μg/mL, IFN-β concentration in the supernatant reached 200 ± 25 pg/mL, which was 8.5 ± 1.2-fold higher than the vehicle control. - In a vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV)-infected RAW 264.7 cell model, pretreatment with DMXAA (1 μg/mL) for 24 hours reduced VSV replication by 70 ± 8% (measured by viral plaque assay) compared to the infected untreated group. Similar antiviral effects were observed in murine embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs): 1 μg/mL DMXAA reduced VSV titers by 65 ± 7% [2] |
||
| ln Vivo |
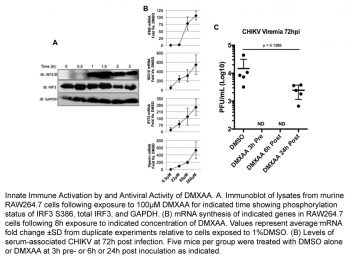
Vadimezan (DMXAA) significantly reduces bioluminescence (BLI) signals in 344SQ-ELuc NSCLC subcutaneous tumors after injection. When vadimezan (DMXAA) is administered to 344SQ-ELuc metastases, photon emission rates do not drop and the tumors retain their histological resemblance to controls. When mice with tiny subcutaneous tumors are administered Vadimezan (DMXAA), photon output falls by approximately 2 logarithmic units at 6 and 24 hours, just like with large subcutaneous tumors [1]. When administered intraperitoneally to influenza-infected mice, Vadimezan (DMXAA) is a substantially less powerful inducer of IFN-β mRNA and a rather poor inducer of TNF-α mRNA in vivo[2].
1. Tumor Vascular Disruption in Murine NSCLC Models: - In C57BL/6 mice bearing subcutaneous Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC, a murine non-small cell lung cancer model), Vadimezan (DMXAA) was administered via intraperitoneal injection at a dose of 25 mg/kg. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) showed that 4 hours post-administration, tumor blood flow decreased by 80 ± 9% compared to the vehicle control; 24 hours post-administration, tumor vascular permeability increased by 2.3 ± 0.3-fold (measured by gadolinium contrast agent accumulation). Histological analysis revealed that DMXAA caused extensive tumor vascular endothelial cell damage (evidenced by CD31⁺ endothelial cell fragmentation) and intratumoral hemorrhage in 75 ± 8% of treated tumors [1] 2. In Vivo Antiviral Activity: - In BALB/c mice infected with VSV via intravenous injection (1 × 10⁶ plaque-forming units, PFU), treatment with Vadimezan (DMXAA) (10 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection) 24 hours post-infection increased the survival rate from 20 ± 5% (vehicle control) to 70 ± 8% at day 7 post-infection. - In the same model, DMXAA (10 mg/kg) reduced viral loads in the liver and lungs by 1.8 ± 0.2 log₁₀ PFU/g and 1.6 ± 0.2 log₁₀ PFU/g, respectively, at 48 hours post-infection. Serum IFN-β levels in treated mice were 350 ± 40 pg/mL, significantly higher than the control group (45 ± 8 pg/mL) [2] |
||
| Enzyme Assay |
Reverse Phase Protein Array (RPPA)[1]
M2-polarized (40 ng/ml IL-4 for 48 hours, N = 3) macrophages were treated with 20 µg/ml DMXAA or DMSO vehicle for 30 min. Cells were then lysed and protein denatured in SDS buffer and samples sent for RPPA analysis. Differential abundance of various proteins and/or their phosphorylation status in response to DMXAA was assessed. Macrophage Polarization and Supernatant Cytokine Assay[1] BMDM were seeded in 6-well plates at 2×106 cells/well and polarized for 48 hours with the addition of 50 ng/ml LPS and 50 ng/ml IFNγ for M1, or 40 ng/ml IL-4 for M2 at 37°C in a 5% CO2 humidified atmosphere. Cells were re-plated in triplicate in 96-well plates, 8×105 cells/well, in media containing 20 µg/ml DMXAA or DMSO control for 24 hours. Supernatants were subjected to a mouse 32-plex cytokine/chemokine discovery array. |
||
| Cell Assay |
Cytotoxicity Assay[1]
Assays for DMXAA and Clodrolip cytotoxicity used 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thialolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazoliumbromide as per instructions provided by the manufacturer. Absorbance values were determined on a Multiskan Ascent Microplate Reader. RT-PCR[1] Subcutaneous tumors and control spleens were snap frozen in liquid N2 prior to being homogenized in QIAzol lysis reagent. M1 and M2 polarized macrophages were treated with 20 µg/ml DMXAA (or dose response) or DMSO vehicle for an additional 24 hours. In addition, M2 polarized macrophages were treated with 20 µg/ml or 40 µg/ml 2′3′-cGAMP in the presence of Lipofectamine-2000. Cells were lysed with QIAzol lysis reagent and RNA was extracted with chloroform and isopropanol. To make cDNA, 1 µg of RNA was treated with DNAse followed by RT-PCR with 10 mM dNTPs, random primers and Superscript II reverse transcriptase. Real-time PCR of cDNAs was carried out on the LightCycler using the LightCycler FastStart DNA MasterPLUS SYBR Green kit. Data were normalized to β-actin mRNA. Primer sequences were as previously described. In vitro and in vivo viral infections[2] RAW 264.7 macrophages were cultured as described previously [22] and plated at 1 × 105 cells/well in a 96-well plate. After overnight incubation at 37°C, cells were treated with medium containing vehicle or DMXAA (100 μg/ml). After 6 h, the culture medium was replaced with serum-free DMEM containing VSV at the indicated MOI for 1 h. Cells were then maintained in complete DMEM with 10% FBS. Twenty-four hours later, cells were washed with PBS, fixed with 10% buffered formalin (Sigma-Aldrich), and rinsed thoroughly with distilled H2O. Adherent cells were stained with crystal violet.[2] Two assays were used to determine the ability of DMXAA to protect cultured cells against influenza infection. MDCK cells were plated and incubated overnight at 37°C. Antiviral activity of DMXAA was assessed by pre-incubating 1 × 103 TCID50 influenza virus (A/Wuhan or A/Br) with the indicated concentrations of DMXAA for 1 h at 37°C. Positive controls were Tamiflu® (0.1–10 μg/ml) and Relenza® (0.12 μg/ml). MDCK cells were then inoculated with the pre-incubated mixture (virus pretreatment). After 96 h, cells were stained with crystal violet, and the absence or presence of CPE was determined at 40× magnification. In addition, antiviral activity was assessed by addition of DMXAA to the cell culture 1 h before inoculation with 1 × 103 TCID50 (“cell pretreatment”). Cells were maintained and CPE quantified as described for the virus pretreatment assay.[2] 1. M2 Macrophage Repolarization Assay: - Murine bone marrow cells were isolated from C57BL/6 mice and cultured in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 20 ng/mL M-CSF for 7 days to obtain bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs). BMDMs were then induced to M2 phenotype with 20 ng/mL IL-4 and 20 ng/mL IL-13 for 48 hours. - Induced M2 macrophages were treated with Vadimezan (DMXAA) (1, 5, 10 μg/mL) or vehicle for 24 hours. Total RNA was extracted, reverse-transcribed to cDNA, and qPCR was performed to detect the expression of M1 (iNOS, TNF-α) and M2 (Arg1, Ym1, Fizz1) marker genes. GAPDH was used as the internal reference gene, and relative expression was calculated by the 2⁻ΔΔCt method [1] 2. IFN-β Detection and Antiviral Cell Assay: - RAW 264.7 macrophages or MEFs were seeded in 24-well plates at a density of 2 × 10⁵ cells/well and cultured overnight. Cells were treated with DMXAA (0.1, 0.5, 1 μg/mL) or vehicle for 16 hours, and supernatants were collected to measure IFN-β concentration by sandwich ELISA. - For antiviral experiments, treated cells were infected with VSV (multiplicity of infection = 0.1) for 1 hour, then washed with PBS and cultured for another 24 hours. Viral titers in supernatants were determined by plaque assay on Vero cells (counting plaques after 48 hours of incubation) [2] |
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Metabolism / Metabolites
DMXAA has known human metabolites that include 6-hydroxy-MXAA and (2S,3S,4S,5R)-6-[2-(5,6-dimethyl-9-oxoxanthen-4-yl)acetyl]oxy-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid. |
||
| References |
|
||
| Additional Infomation |
Vadimezan is a monocarboxylic acid that is acetic acid in which one of the methyl hydrogens is replaced by a 5,6-dimethyl-9-oxoxanthen-4-yl group. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent. It is a member of xanthones and a monocarboxylic acid.
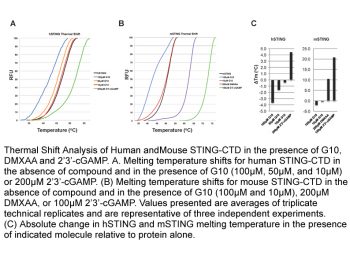
Vadimezan is a fused tricyclic analogue of flavone acetic acid with potential antineoplastic activity. Vadimezan induces the cytokines tumor necrosis alpha (TNF-alpha), serotonin and nitric oxide, resulting in hemorrhagic necrosis and a decrease in angiogenesis. This agent also stimulates the anti-tumor activity of tumor-associated macrophages. Drug Indication Investigated for use/treatment in solid tumors, lung cancer, ovarian cancer, and prostate cancer. Mechanism of Action ASA404 (DMXAA) is a small-molecule vascular disrupting agent which targets the blood vessels that nourish tumours. The proposed mechanism of action for ASA404 is directly increasing permeability of the tumor's endothelial cells. Vasoactive mediators such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) may also be implicated. Increased permeability of tumor cell vasculature may allow increased permeation of anticancer treatments such as cytotoxic drugs, antibodies, drug conjugates and gene therapy. 1. Mechanism of Action: - Vadimezan (DMXAA) exerts anti-tumor effects primarily by disrupting tumor-specific blood vessels: it induces damage to tumor vascular endothelial cells, reduces tumor blood flow, and causes intratumoral hemorrhage, thereby inhibiting tumor nutrient supply. Additionally, it repolarizes M2 macrophages (tumor-promoting) to M1 macrophages (pro-inflammatory and anti-tumor), enhancing anti-tumor immune responses [1] - DMXAA exerts antiviral effects by inducing the secretion of IFN-β: IFN-β activates the antiviral immune response, inhibits viral replication, and reduces viral load in infected tissues [2] 2. Comparative Activity with Endogenous Agonists: - In M2 macrophage repolarization experiments, the activity of Vadimezan (DMXAA) (10 μg/mL) was comparable to that of the endogenous STING agonist 2'3'-cGAMP (10 μg/mL), both significantly reducing M2 marker expression and increasing M1 marker expression [1] 3. Therapeutic Application Direction: - Vadimezan (DMXAA) has potential therapeutic applications in non-small cell lung cancer (via tumor vascular disruption) and viral infections (via IFN-β-induced antiviral activity) [1][2] |
| Molecular Formula |
C17H14O4
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
282.29
|
|
| Exact Mass |
282.089
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 72.33; H, 5.00; O, 22.67.
|
|
| CAS # |
117570-53-3
|
|
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
123964
|
|
| Appearance |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| Density |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| Boiling Point |
520.9±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| Melting Point |
264 °C
|
|
| Flash Point |
197.1±23.6 °C
|
|
| Vapour Pressure |
0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| Index of Refraction |
1.633
|
|
| LogP |
3.6
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
1
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
4
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
2
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
21
|
|
| Complexity |
433
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
CC1=C(C2=C(C=C1)C(=O)C3=CC=CC(=C3O2)CC(=O)O)C
|
|
| InChi Key |
XGOYIMQSIKSOBS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H14O4/c1-9-6-7-13-15(20)12-5-3-4-11(8-14(18)19)17(12)21-16(13)10(9)2/h3-7H,8H2,1-2H3,(H,18,19)
|
|
| Chemical Name |
(5,6-Dimethyl-9-oxo-9H-xanthen-4-yl)-acetic acid
|
|
| Synonyms |
NSC 640488, NSC-640488, 117570-53-3; 5,6-Mexaa; 5,6-Dimethylxantheonone-4-acetic Acid; 2-(5,6-dimethyl-9-oxo-9H-xanthen-4-yl)acetic acid; DMXAA (Vadimezan); NSC640488, ASA-404, Vadimezan; ASA404; ASA 404; AS1404; AS 1404; AS1404; DMXAA
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 0.71 mg/mL (2.52 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 7.1 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 0.71 mg/mL (2.52 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 7.1 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: 30% PEG400+0.5% Tween80+5% propylene glycol:30 mg/mL Solubility in Formulation 4: 5 mg/mL (17.71 mM) in 50% PEG300 50% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5425 mL | 17.7123 mL | 35.4246 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7085 mL | 3.5425 mL | 7.0849 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3542 mL | 1.7712 mL | 3.5425 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT01299415 | Terminated | Drug: Vadimezan™ | Solid Tumors | Novartis Pharmaceuticals | August 2009 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01285453 | Completed | Drug: vadimezan | Advanced or Recurrent Solid Tumors | Novartis Pharmaceuticals | March 2009 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01290380 | Terminated | Drug: ASA404, DMXAA, DXAA | Solid Tumor Malignancies | Novartis Pharmaceuticals | February 2010 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01299701 | Terminated | Drug: ASA404 | Advanced Solid Tumors | Novartis Pharmaceuticals | December 2008 | Phase 1 |
DMXAA inhibits influenza A/Wuhan and Tamiflu®-resistant influenza A/Br replication in vitro.J Leukoc Biol.2011 Mar;89(3):351-7. |
Differential induction of IFN-β and TNF-α mRNA expression by DMXAA and LPS in vivo.J Leukoc Biol.2011 Mar;89(3):351-7. |
IFN-β-dependent, DMXAA-mediated protection of mice against influenza-induced lethality.J Leukoc Biol.2011 Mar;89(3):351-7. |
 |
 |
 |