
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
Purity: ≥98%
Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate (also known as D-2-HGA, or 2-HG) is a potent and competitive inhibitor of α-ketoglutarate (α-KG)-dependent dioxygenases with Ki value of 0.628 mM. In U-87MG cells, (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate acts as weak antagonists of α-KG to inhibit α-KG-dependent histone demethylases and increases dimethylation on both H3K9 and H3K79. Besides, (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate also inhibits ATP synthase and mTOR signaling, and therefore causes growth arrest and tumor cell killing. Inhibition of ATP synthase by 2-HG or α-KG in glioblastoma cells is sufficient for growth arrest and tumor cell killing under conditions of glucose limitation, e.g., when ketone bodies (instead of glucose) are supplied for energy. These findings inform therapeutic strategies and open avenues for investigating the roles of 2-HG and metabolites in biology and disease.
| Targets |
Endogenous Metabolite; α-KG-dependent dioxygenases
|
|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) 1 and 2 gene mutations cause the accumulation of D-α-hydroxyglutaric acid disodium ((R)-2-hydroxyglutarate) in human malignancies [1][2]. KDM7A partially inhibited H3K9me2 and H3K27me2 peptides when 50 mM D-2-HG and 100 μM α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) were present. If 300 μM α-KG is added, it can counteract the inhibitory action of 50 mM D-2-HG on CeKDM7A, proving that D-α-Hydroxyglutaric acid disodium is merely a weak competitive inhibitor of α-KG directed at CeKDM7A demethylase[1]. TET hydroxylase is weakly inhibited by D-α-Hydroxyglutaric acid disodium. When 10 mM D-α-hydroxyglutarate was added in the presence of 0.1 mM α-KG, TET2 was partially (33%) inhibited, and higher inhibition (83%) was observed when 50 mM D-α-hydroxyglutarate was added. TET1 is less obviously inhibited by D-α-hydroxyglutaric acid [1].
|
| ln Vivo |
In rat cerebral cortex, human skeletal muscle, and bovine heart mitochondrial granules, D-α-hydroxyglutaric acid significantly inhibits glucose utilization, CO2 generation, and the respiratory chain, indicating decreased aerobic metabolism [5]. Due to its ability to stimulate the particular NMDA glutamate receptor, D-α-hydroxyglutaric acid is also regarded as an endogenous excitotoxic organic acid since it severely lowers cell survival in cultures of chick embryo telencephalon and newborn rat hippocampus neurons[5]. In the cortical supernatants of 30-day-old rats (TAR) value, D-α-Hydroxyglutaric acid disodium (0.01-1 mM) significantly reduces overall antioxidant reactivity and enhances chemiluminescence and thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBA-RS)[5].
|
| Enzyme Assay |
Enzymatic Assays[1]
To assay human JHDM1A/KDM2A demethylase activity toward H3K36me2, His tagged JHDM1A was first obtained by transforming pET28a-JHDM1A into Escherichia coli BL21 and protein expression was induced by addition of 1 mM IPTG at 30° C when cell density reaches 0.5 OD600 units. Cells were lysed by sonication and Ni-NTA agarose was used to purify His-JHDM1A fusion proteins. Histone demethylase assay was carried out by incubating 2 μg oligonucleosomes, 4 μg purified His-JHDM1A, and/or 10–50 mM L- or D-2-HG in histone demethylation buffer [50 mM HEPES (pH 8.0), 625 μM Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2, 0.1–0.5 mM α-KG, 2 mM ascorbate] at 37° C for 2–3 hr and the reactions were stopped by the addition of SDS loading buffer and subsequently analyzed by western blotting using anti-H3K36me2 antibody. To measure CeKDM7A demethylase activity toward H3K9me2 and H3K27me2, two synthetic dimethylated peptides H3K9me2 [ARTKQTARK (me2)STGGKA] and H3K27me2 [QLATKAARK (me2)SAPAS] were used as substrates. Demethylase assays were carried out in the presence of 10 μg enzyme, 1 μg peptide in 20 μl buffer 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl, 50 μM (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2, 100 μM α-KG, 2 mM Vc, 10 mM PMSF for 3 hr. The demethylation reaction mixture was desalted by passing through a C18 ZipTip (Millipore). To examine the inhibitory effect of 2-HG, various concentrations of 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG) were incubated with KDM7A briefly before adding other reaction mixtures. The samples were analyzed by a MALDI-TOF/TOF mass spectrometer. In vitro TET-catalyzed 5mC-to-5hmC conversion was assayed as described previously (Ito et al., 2010) and described in detail in the Supplemental Experimental Procedures. Briefly, 5 μg purified proteins were incubated with 0.5 μg double-stranded oligonucleotide substrates in 50 mM HEPES (pH 8), 75 μM Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2, 2 mM ascorbate, and 0.1 mM α-KG with or without a various amount of 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG) for 3 hr at 37° C. Oligonucleotide substrates were purified and then digested with MspI. 5′-end of the digested DNA was treated with calf alkaline phosphatase and labeled with [γ-32P]ATP and T4 polynucleotide kinase. Labeled fragments were ethanol-precipitated and digested with 10 μg of DNase I and 10 μg Phosphodiesterase I in the presence of 15 mM MgCl2, 2 mM CaCl2 at 37° C. One microliter digestion product was spotted on a PEI-cellulose TLC plate and separated in an isobutyric acid/water/ammonium hydroxide (66:20:2) running buffer. |
| Cell Assay |
It was discovered recently that the central metabolite α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) extends the lifespan of C. elegans through inhibition of ATP synthase and TOR signaling. Here we find, unexpectedly, that (R)-2-hydroxyglutarate ((R)-2HG), an oncometabolite that interferes with various α-KG-mediated processes, similarly extends worm lifespan. (R)-2HG accumulates in human cancers carrying neomorphic mutations in the isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) 1 and 2 genes. We show that, like α-KG, both (R)-2HG and (S)-2HG bind and inhibit ATP synthase and inhibit mTOR signaling. These effects are mirrored in IDH1 mutant cells, suggesting a growth-suppressive function of (R)-2HG. Consistently, inhibition of ATP synthase by 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG) or α-KG in glioblastoma cells is sufficient for growth arrest and tumor cell killing under conditions of glucose limitation, e.g., when ketone bodies (instead of glucose) are supplied for energy. These findings inform therapeutic strategies and open avenues for investigating the roles of 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG) and metabolites in biology and disease.[3]
D-2-hydroxyglutarate (D-2HG) is released by various types of malignant cells including acute myeloid leukemia (AML) blasts carrying isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) gain-of-function mutations. D-2HG acting as an oncometabolite promotes proliferation, anoikis, and differentiation block of hematopoietic cells in an autocrine fashion. However, prognostic impact of IDH mutations and high D-2HG levels remains controversial and might depend on the overall mutational context. An increasing number of studies focus on the permissive environment created by AML blasts to promote immune evasion. Impact of D-2HG on immune cells remains incompletely understood. Here, we sought out to investigate the effects of D-2HG on T-cells as key mediators of anti-AML immunity. D-2HG was efficiently taken up by T-cells in vitro, which is in line with high 2-HG levels measured in T-cells isolated from AML patients carrying IDH mutations. T-cell activation was slightly impacted by D-2HG. However, D-2HG triggered HIF-1a protein destabilization resulting in metabolic skewing towards oxidative phosphorylation, increased regulatory T-cell (Treg) frequency, and reduced T helper 17 (Th17) polarization. Our data suggest for the first time that D-2HG might contribute to fine tuning of immune responses.[4] |
| Animal Protocol |
Large amounts of d-2-hydroxyglutaric acid (DGA) accumulate in d-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria (D-2-OHGA), an inherited neurometabolic disorder characterized by severe neurological dysfunction and cerebral atrophy. Despite the significant brain abnormalities, the neurotoxic mechanisms of brain injury in this disease are virtually unknown. In this work, the in vitro effect of DGA on various parameters of oxidative stress was investigated; namely chemiluminescence, thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBA-RS), total radical-trapping antioxidant potential (TRAP), total antioxidant reactivity (TAR) and the activities of the antioxidant enzymes catalase, glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase in cerebral cortex from 30-day-old-rats. DGA significantly increased chemiluminescence and TBA-RS and decreased TAR values in the cortical supernatants. In contrast, TRAP and the antioxidant enzyme activities were not altered by the metabolite. Furthermore, the DGA-induced increase of TBA-RS was fully prevented by the free radical scavengers ascorbic acid plus Trolox (water-soluble alpha-tocopherol) and attenuated by the inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase Nomega-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME), suggesting the role of superoxide, hydroxyl and nitric oxide radicals in this action. The data indicate a stimulation of lipid peroxidation through the production of free radicals and a reduction of the brain capacity to efficiently modulate the damage associated with the enhanced generation of free radicals by DGA. In the case that these findings also occur in human D-2-OHGA, it is feasible that oxidative stress may be involved in the pathophysiology of the brain injury observed in patients with this disease.[5]
|
| References |
|
| Additional Infomation |
IDH1 and IDH2 mutations occur frequently in gliomas and acute myeloid leukemia, leading to simultaneous loss and gain of activities in the production of α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) and 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG), respectively. Here we demonstrate that 2-HG is a competitive inhibitor of multiple α-KG-dependent dioxygenases, including histone demethylases and the TET family of 5-methlycytosine (5mC) hydroxylases. 2-HG occupies the same space as α-KG does in the active site of histone demethylases. Ectopic expression of tumor-derived IDH1 and IDH2 mutants inhibits histone demethylation and 5mC hydroxylation. In glioma, IDH1 mutations are associated with increased histone methylation and decreased 5-hydroxylmethylcytosine (5hmC). Hence, tumor-derived IDH1 and IDH2 mutations reduce α-KG and accumulate an α-KG antagonist, 2-HG, leading to genome-wide histone and DNA methylation alterations.[1]
The organic acidurias D: -2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria (D-2-HGA), L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria (L-2-HGA), and combined D,L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria (D,L-2-HGA) cause neurological impairment at young age. Accumulation of D-2-hydroxyglutarate (D-2-HG) and/or L-2-hydroxyglutarate (L-2-HG) in body fluids are the biochemical hallmarks of these disorders. The current review describes the knowledge gathered on 2-hydroxyglutaric acidurias (2-HGA), since the description of the first patients in 1980. We report on the clinical, genetic, enzymatic and metabolic characterization of D-2-HGA type I, D-2-HGA type II, L-2-HGA and D,L-2-HGA, whereas for D-2-HGA type I and type II novel clinical information is presented which was derived from questionnaires.[3] |
| Molecular Formula |
C5H6NA2O5
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
192.08
|
|
| Exact Mass |
192.001
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 31.27; H, 3.15; Na, 23.94; O, 41.65
|
|
| CAS # |
103404-90-6
|
|
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
51051608
|
|
| Appearance |
White to light yellow solid powder
|
|
| Melting Point |
>291°C (dec.)
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
1
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
5
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
2
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
12
|
|
| Complexity |
130
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
C(CC(=O)[O-])[C@H](C(=O)[O-])O.[Na+].[Na+]
|
|
| InChi Key |
DZHFTEDSQFPDPP-HWYNEVGZSA-L
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C5H8O5.2Na/c6-3(5(9)10)1-2-4(7)8;;/h3,6H,1-2H2,(H,7,8)(H,9,10);;/q;2*+1/p-2/t3-;;/m1../s1
|
|
| Chemical Name |
2R-hydroxy-pentanedioic acid, disodium salt
|
|
| Synonyms |
D-alpha-Hydroxyglutaric acid disodium salt; Disodium (R)-2-hydroxyglutarate; 103404-90-6; Sodium (R)-2-hydroxypentanedioate; Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate; D-2-Hydroxypentanedioic acid disodium salt; MDK4906; D-alpha-Hydroxyglutaric acid disodium; disodium (2R)-2-hydroxypentanedioate; MFCD00069573; D-2-HGA; 2R-hydroxy-pentanedioic acid, disodium salt
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: 100 mg/mL (520.62 mM) in PBS (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with sonication (<60°C).
(Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.2062 mL | 26.0308 mL | 52.0616 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.0412 mL | 5.2062 mL | 10.4123 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.5206 mL | 2.6031 mL | 5.2062 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
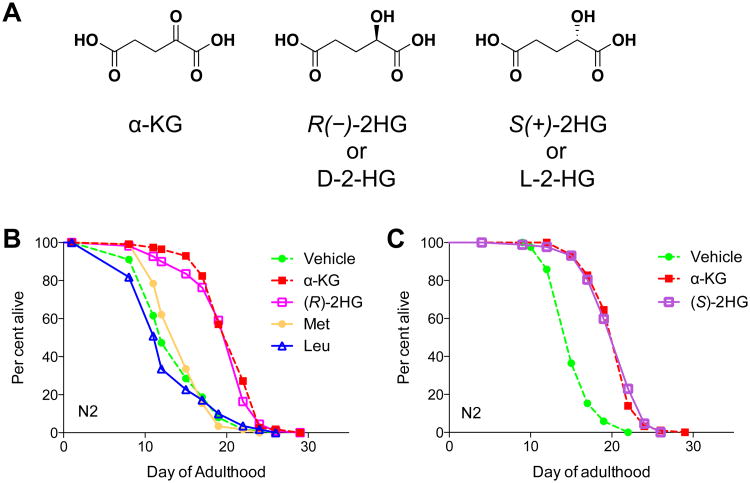 2-HG extends the lifespan of adultC. elegans.Cell Metab.2015 Sep 1;22(3):508-15. |
|---|
2-HG binds and inhibits ATP synthase.Cell Metab.2015 Sep 1;22(3):508-15. |
Inherent vulnerability, or the loss of cell viability, characteristic of cells with ATP5B knockdown, 2-HG accumulation, or IDH mutations.Cell Metab.2015 Sep 1;22(3):508-15. |