
| Size | Price | |
|---|---|---|
| 50mg | ||
| 100mg |
Purity: ≥98%
BIIE0246 (BIIE-0246) is a newly synthesized, potent and highly selective non-peptide neuropeptide Y (NPY) Y2 receptor antagonist with an IC50 of 15 nM. It was able to compete with high affinity (8 to 15 nM) for specific [(125)I]PYY(3 - 36) binding sites in HEK293 cells transfected with the rat Y(2) receptor cDNA, and in rat brain and human frontal cortex membrane homogenates. Interestingly, in rat brain homogenates while NPY, C2-NPY and PYY(3 - 36) inhibited all specific [(125)I]PYY(3 - 36) labelling, BIIE0246 failed to compete for all specific binding suggesting that [(125)I]PYY(3 - 36) recognized, in addition to the Y(2) subtype, another population of specific NPY binding sites, most likely the Y(5) receptor. Quantitative receptor autoradiographic data confirmed the presence of [(125)I]PYY(3 - 36)/BIIE0246-sensitive (Y(2)) and-insensitive (Y(5)) binding sites in the rat brain as well as in the marmoset monkey and human hippocampal formation. In the rat vas deferens and dog saphenous vein (two prototypical Y(2) bioassays), BIIE0246 induced parallel shifts to the right of NPY concentration-response curves with pA(2) values of 8.1 and 8.6, respectively. In the rat colon (a Y(2)/Y(4) bioassay), BIIE0246 (1 microM) completely blocked the contraction induced by PYY(3 - 36), but not that of [Leu(31), Pro(34)]NPY (a Y(1), Y(4) and Y(5) agonist) and hPP (a Y(4) and Y(5) agonist). Additionally, BIIE0246 failed to alter the contractile effects of NPY in prototypical Y(1) in vitro bioassays. Taken together, these results demonstrate that BIIE0246 is a highly potent, high affinity antagonist selective for the Y(2) receptor subtype. It should prove most useful to establish further the functional role of the Y(2) receptor in the organism. europeptide Y (NPY) plays an important role in the regulation of energy homeostasis in the level of central and sympathetic nervous systems (SNSs).
| Targets |
Non-peptide neuropeptide Y (NPY) Y2 receptor (IC50 = 15 nM)
|
|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
In HEK 293 cells transfected with rat Y2 receptor cDNA, receptor binding tests demonstrated that BIIE-0246 competes for the particular [125I]PYY3-36 binding site with a high affinity (IC50=15±3 nM). On the other hand, in transfected HEK 293 cells, BIIE-0246 was not able to compete for the numerous specific [125I]GR231118, [125I]hPP, and [125I][Leu31, Pro34]PYY binding sites, even at concentrations up to 10 μM. They are cDNA for the rat Y1, Y4, or Y5 receptor [1].
|
| ln Vivo |
Genetically fat NPY mice have higher body weights and levels of adiposity when fed a chow diet. In both genotypes, BIIE-0246 therapy led to weight growth after 4.5 and 2 weeks. On fat mass increase, BIIE-0246 had no discernible effect. Body weight and composition in DIO were affected by BIIE-0246 differently depending on genotype (treatment × genotype interaction, P < 0.05 for body weight, P < 0.001 for fat mass, and P < 0.05 for lean mass). Post hoc analyses revealed a trend toward lower gains in lean mass and higher gains in body weight and fat mass in the DIO-WT group. BIIE-0246 prevented DIO-NPY from experiencing an increase in fat mass (P=0.05). It's interesting to note that higher cholesterol levels were not seen in the 4.5-week cohort, but were present in WT mice given BIIE-0246 for two weeks. In both DIO-NPY treatment groups (P<0.01 for DIO-NPY vehicle; P<0.001 for DIO-NPY BIIE-0246), cholesterol levels were positively correlated with body fat mass; this relationship was not observed in any other group. Additionally, the regression curves for fat mass and cholesterol were significantly lower in the DIO-NPY group treated with BIIE-0246 than in the vehicle-treated group [2].
|
| Enzyme Assay |
Binding assays [1]
All binding assays were initiated by adding 100 μl of membrane or cell preparations in a final volume of 500 μl of KRP containing 0.1% (w v−1) BSA, 0.05% (w v−1) bacitracin radiolabelled probes and unlabelled peptide or competitor as needed. Isotherm saturations were performed in the presence of increasing concentrations of radiolabelled probes while competition binding experiments were performed using 30–35 pM of radiolabelled probes in the presence and absence of various competitors at concentrations ranging from 10−12–10−6 M. In the rat brain homogenates, Y1-like and Y2-like receptors were studied using [125I[Leu31,Pro34]PYY and [125I]PYY3–36, respectively and as previously described (Dumont et al., 1995). [125I]GR231118 and [125I][Leu31,Pro34]PYY were used in HEK 293 cells transfected with rat Y1 and Y5 receptor cDNA, respectively. Binding in HEK 293 cells transfected with rat Y2 and Y4 receptor cDNA was performed using [125I]PYY3–36 and [125I]hPP, respectively. Non-specific binding was determined in the presence of 1 μM pNPY. Following a 2 h incubation, the binding reaction was terminated by rapid filtration through Schleicher and Schuell #32 glass filters (previously soaked in 1.0% polyethyleneimine) using a cell harvester filtering apparatus. Filters were rinsed three times with 3 ml of cold KRP and the radioactivity remaining on filters was quantified using a gamma counter with 85% efficiency. [1] All binding experiments were repeated three to six times, each in triplicate, and results expressed as percentage of specific binding (competition) or fmol (saturation). Kd values (i.e. the concentration of radioligand needed to occupy 50% of the total receptor population) were calculated from data obtained in saturation isotherm binding experiments using GraphPad Prism softwar with a fit to a one site hyperbola curve. IC50 values (i.e. concentration of unlabelled peptide required to compete for 50% of specific binding of the radioligand) of the various peptides and antagonists were calculated from the competition binding assays data using the GraphPad Prism software with a fit to a sigmoidal dose response curve. Quantitative receptor autoradiography [1] Receptor autoradiography was performed as described in detail elsewhere (Dumont et al., 1996; 1998a,1998b; Jacques et al., 1997). All sections (20 μm) were obtained using a cryomicrotome at −17°C, mounted on gelatin-chrome-alum-coated slides, dried overnight in a desiccator at 4°C, and then kept at −80°C until use. [1] On the days of the experiments, adjacent coronal sections were preincubated for 60 min at room temperature in a KRP buffer at pH 7.4 and then incubated for 120 min in a fresh preparation of KRP buffer containing 0.1% BSA, 0.05% bacitracin, 30 pM [125I]PYY3–36 and various concentrations of BIIE0246 (10−10–10−5 M). Following a 2 h incubation, sections were washed four times, 2 min each in ice-cold KRP buffer then dipped in deionized water to remove salts and rapidly dried. Non-specific binding was determined using 1 μM NPY. Incubated sections were apposed against 3H-Hyperfilms for 6 days alongside radioactive standards. Films were developed and quantified as described in detail elsewhere (Dumont et al., 1996; 1998a). |
| Cell Assay |
In vitro bioassays [1]
The rabbit (Cadieux et al., 1993) and dog (Pheng et al., 1997) saphenous veins, the rat vas deferens (Martel et al., 1990; Dumont et al., 1994), the rat colon (Pheng et al., 1999) and human cerebral arteries (Abounader et al., 1995) were prepared as described in details elsewhere. Concentration-response curves to NPY were generated by the cumulative addition of peptides for the rabbit saphenous vein and human cerebral arteries (NPY-induced contractions), and the rat vas deferens (NPY-inhibition of electrically stimulated twitch response) while a non-cumulative manner was used for the rat colon (NPY-induced contraction). In these tissues, the antagonistic properties of BIIE0246 were investigated by applying various concentrations or a single maximal concentration (1 μM) of BIIE0246 10 min prior to NPY. In the dog saphenous vein, the ability of BIIE0246 to block the contractile effects of NPY was investigated by the cumulative addition of BIIE0246 on tissues pre-contracted with NPY. [1] Concentration-response curves were constructed by plotting the molar concentration of NPY versus response expressed as percentage of the maximal response. From these plots, EC50 values were calculated by non-linear regression analysis (sigmoidal dose-response curve). EC50 values were calculated from each individual curve and the mean±s.e.mean was calculated from these data for the rat vas deferens, the rabbit saphenous vein and the human cerebral arteries. For each concentration of antagonist used, concentration-ratio was calculated by dividing the EC50 value for NPY in the presence of the antagonist by the EC50 obtained in the absence of the blocker. Schild plots were constructed and linear regression used to determine the x-intercept (pA2 value). For the dog saphenous vein, the pA2 value was determined as the concentration of BIIE0246 required to reduce by 50% the contractile effects of NPY. Transfected cells [1] HEK 293 cells were maintained in Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium (D-MEM) supplemented with 10% foetal calf serum and antibiotics (penicillin G sodium, streptomycin sulphate and amphotericin B). Cultured cells were transfected with either of the rat Y1, Y2, Y4 or Y5 receptor cDNA using a calcium phosphate method (Tong et al., 1995). Briefly, 125 μl of 2.5 M calcium phosphate was added to 1.125 ml water containing 50 μg of either rat Y1, Y2, Y4 or Y5 receptor cDNA which was previously inserted in expressing pcDNA3 vectors and was slowly mixed with 1.25 ml 2× HEPES buffer at pH 7.05 and left at room temperature for 20 min. The mixture was added to a 150 mm dish containing HEK 293 cells at 30% confluent and returned to the incubator. The medium was changed the next morning. Forty-eight hours later, cells were washed with KRP buffer pH 7.4 and scraped. Detached cells were then centrifuged at 400×g for 10 min and the pellet washed with KRP buffer (pH 7.4), recentrifuged twice, and resuspended in 8 ml of KRP buffer pH 7.4 and used for receptor binding assay. |
| Animal Protocol |
Drug treatment was studied at the age of 20 weeks. Prior to treatments the mice were habituated for 2 weeks to the handling stress with daily saline injections (i.p.). Half of the chow-fed mice (n = 10–13/group) were treated for 4.5 weeks, and half were sacrificed and tissues collected already after 2-week treatment (n = 7–14/group). DIO mice (n = 7–12/group) were treated for 2 weeks. (The study protocol is presented in Supplementary Figure 1). Mice received 1.3 mg/kg of Y2-receptor antagonist (BIIE0246, Tocris Bioscience, Bristol, United Kingdom) or vehicle (DMSO, Tween® 80) (Fisher Scientific, Fair Lawn, NJ, United States and 0.9% NaCl, 1:1:18, respectively) with daily intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections. BIIE0246 with a dose of 2 mg/kg has previously been used in a study with acute administration (Forbes et al., 2012), which supports rationality of the dose (1.3 mg/kg) being used with repeated dosing in the present study. The half-life of BIIE0246 in mouse is less than 3 h, but markedly longer than the half-life of the other Y2-receptor antagonists, thus making it the most suitable Y2-receptor antagonist for chronic administration (Brothers et al., 2010). [2]
|
| References |
|
| Additional Infomation |
1. BIIE0246, a newly synthesized non-peptide neuropeptide Y (NPY) Y(2) receptor antagonist, was able to compete with high affinity (8 to 15 nM) for specific [(125)I]PYY(3 - 36) binding sites in HEK293 cells transfected with the rat Y(2) receptor cDNA, and in rat brain and human frontal cortex membrane homogenates. 2. Interestingly, in rat brain homogenates while NPY, C2-NPY and PYY(3 - 36) inhibited all specific [(125)I]PYY(3 - 36) labelling, BIIE0246 failed to compete for all specific binding suggesting that [(125)I]PYY(3 - 36) recognized, in addition to the Y(2) subtype, another population of specific NPY binding sites, most likely the Y(5) receptor. 3. Quantitative receptor autoradiographic data confirmed the presence of [(125)I]PYY(3 - 36)/BIIE0246-sensitive (Y(2)) and-insensitive (Y(5)) binding sites in the rat brain as well as in the marmoset monkey and human hippocampal formation. 4. In the rat vas deferens and dog saphenous vein (two prototypical Y(2) bioassays), BIIE0246 induced parallel shifts to the right of NPY concentration-response curves with pA(2) values of 8.1 and 8.6, respectively. In the rat colon (a Y(2)/Y(4) bioassay), BIIE0246 (1 microM) completely blocked the contraction induced by PYY(3 - 36), but not that of [Leu(31), Pro(34)]NPY (a Y(1), Y(4) and Y(5) agonist) and hPP (a Y(4) and Y(5) agonist). Additionally, BIIE0246 failed to alter the contractile effects of NPY in prototypical Y(1) in vitro bioassays. 5. Taken together, these results demonstrate that BIIE0246 is a highly potent, high affinity antagonist selective for the Y(2) receptor subtype. It should prove most useful to establish further the functional role of the Y(2) receptor in the organism.[1]
In summary, we have demonstrated using several receptor binding assays and in vitro bioassays that BIIE0246 is a potent and selective Y2 receptor antagonist devoid of high affinity for the Y1, Y4 and Y5 subtypes. To our knowledge, BIIE0246 represents the first potent and selective tool to precisely establish the potential roles of the Y2 receptor in various tissues and to molecularly dissect features of agonist vs antagonist recognition sites on this receptor. The availability of BIIE0246, in addition to Y2 knockout mice (Naveilhan et al., 1999) should also prove critical to demonstrate the involvement of this subtype in a given effect induced by NPY and related peptides.[1] Neuropeptide Y (NPY) plays an important role in the regulation of energy homeostasis in the level of central and sympathetic nervous systems (SNSs). Genetic silencing of peripheral Y2-receptors have anti-obesity effects, but it is not known whether pharmacological blocking of peripheral Y2-receptors would similarly benefit energy homeostasis. The effects of a peripherally administered Y2-receptor antagonist were studied in healthy and energy-rich conditions with or without excess NPY. Genetically obese mice overexpressing NPY in brain noradrenergic nerves and SNS (OE-NPYDβH) represented the situation of elevated NPY levels, while wildtype (WT) mice represented the normal NPY levels. Specific Y2-receptor antagonist, BIIE0246, was administered (1.3 mg/kg/day, i.p.) for 2 or 4.5 weeks to OE-NPYDβH and WT mice feeding on chow or Western diet. Treatment with Y2-receptor antagonist increased body weight gain in both genotypes on chow diet and caused metabolic disturbances (e.g., hyperinsulinemia and hypercholesterolemia), especially in WT mice. During energy surplus (i.e., on Western diet), blocking of Y2-receptors induced obesity in WT mice, whereas OE-NPYDβH mice showed reduced fat mass gain, hepatic glycogen and serum cholesterol levels relative to body adiposity. Thus, it can be concluded that with normal NPY levels, peripheral Y2-receptor antagonist has no potential for treating obesity, but oppositely may even induce metabolic disorders. However, when energy-rich diet is combined with elevated NPY levels, e.g., stress combined with an unhealthy diet, Y2-receptor antagonism has beneficial effects on metabolic status.[2] |
| Molecular Formula |
C49H57N11O6
|
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
896.046980000001
|
| Exact Mass |
895.449
|
| CAS # |
246146-55-4
|
| Related CAS # |
BIIE-0246 hydrochloride
|
| PubChem CID |
9811493
|
| Appearance |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| Index of Refraction |
1.7
|
| LogP |
5.48
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
5
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
8
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
16
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
66
|
| Complexity |
1710
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
1
|
| SMILES |
C1CCC(C1)(CC(=O)N[C@@H](CCCN=C(N)N)C(=O)NCCN2C(=O)N(N(C2=O)C3=CC=CC=C3)C4=CC=CC=C4)CC(=O)N5CCN(CC5)C6C7=CC=CC=C7C(=O)NC8=CC=CC=C68
|
| InChi Key |
RSJAXPUYVJKAAA-JPGJPTAESA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C49H57N11O6/c50-46(51)53-25-13-22-40(45(64)52-26-27-58-47(65)59(34-14-3-1-4-15-34)60(48(58)66)35-16-5-2-6-17-35)54-41(61)32-49(23-11-12-24-49)33-42(62)56-28-30-57(31-29-56)43-36-18-7-8-19-37(36)44(63)55-39-21-10-9-20-38(39)43/h1-10,14-21,40,43H,11-13,22-33H2,(H,52,64)(H,54,61)(H,55,63)(H4,50,51,53)/t40-,43?/m0/s1
|
| Chemical Name |
(2S)-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)-N-[2-(3,5-dioxo-1,2-diphenyl-1,2,4-triazolidin-4-yl)ethyl]-2-[[2-[1-[2-oxo-2-[4-(6-oxo-5,11-dihydrobenzo[c][1]benzazepin-11-yl)piperazin-1-yl]ethyl]cyclopentyl]acetyl]amino]pentanamide
|
| Synonyms |
AR-H 053591; BIIE-0246; CHEMBL540989; BIIE-0246; BIIE 0246; 246146-55-4; BIIE0246; Ar-H-053591; (2S)-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)-N-[2-(3,5-dioxo-1,2-diphenyl-1,2,4-triazolidin-4-yl)ethyl]-2-[[2-[1-[2-oxo-2-[4-(6-oxo-5,11-dihydrobenzo[c][1]benzazepin-11-yl)piperazin-1-yl]ethyl]cyclopentyl]acetyl]amino]pentanamide; N3Z657H81X; Cyclopentaneacetamide, N-((1S)-4-((aminoiminomethyl)amino)-1-(((2-(3,5-dioxo-1,2-diphenyl-1,2,4-triazolidin-4-yl)ethyl)amino)carbonyl)butyl)-1-(2-(4-(6,11-dihydro-6-oxo-5H-dibenz(b,E)azepin-11-yl)-1-piperazinyl)-2-oxoethyl)-; GTPL1547; AR H 053591; BIIE-0246; AR-H-053591; AR H053591; ARH053591; BIIE 0246; CTK8E9439; BIIE0246;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~111.60 mM)
|
|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (2.79 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (2.79 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (2.79 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.1160 mL | 5.5800 mL | 11.1601 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2232 mL | 1.1160 mL | 2.2320 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1116 mL | 0.5580 mL | 1.1160 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
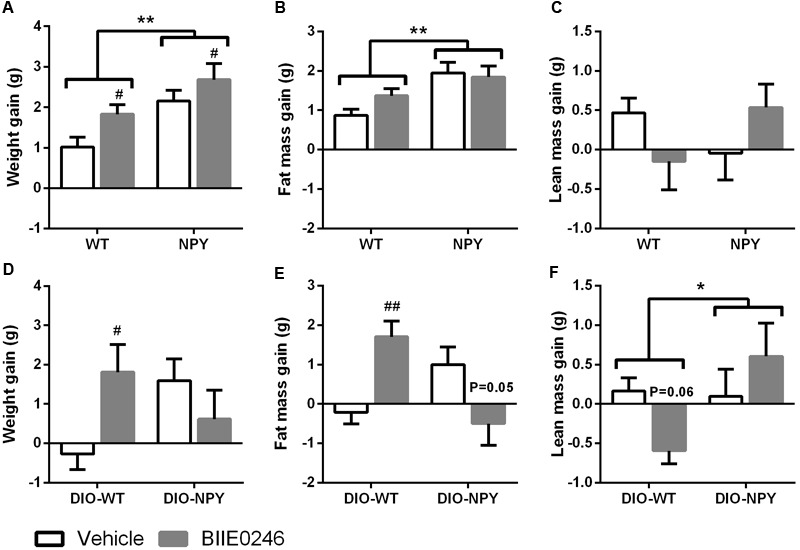 (A,D)Body weight,(B,E)fat mass and(C,F)lean mass gain in OE-NPYDβHand WT mice on chow (n= 11–12/group)(A–C)or Western diet (n= 7–11/group)(D–F)treated with Y2-receptor antagonist (BIIE0246) or vehicle for 4.5 or 2 weeks, respectively.Front Pharmacol.2018 Apr 5;9:319. |
|---|
(A)Representative H&E stainings of liver slides with × 20 magnification (scale bar 100 μm), and(B)triglycerides and(C)cholesterol in the livers of mice on chow diet treated with Y2-receptor antagonist (BIIE0246) or vehicle for 4.5 weeks (n= 8–12/group).Front Pharmacol.2018 Apr 5;9:319. |
(A–D)mRNA expression ofNpy,(E–H)Th(I,J)Pomcand(K,L)Y2rin the hypothalamus and the brainstem of chow-(A,B,E,F,I,K)or Western-diet-fed(C,D,G,H,J,L)OE-NPYDβHand WT mice (n= 6–12/group) after 2-week Y2-receptor antagonist (BIIE0246) or vehicle |