
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
ML346 (CID767276) is a novel and potent activator of heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) (EC50 = 4600 nM in HeLa cell toxicity assay). ML346 is a member of the barbituric acid class of substances that, in conformational disease models, induce HSF-1-dependent chaperone expression and restore folding of proteins.
| Targets |
HSP70 ( EC50 = 4.6 μM )
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
|
||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Enzyme Assay |
The procedure involves incubating HeLa cells for three or six hours with either DMSO (negative control), the PRs A1, A3, and ML346 (F1), or the positive controls MG132 (10 μM) and lactacystin (6 μM). After lysing the cells for five minutes on ice in homogenization buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH7.5, 250 mM sucrose, 5 mM MgCl2, 2 mM ATP, 1 mM DTT, 0.5 mM EDTA, and 0.025% digitonin), the total protein content of the whole cell extract is calculated. The assay buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 40 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM ATP, 1 mM DTT, 0.05 mg/mL BSA) is mixed with 3 μg of whole cell extracts in a black 96-well plate. The reaction is started by adding a 2× (200 μM) fluorogenic peptide substrate Suc-LLVY-AMC. Fluorescence is measured with a Synergy H4 multi-mode microplate reader every ten minutes[2].
|
||
| Cell Assay |
HeLa cells are plated in 100 μL of DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS and 1% Pen/Strep/Neo at a density of 10,000 cells per well in black 96-well plates. Before adding the compound, the plates are incubated for 16 hours at 37°C, 5% CO2, and 95% relative humidity. To the sample or control wells, 1 μL of hit compounds (ML346) in DMSO or DMSO alone is added, respectively. After that, the plates are kept in the incubator for a full day. Following incubation, 200 μL of PBS is used to wash the cells twice, and 200 μL of calcein AM (1 μg/mL) solution is added to each well. Following a 45-minute incubation period at 37°C and 5% CO2, the cells are fluoresced using an Analyst GT multimode reader. The expressed percentage of cytotoxicity is in relation to wells containing cells that were treated with DMSO alone (100%)[2].
|
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References |
|
| Molecular Formula |
C14H12N2O4
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
272.26
|
|
| Exact Mass |
272.08
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 61.76; H, 4.44; N, 10.29; O, 23.51
|
|
| CAS # |
100872-83-1
|
|
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| Appearance |
Orange to red solid powder
|
|
| SMILES |
COC1=CC=C(C=C1)/C=C/C=C2C(=O)NC(=O)NC2=O
|
|
| InChi Key |
IXYLVJHFJKDHRM-NSCUHMNNSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C14H12N2O4/c1-20-10-7-5-9(6-8-10)3-2-4-11-12(17)15-14(19)16-13(11)18/h2-8H,1H3,(H2,15,16,17,18,19)/b3-2+
|
|
| Chemical Name |
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 1.25 mg/mL (4.59 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 12.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.6730 mL | 18.3648 mL | 36.7296 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7346 mL | 3.6730 mL | 7.3459 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3673 mL | 1.8365 mL | 3.6730 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
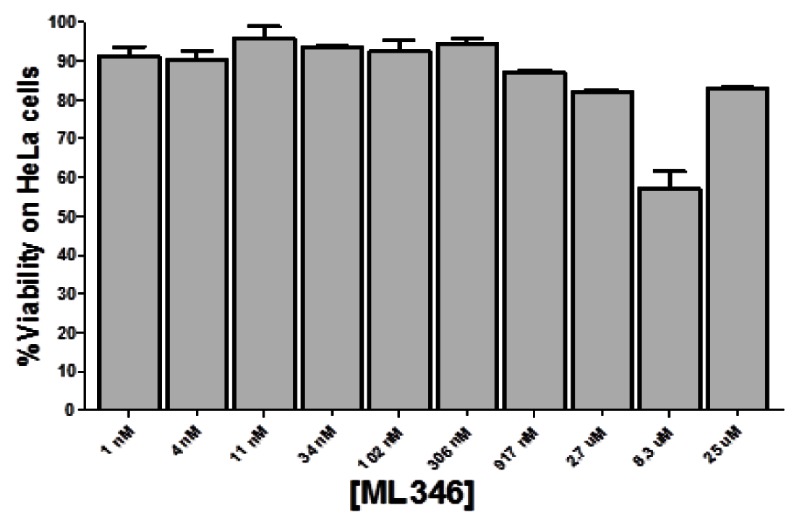 Probe ML346 is not toxic to HeLa cells.Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program |
|---|
 Probe ML346 (“F1”) induces Hsp70 mRNA expression.Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program |
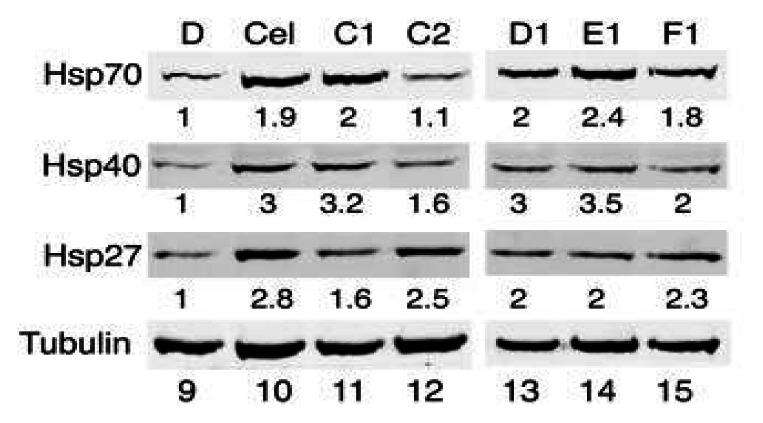 Probe ML346 (“F1”) induces chaperone protein expression.Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program |
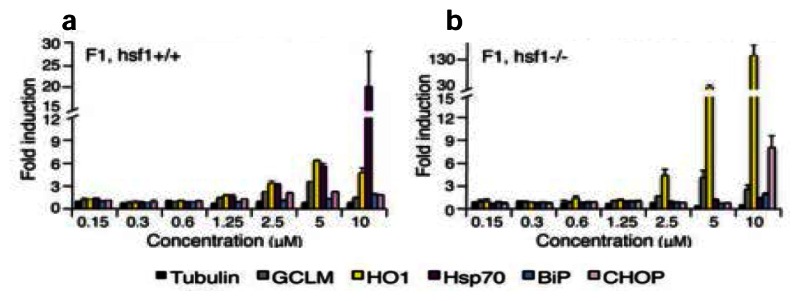 a,Wild type (hsf-1+/+) andb,HSF-1 null (hsf-1−/−) (MEFs) were treated for 4 h with probeML346(compound F1) at the indicated concentrations. |
|---|
 Probe ML346 restores proteostasis. |
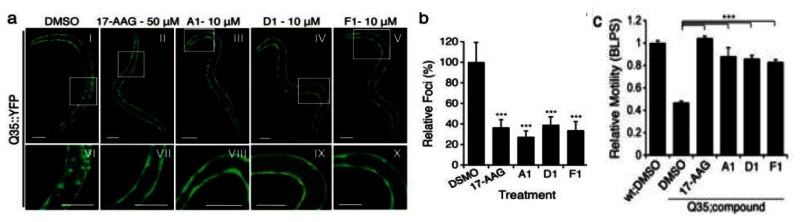 Probe ML346 (compound F1) reduces aggregation/toxicity inC. elegansmodels of diseases associated with polyQ expansions.Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program |